Update April 12, 2024
Information for u.s. citizens in the middle east.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |

Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Bolivia Travel Advisory
Travel advisory june 6, 2023, bolivia - level 2: exercise increased caution.
Reissued with updates to health information.
Exercise increased caution in Bolivia due to civil unrest. Some areas have increased risk. Read the entire Travel Advisory.
Do not travel to:
- Chapare region due to crime .
Reconsider travel to:
- Yungas region due to crime .
Country Summary: Demonstrations, strikes, and roadblocks can occur at any time in Bolivia. Demonstrations can result in violence. Roadblocks and strikes may cut off traffic and restrict the flow of goods and services around the country. Domestic and international flights may be delayed or unexpectedly cancelled.
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Bolivia.
If you decide to travel to Bolivia :
- Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to adjust your plans.
- Contact your airline or travel agency prior to travel.
- Avoid demonstration and crowds.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program ( STEP ) to receive Alerts and make it easier to locate you in an emergency.
- Follow the Department of State on Facebook , Twitter , and Instagram .
- Review the Country Security Report for Bolivia.
- Prepare a contingency plan for emergency situations. Review the Traveler’s Checklist .
Chapare Region: Do Not Travel
Due to a high level of violent crime , the U.S. government is limited in its ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in the Chapare region. U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization to travel there.
Visit our website for Travel to High-Risk Areas .
Yungas Region: Reconsider Travel
Organized criminal groups near Corioco and Carnavi in Yungas have committed carjackings and robberies . The U.S. government is limited in its ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens in the Yungas area. U.S. government employees must obtain special authorization to travel there.
Travel Advisory Levels
Assistance for u.s. citizens, bolivia map, search for travel advisories, external link.
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
Bolivia travel advice
Latest updates: The Health section was updated - travel health information (Public Health Agency of Canada)
Last updated: April 19, 2024 11:06 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, bolivia - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in Bolivia due to the continuing political and social tensions and frequent illegal roadblocks throughout the country.
Back to top
Roadblocks are common, may be erected suddenly, and can lead to significant disruptions to traffic and public transportation. They have stranded travellers for several days. The following are particularly vulnerable to blockades:
- all roads in border areas, especially along the Bolivia–Peru border
- roads leading to international airports
- main roads leading to large cities
Before departure, check with your airline to determine if there are delays or changes in flight schedules.
If you plan to take a road trip:
- review your travel plans to determine if they will be affected by demonstrations or civil unrest
- take personal security measures
- monitor local media
Once a roadblock is in place, local authorities, officials and vendors will not be able to enter or exit the city to provide supplies to stranded travellers. As a precaution, you should take extra:
- warm clothing
Don't cross roadblocks, even if they appear unattended. This may aggravate the situation and lead to physical harm. Instead, consider:
- taking an alternative safer route
- returning to your place of departure
Road closures and blockages – Bolivian Highway Administrator (in Spanish)
Demonstrations
Demonstrations and labour strikes occur frequently, often with little or no notice. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Protesters often use dynamite during protests.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, is common in large cities, including La Paz and Santa Cruz. Thieves target tourist areas and public transport.
Criminals often operate in organized groups. They will distract victims while an accomplice steals from them. Strategies include:
- staging a fight
- starting a conversation or offering help
- blocking a sidewalk
- throwing an object or liquid on the victims, then offering to help clean up
- posing as a victim of crime
- posing as a law enforcement officer
- using a young child to lure a tourist to a separate location
To avoid becoming a victim of theft:
- ensure that your belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- don't travel alone, especially at night
- be cautious of strangers approaching you
- remain alert to your surroundings at all times
- avoid showing signs of affluence
- avoid carrying large sums of money
- keep cellphones, cameras and other electronic equipment out of sight
Violent and drug-related crime
Violent crime against tourists is uncommon but does occur. Foreigners have been victims of armed robberies and assaults at tourist destinations.
Violent crime, carjacking and civil unrest, mainly associated with drug trafficking, pose risks in:
- the Chapare area between Santa Cruz and Cochabamba
- the Yungas region, northeast of La Paz
- all borders with Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay and Peru
You should avoid visits to prisons offered by unscrupulous guides, as prison guards cannot guarantee your security.
Express kidnapping
Express kidnappings have occurred at tourist destinations. Criminals ask for small, immediate ransoms. The kidnappers usually force their victims to withdraw funds from an ATM or to arrange for family or friends to pay the ransom. This ploy is often used by criminal taxi drivers, who pick up the victim and then stop to pick up associates. These kidnappings are committed by organized gangs and occur throughout the country.
- Use only reputable taxi companies or ride-sharing apps
- Avoid hailing taxis on the street
- If armed criminals threaten you, cooperate and don't resist
Vehicle and auto-parts theft, as well as theft from vehicles, are a problem throughout Bolivia.
- Keep valuables in the trunk, and only when necessary
- Park your car in a supervised lot
- Keep windows and doors locked at all times
Credit card and ATM fraud
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. When using debit or credit cards:
- Pay careful attention when others are handling your cards
- Use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- Avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- Cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- Check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Fraudulent police officers
Criminals often pose as police officers and ask to examine the traveller's belongings or ask the traveller to accompany them to a bogus police station, sometimes in collusion with a criminal posing as a taxi driver or another passenger.
Under Bolivian law, there's no obligation to go with an officer to a police station unless they have a formal written request from a judge with your name on it. Any search or seizure must occur at a genuine police station in the presence of the prosecutor.
If you're stopped while travelling by someone claiming to be a local authority, ask to see their official identification.
Medical scams
Canadians visiting Bolivia for surgical procedures have reported falling victim to scams by medical companies that insist on retaining passports as collateral. Once the procedure is complete, the company attempts to extort more money from the patient before returning their passport.
If your passport is inaccessible due to such a situation, you may not be able to receive full passport services. You may also be subject to investigation by Passport Canada.
- Carefully research medical clinics if you plan to travel to Bolivia for medical services
- Never hand over your passport to anyone
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances, as the items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Women's safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse.
Sexual assaults occur periodically, including at clubs and hostels.
- Be cautious when dealing with strangers and new acquaintances
- Lock your room when you return to your hotel/hostel.
Advice for women travellers
Water activities
Rescue services may not be consistent with international standards.
- Consult residents and tour operators for information on possible hazards and safe swimming areas
- Follow the instructions and warnings of local authorities
If you take a boat tour:
- make sure the vessel you are boarding is carrying appropriate safety equipment and that life jackets are provided for all passengers and accessible at all times
- don't board vessels that appear overloaded or unsafe
- verify the safety standards of ferries with your tour operator
If in doubt about the safety of the facilities or equipment, don't use them.
Water safety abroad
Adventure tourism
There are no official minimum safety standards for tour operators.
Only participate in tours in Uyuni, jungle expeditions, boat trips, mountain biking and other adventure activities with well-established companies. Ensure that your travel insurance covers your recreational activities.
Hiking and trekking
Be vigilant when hiking or trekking:
- in the areas surrounding La Paz, such as the Muela del Diablo
- near Rurrenabaque
- the Bolivian Andes
- in the Yungas region
- on the Inca trail
Criminals have targeted tourists in these areas.
If you intend to hike or trek:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you're properly equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, which can be fatal
- stay away from stray dogs, which can be aggressive and carry rabies
- obtain detailed information on hiking routes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails or slopes
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies involving hallucinogenic substances (ayahuasca, peyote, San Pedro, etc.) have led to serious illness, injury, assault and even the deaths of several tourists.
Ceremonies involve consuming substances that can cause medical complications and severely impair cognitive and physical abilities. They often take place in remote areas with no access to medical or mental health facilities or resources. Often, there is no access to communications with local authorities. Facilities generally lack basic first aid or emergency plans to help those suffering from physical or psychological illness during these ceremonies.
Spiritual cleansing ceremonies are not regulated and individuals offering them are not licensed. There is no way to assess the safety of any of the services or the operators.
Avoid participating in spiritual cleansing ceremonies using hallucinogenic substances.
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are poor throughout the country. Accidents and fatalities are common.
Driving conditions may be hazardous during the rainy season.
Although improved highways connect Cochabamba, La Paz, Santa Cruz and Sucre, many roads in Bolivia are unpaved. The old Yungas road is considered one of the world's most dangerous roads.
Many vehicles are poorly maintained.
Outside major cities, four-wheel-drive vehicles are necessary, especially in mountainous areas.
Common road hazards include:
- narrow, winding roads
- lack of guardrails on mountain roads
- inadequate or non-existent street lighting
- lack of signage
- poorly marked construction sites
- unpaved roads and potholes
- unfavourable weather conditions, sometimes causing landslides
Many drivers lack formal training and don't respect traffic laws. They may drive:
- aggressively and recklessly
- at high speeds
- while intoxicated
- without lights turned on at night
Public transportation
Public transportation, including buses, trains, shared and unlicensed taxis, and mini-buses, is unsafe. The level of crime is high in vehicles and at transportation hubs. Accidents are common due to:
- poor maintenance of vehicles
- lack of safety standards
- poor road conditions
Local and intercity buses are frequently involved in traffic accidents, especially overnight buses. Accidents involving less reputable, poorly maintained tourist buses have caused injuries and fatalities among tourists.
Use only tour buses operated by well-known, reputable companies for trips. If you have any doubt about the safety of a bus or its driver, use another company.
If you choose to travel by intercity bus, exercise caution in:
- La Paz bus terminals, including the main bus terminal on Peru Avenue in Zona Norte, the terminal near the La Paz cemetery, and the Minasa terminal in Zona Villa Fatima, due to petty crime
- the Santa Cruz bus/train terminal, where violent crimes against foreigners have occurred
- Coronilla Hill, adjacent to the main bus terminal in Cochabamba, due to assaults
Many taxis are poorly maintained and may not have functional seatbelts.
Avoid hailing taxis on the street. Instead, call radio taxi companies that are registered with authorities from a landline or from a hotel. Radio taxis are identifiable by the telephone number and name of the taxi company on the vehicle's roof.
- Take note of the taxi's registration and telephone numbers before you depart
- Pay special attention when taking taxis to and from airports, particularly in Santa Cruz and La Paz, where bandits are known to rob tourists
- Decline transportation from people offering cheaper fares
- Never share a taxi with strangers
- Avoid taking motorcycle taxis
- Negotiate the fare with the driver before departure, as taxis are not equipped with meters
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Bolivian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months from the date you arrive in Bolivia.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: not required for stays up to 30 days Business visa: required Student visa: required Volunteer work visa: required
Registration
All foreign residents and tourists must register their home or accommodation address online, using the web-based registration process (SIGEMIG). This can be done prior to arrival in Bolivia.
If you have not completed the electronic registration prior to arriving in Bolivia, immigration inspectors at the port of entry will register you and give you further instructions. Your registration must include lodging information for your entire stay. If you fail to comply, you will be subject to fines upon leaving the country.
Address registration – General Directorate of Migration (in Spanish)
Extensions of stay
If you’re a tourist wishing to stay for more than 30 days, you must apply at the General Directorate of Migration to obtain a tourist visa for another 30 days before the end of the first 30-day period. This extension can be obtained twice, at no extra cost and to a maximum of 90 days during one calendar year.
If you have overstayed the 90-day period without proper authorization, you may be fined upon departure.
General Directorate of Migration - Government of Bolivia
Other entry and exit requirements
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
Immigration officials will give you an immigration card when you arrive. Make sure to keep it, as they will ask for it when you leave the country.
When arriving by land, ensure your passport receives an exit stamp from the country you’re leaving and an entry stamp from Bolivia. If you fail to do so, you’ll be fined upon departure. Avoid travelling at night, when border officials and police may not be present.
Children and travel
Bolivia has strict requirements for the entry and exit of persons under the age of 18, including special documentation.
Parents of children travelling alone, with 1 parent or with another individual are strongly encouraged to contact the nearest Bolivian embassy or consulate before departure to ensure that the latest entry and exit requirements, which may change without notice, are met.
- Travelling with children
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
- Dengue: Advice for travellers - 8 April, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is a risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is recommended depending on your itinerary.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites .
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease) is a risk in this country. It is caused by a parasite spread by infected triatomine bugs. The infection can be inactive for decades, but humans can eventually develop complications causing disability and even death.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from triatomine bugs, which are active at night, by using mosquito nets if staying in poorly-constructed housing. There is no vaccine available for Chagas disease.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
Quality of health care varies greatly throughout the country. Good health care is available only in private hospitals in larger cities. Public medical services and facilities don’t meet Canadian standards. There’s limited access to health care facilities in rural areas, and very limited ambulance service throughout Bolivia. Evacuation by air ambulance can be difficult. Some air ambulance providers are unable to fly into locations at higher altitudes, such as La Paz.
Many clinics and hospitals accept payment in cash only. They may require upfront payment or refuse to allow you to leave their premises until you’ve paid for services.
Medical evacuation can be very expensive. You may need it in case of serious illness or injury.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
If you take prescription medications, it’s your responsibility to determine their legality in Bolivia.
- Bring sufficient quantities with you
- Always keep them in the original container
- Pack them in your carry-on luggage
- Carry a copy of your prescriptions
Some prescription medications are considered as narcotics in Bolivia. Consult the list of controlled substances to avoid trouble.
Bolivia’s list of controlled substances – Vice Ministry of Social Defence and Controlled Substances (in Spanish)
Altitude sickness
Some parts of Bolivia, including La Paz, Salar de Uyuni and Lake Titicaca, are located at high altitudes. Some travellers may develop altitude sickness, which can be fatal. Seek medical attention if you develop symptoms.
Travel to High Altitudes – U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Bolivian drug laws include a zero tolerance policy. Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect lengthy prison sentences and heavy fines.
Travellers have fallen victim to scams in which illegal drugs are hidden inside objects or luggage that an acquaintance has asked them to bring to or take away from Bolivia. Dating websites are reportedly a source of such scams.
- Pack your own luggage
- Never transport luggage or packages on behalf of another person
Unlicensed bars
Unlicensed bars in Bolivia are illegal. They are known to sell drugs and should be avoided. Police may detain and question you if they raid the establishment, even if you’re not consuming any illegal substances.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
It’s illegal to export any item that the Bolivian government considers a national treasure ( patrimonio cultural ) without formal written permission from the Ministry of Culture, including:
- pre-Columbian artifacts
- historical paintings
- items of Spanish colonial architecture and history
- native textiles
- flora, fauna and fossils
Any type of excavation for fossils or collection of fossils without prior written authorization is illegal.
Identification
Police and immigration officials occasionally conduct identification checks. Carry copies of the identification and Bolivian entry stamp pages of your passport when you’re out.
Photography
Locals may find the presence of photographers intrusive, particularly in remote areas.
- Be careful when travelling with cameras and communications devices
- Ask for permission before you photograph people, especially children
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Bolivian law does not prohibit sexual acts between individuals of the same sex.
Homosexuality is increasingly socially accepted, but much of Bolivian society remains conservative. 2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression or sex characteristics.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Dual citizenship is legally recognized in Bolivia.
If you are a Canadian citizen, but also a citizen of Bolivia, our ability to offer you consular services may be limited while you're there. You may also be subject to different entry/exit requirements .
Travellers with dual citizenship
Military service
Military service is compulsory in Bolivia. Males aged 18 or over who are dual citizens must undertake military service upon arrival in the country.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Bolivia.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Bolivia by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Bolivia to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children’s Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre.
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country’s judicial affairs.
- International Child Abduction: A Guidebook for Left-Behind Parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Emergency Watch and Response Centre
You must carry an international driving permit to rent or drive a vehicle.
The legal blood alcohol limit is 0.00%. If the police suspect you of drinking and driving, they could confiscate your driver’s licence on the spot and apply heavy fines and jail sentences.
If you’re involved in a traffic accident, remain at the scene until local police arrive. Attempting to leave the scene violates Bolivian law.
International Driving Permit
The currency in Bolivia is the boliviano (BOB).
Credit and debit cards are not widely accepted outside urban centres. Carry small bank notes to facilitate daily transactions such as:
- street food
U.S. dollars are widely accepted. There is a shortage of U.S. dollars. Banks and ATMs are currently not dispensing U.S. dollars.
It’s difficult to exchange Canadian dollars in Bolivia. Bring U.S. dollars if you need to exchange cash.
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged. Heavy rains may contribute to dangerous landslides. In particular, the Uyuni Salt Flats become dangerous to visit in the rainy season.
If you decide to travel to Bolivia during the rainy season:
- know that you expose yourself to serious risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
There is a risk of forest fires during the dry season, from July to October. The air quality in areas near active fires may deteriorate due to heavy smoke.
In case of a significant fire:
- stay away from affected areas, particularly if you suffer from respiratory ailments
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
- follow the advice of local authorities
Latest alerts – Vice Ministry of Civil Defence
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 110
- firefighters: 119
- gender-based violence: 800-14-0348
- ambulance service in La Paz: 165
- tourist police in La Paz: +591-2-222-5016
Consular assistance
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Bolivia (Program Office), in La Paz, and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
- Contact Tracing
- Pandemic Data Initiative
- All Regions
- Events & News
JHU has stopped collecting data as of
After three years of around-the-clock tracking of COVID-19 data from...
Group 41 Overview
Confirmed cases, group 17 notes.
Reduced counts in U.S. cases and deaths are the result of states and territories not reporting the information for some or all of the weekend. Those states and territories are: Alaska, Colorado, Connecticut, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Guam, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Mexico, North Carolina, Northern Mariana Islands, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Utah, U.S. Virgin Islands, Virginia, Washington, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Wyoming. Typically, these states' Monday updates include the weekend totals.
World Countries
Last updated July 15, 2022
There have been 952,456 infections and 21,973 coronavirus-related deaths reported in the country since the pandemic began.
Daily reported trends
How bolivia compares.
There is no one perfect statistic to compare the outbreaks different countries have experienced during this pandemic. Looking at a variety of metrics gives you a more complete view of the virus’ toll on each country.
These charts show several different statistics, each with their own strengths and weaknesses, that mark the various ways each country’s outbreak compares in its region and the world.
What it tells you...
Gives the true human toll of the virus on a country.
What it doesn’t
Can minimize the scale of the virus’ impact on smaller countries.
Infections in Latin America and the Caribbean
Infections, globally, deaths in latin america and the caribbean, deaths, globally, about this data.
Reuters is collecting daily COVID-19 infections and deaths data for 240 countries and territories around the world, updated regularly throughout each day.
Every country reports those figures a little differently and, inevitably, misses undiagnosed infections and deaths. With this project we are focusing on the trends within countries as they try to contain the virus’ spread, whether they are approaching or past peak infection rates, or if they are seeing a resurgence of infections or deaths.
Read more about our methodology
Where Bolivia COVID-19 data comes from
- Ministry of Health, Bolivia
The latest coronavirus news from Reuters
Breaking international news & views, where u.s. coronavirus cases are on the rise.
The states where the outbreak is growing fastest
New normal: How far is safe enough?
How countries are adapting social distancing rules and what we know about the risks of coronavirus in public places.
Global tracker
- Liechtenstein
- North Macedonia
- Switzerland
- Isle of Man
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Netherlands
- Czech Republic
- Aland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
Asia and the Middle East
- United Arab Emirates
- Saudi Arabia
- South Korea
- Philippines
- Afghanistan
- Mainland China
- Timor-Leste
- Palestinian territories
Latin America and the Caribbean
- El Salvador
- Dominican Republic
- Cayman Islands
- Trinidad and Tobago
- French Guiana
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Lucia
- Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Saint Martin
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Falkland Islands
- Turks and Caicos
- Sint Maarten
- British Virgin Islands
- Equatorial Guinea
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Ivory Coast
- Burkina Faso
- Guinea-Bissau
- Sierra Leone
- Central African Republic
- Sao Tome and Principe
- South Africa
- Republic of the Congo
- Western Sahara
- South Sudan
- New Zealand
- New Caledonia
- French Polynesia
- Papua New Guinea
Northern America
- United States
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Data sources Local state agencies, local media, Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker , Our World in Data , The World Bank , Reuters research
Design and development Gurman Bhatia , Prasanta Kumar Dutta , Chris Canipe and Jon McClure
Data collection and research Abhishek Manikandan, Aditya Munjuluru, Ahmed Farhatha, Amal Maqbool, Aniruddha Chakrabarty, Anna Banacka, Anna Pruchnicka, Anurag Maan, Anuron Kumar Mitra, Arpit Nayak, Arundhati Sarkar, Cate Cadell, Chaithra J, Chinmay Rautmare, Christine Chan, Daniela Desantis, Diana Mandia Alvarez, Elizaveta Gladun, Emily Isaacman, Enrico Sciacovelli, Gautami Khandke, Gayle Issa, Hardik Vyas, Harshith Aranya, Javier Lopez, Joao Manuel Vicente Mauricio, Juliette Portala, K. Sathya Narayanan, Kanupriya Kapoor, Kavya B., Lakshmi Siddappa, Lisa Shumaker, Mrinalika Roy, Nallur Sethuraman, Natalie Vaughan, Nikhil Subba, Olga Beskrovnova, Padraic Cassidy, Rohith Nair, Roshan Abraham, Sabahatjahan Contractor, Sanjana Vijay Kumar, Seerat Gupta, Shaina Ahluwalia, Shashank Nayar, Shreyasee Raj, Nivedha S., Simon Jennings, Sridhar Shrivathsa, Veronica Snoj, Wen Foo, Yajush Gupta, Aparupa Mazumder, Rittik Biswas and Maneesh Kumar
Translation Samuel Granados, Marco Hernandez, Erica Soh, Junko Tagashira, Momoko Honda, Kyoko Yamaguchi, Hiroko Terui, Pedro Fonseca, Olivier Cherfan, Kate Entringer, Dagmarah Mackos, Diana Mandia, Federica Mileo, Juliette Portala, Kate Entringer and Piotr Lipinski
We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
Bolivia Travel Restrictions
Traveller's COVID-19 vaccination status
Travelling from Canada to Bolivia
Open for vaccinated visitors
COVID-19 testing
Not required
Not required for vaccinated visitors
Restaurants
Not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Ready to travel?
Find flights to bolivia, find stays in bolivia, explore more countries on travel restrictions map, destinations you can travel to now, dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, united arab emirates, united kingdom, united states, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Can I travel to Bolivia from Canada?
Most visitors from Canada, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Can I travel to Bolivia if I am vaccinated?
Fully vaccinated visitors from Canada can enter Bolivia without restrictions.
Can I travel to Bolivia without being vaccinated?
Unvaccinated visitors from Canada can enter Bolivia without restrictions.
Do I need a COVID test to enter Bolivia?
Visitors from Canada are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Bolivia.
Can I travel to Bolivia without quarantine?
Travellers from Canada are not required to quarantine.
Do I need to wear a mask in Bolivia?
Mask usage in Bolivia is not required in public spaces and public transportation.
Are the restaurants and bars open in Bolivia?
Restaurants in Bolivia are open. Bars in Bolivia are .
International Travel Restrictions by Country
Find out where you can travel and covid-19 policies.
Select origin country, search destination or select a country on the map to see travel restrictions.
The travel status of individual countries can change suddenly, and we know it can be hard to stay on top of it all. That's why we're getting you the information you need to consider when planning travel. Learn about country-specific entry requirements such as the border status, COVID-19 testing requirements, and quarantine requirements. Many countries are reopening their borders for international travel. Find out which countries are open to vaccinated travelers.
Just enter your departure country above - the map will update to reflect countries' opening status and any entry requirements for air travelers. Before you book, be sure to double check your country's official government site.
Destinations you can travel to now
Dominican republic, netherlands, philippines, puerto rico, switzerland, united arab emirates, united kingdom, know when to go.
Sign up for email alerts as countries begin to open - choose the destinations you're interested in so you're in the know.
Filter by region, status and more
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Albania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Algeria.
American Samoa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter American Samoa.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Angola.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Anguilla.
Antigua And Barbuda
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Antigua And Barbuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Argentina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Armenia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Aruba.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Australia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Austria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Azerbaijan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bahrain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bangladesh.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Barbados.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belgium.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Belize.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Benin.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bermuda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bhutan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Botswana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brazil.
British Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the British Virgin Islands.
Brunei Darussalam
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Brunei Darussalam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bulgaria.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Burundi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cambodia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cameroon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Canada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cape Verde.
Caribbean Netherlands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Caribbean Netherlands.
Cayman Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cayman Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chad.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Chile.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter China.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Colombia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Comoros.
Cook Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Cook Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Costa Rica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Croatia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Curaçao.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Cyprus.
Czech Republic
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Czech Republic.
Democratic Republic of the Congo
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Denmark.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Djibouti without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Dominica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Dominican Republic.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, need to quarantine to enter East Timor.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ecuador.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Egypt.
El Salvador
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter El Salvador.
Equatorial Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Equatorial Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eritrea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Estonia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Eswatini.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ethiopia.
Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas)
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Falkland Islands (Islas Malvinas).
Faroe Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Faroe Islands.
Federated States of Micronesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Federated States of Micronesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Fiji.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Finland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter France.
French Guiana
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Guiana.
French Polynesia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter French Polynesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gabon.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Gambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Georgia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Germany.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ghana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Gibraltar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greece.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Greenland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Grenada.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guadeloupe.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guam.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guatemala.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guinea-Bissau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Guyana.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Honduras.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hong Kong.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Hungary.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Iceland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter India.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Indonesia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ireland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Italy.
Ivory Coast
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Ivory Coast.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jamaica.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Japan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jersey.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Jordan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kazakhstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kenya.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kiribati.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kosovo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kuwait.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Kyrgyzstan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Laos.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Latvia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lesotho.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liberia.
Liechtenstein
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Liechtenstein.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Lithuania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Luxembourg.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Macau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Madagascar.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malawi.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malaysia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Maldives.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Malta.
Marshall Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Marshall Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Martinique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mauritius.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mayotte.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mexico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Moldova.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mongolia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montenegro.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Montserrat.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Mozambique.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Namibia.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Nauru without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nepal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Netherlands.
New Caledonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Caledonia.
New Zealand
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter New Zealand.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nicaragua.
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Niger without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Nigeria.
North Macedonia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter North Macedonia.
Northern Mariana Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Northern Mariana Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Norway.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Oman.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Pakistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Palau.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Panama.
Papua New Guinea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Papua New Guinea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Paraguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Peru.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Philippines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Poland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Portugal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Puerto Rico.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Qatar.
Republic of the Congo
Fully vaccinated visitors from the United States can enter Republic of the Congo without restrictions.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Réunion.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Romania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Rwanda.
Saint Barthélemy
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Barthélemy.
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Kitts and Nevis.
Saint Lucia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Lucia.
Saint Martin
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Martin.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Samoa.
São Tomé and Príncipe
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter São Tomé and Príncipe.
Saudi Arabia
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Saudi Arabia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Senegal.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Serbia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Seychelles.
Sierra Leone
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sierra Leone.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Singapore.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovakia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Slovenia.

Solomon Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Solomon Islands.
South Africa
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Africa.
South Korea
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter South Korea.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Spain.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sri Lanka.
St. Maarten
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter St. Maarten.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sudan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Suriname.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Sweden.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Switzerland.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Taiwan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tajikistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tanzania.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Thailand.
The Bahamas
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter The Bahamas.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Togo.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tonga.
Trinidad and Tobago
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Trinidad and Tobago.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tunisia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Türkiye.
Turkmenistan
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Turkmenistan.
Turks and Caicos Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Tuvalu.
U.S. Virgin Islands
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the U.S. Virgin Islands.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uganda.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Arab Emirates.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter the United Kingdom.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uruguay.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Uzbekistan.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vanuatu.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Vietnam.
Wallis and Futuna
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Wallis and Futuna.
Western Sahara
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, will not be allowed to enter Western Sahara.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zambia.
Most visitors from the United States, regardless of vaccination status, can enter Zimbabwe.

Get trip-ready with at-home COVID-19 tests
How often is the data on this page updated.
We check for travel restriction information from government authorities daily, and update the page any time we get new information. The following information regarding travel restrictions for each country is correct to the best of our knowledge at the time of publication.
How many countries are closed to visitors?
As of Sep 11, 2 countries have completely restricted entry to non-citizens and 5 are open but require quarantine and/or a negative COVID test.
Where can I travel without COVID restrictions?
Currently you can travel from the United States to 197 countries without restrictions. Please check our map to learn more.
Are there any other types of travel restrictions besides COVID-19 tests and quarantines?
These are the two main types of restrictions or requirements needed to travel into another country. However, the COVID-19 testing options are continually widening as new methods are developed. Different countries may accept results from different or multiple test types, so be sure to check the individual country's specific requirements.
What should I do if I get COVID-19 while in another country?
If you get COVID-19 while in another country, follow the local authority's recommendations. These may include hospitalization, self-isolating and testing in that country. Be sure to contact your travel insurance company and travel provider as well and inform them of your situation.
What should I do if the borders of the country I am visiting close?
Depending on your home country, you may need to change your departure date and return home as soon as possible. If that's the case, contact your travel provider to find the earliest departure.
Additional resources
- What you need to know
- Airline policies
- Hotel policies
- Car policies
- Tips for flying
- Tips for hotel
- Tips for vacation rental
If you're looking for personalized travel advice for your own travel plans like whether or not a restriction applies to your trip, we won't be able to answer any questions or offer advice. Please consult your local government's resources.

Bolivia: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile
Research and data: Edouard Mathieu, Hannah Ritchie, Lucas Rodés-Guirao, Cameron Appel, Daniel Gavrilov, Charlie Giattino, Joe Hasell, Bobbie Macdonald, Saloni Dattani, Diana Beltekian, Esteban Ortiz-Ospina, and Max Roser
- Coronavirus
- Data explorer
- Hospitalizations
Vaccinations
- Mortality risk
- Excess mortality
- Policy responses
Build on top of our work freely
- All our code is open-source
- All our research and visualizations are free for everyone to use for all purposes
Select countries to show in all charts
Confirmed cases.
- What is the daily number of confirmed cases?
- Daily confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
- What is the cumulative number of confirmed cases?
- Cumulative confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
- Biweekly cases : where are confirmed cases increasing or falling?
- Global cases in comparison: how are cases changing across the world?
Bolivia: What is the daily number of confirmed cases?
Related charts:.
Which world regions have the most daily confirmed cases?
This chart shows the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases per day . This is shown as the seven-day rolling average.
What is important to note about these case figures?
- The reported case figures on a given date do not necessarily show the number of new cases on that day – this is due to delays in reporting.
- The number of confirmed cases is lower than the true number of infections – this is due to limited testing. In a separate post we discuss how models of COVID-19 help us estimate the true number of infections .
→ We provide more detail on these points in our page on Cases of COVID-19 .
Five quick reminders on how to interact with this chart
- By clicking on Edit countries and regions you can show and compare the data for any country in the world you are interested in.
- If you click on the title of the chart, the chart will open in a new tab. You can then copy-paste the URL and share it.
- You can switch the chart to a logarithmic axis by clicking on ‘LOG’.
- If you move both ends of the time-slider to a single point you will see a bar chart for that point in time.
- Map view: switch to a global map of confirmed cases using the ‘MAP’ tab at the bottom of the chart.
Bolivia: Daily confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
Differences in the population size between different countries are often large. To compare countries, it is insightful to look at the number of confirmed cases per million people – this is what the chart shows.
Keep in mind that in countries that do very little testing the actual number of cases can be much higher than the number of confirmed cases shown here.
Three tips on how to interact with this map
- By clicking on any country on the map you see the change over time in this country.
- By moving the time slider (below the map) you can see how the global situation has changed over time.
- You can focus on a particular world region using the dropdown menu to the top-right of the map.
Bolivia: What is the cumulative number of confirmed cases?
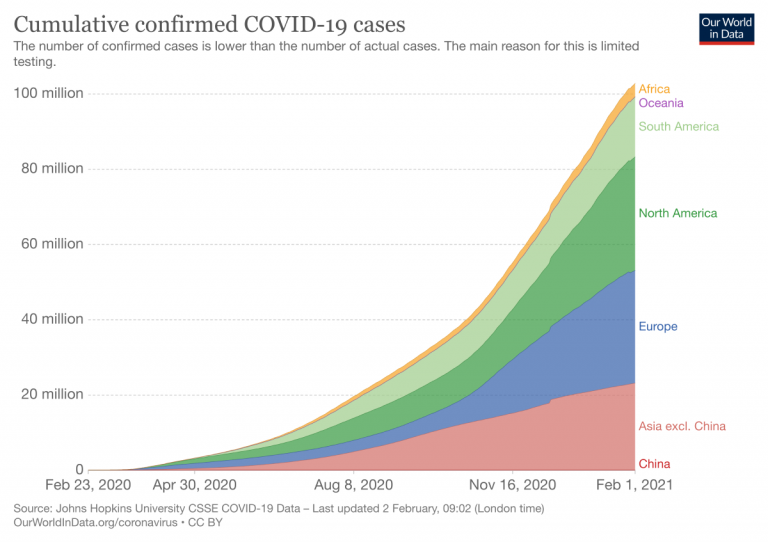
Which world regions have the most cumulative confirmed cases?
How do the number of tests compare to the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases?
The previous charts looked at the number of confirmed cases per day – this chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed cases since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In all our charts you can download the data
We want everyone to build on top of our work and therefore we always make all our data available for download. Click on the ‘Download’-tab at the bottom of the chart to download the shown data for all countries in a .csv file.
Bolivia: Cumulative confirmed cases: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed cases per million people.
Bolivia: Biweekly cases : where are confirmed cases increasing or falling?
Why is it useful to look at biweekly changes in confirmed cases.
For all global data sources on the pandemic, daily data does not necessarily refer to the number of new confirmed cases on that day – but to the cases reported on that day.
Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of cases – it is helpful to look at a longer time span that is less affected by the daily variation in reporting. This provides a clearer picture of where the pandemic is accelerating, staying the same, or reducing.
The first map here provides figures on the number of confirmed cases in the last two weeks. To enable comparisons across countries it is expressed per million people of the population.
And the second map shows the percentage change (growth rate) over this period: blue are all those countries in which the case count in the last two weeks was lower than in the two weeks before. In red countries the case count has increased.
What is the weekly number of confirmed cases?
What is the weekly change (growth rate) in confirmed cases?
Bolivia: Global cases in comparison: how are cases changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 cases , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in cases compare across the world.
Confirmed deaths
- What is the daily number of confirmed deaths?
- Daily confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
- What is the cumulative number of confirmed deaths?
- Cumulative confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
- Biweekly deaths : where are confirmed deaths increasing or falling?
- Global deaths in comparison: how are deaths changing across the world?
Bolivia: What is the daily number of confirmed deaths?
Which world regions have the most daily confirmed deaths?
This chart shows t he number of confirmed COVID-19 deaths per day .
Three points on confirmed death figures to keep in mind
All three points are true for all currently available international data sources on COVID-19 deaths:
- The actual death toll from COVID-19 is likely to be higher than the number of confirmed deaths – this is due to limited testing and challenges in the attribution of the cause of death. The difference between confirmed deaths and actual deaths varies by country.
- How COVID-19 deaths are determined and recorded may differ between countries.
- The death figures on a given date do not necessarily show the number of new deaths on that day, but the deaths reported on that day. Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of deaths – it is helpful to view the seven-day rolling average of the daily figures as we do in the chart here.
→ We provide more detail on these three points in our page on Deaths from COVID-19 .
Bolivia: Daily confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the daily confirmed deaths per million people of a country’s population.
Why adjust for the size of the population?
Differences in the population size between countries are often large, and the COVID-19 death count in more populous countries tends to be higher . Because of this it can be insightful to know how the number of confirmed deaths in a country compares to the number of people who live there, especially when comparing across countries.
For instance, if 1,000 people died in Iceland, out of a population of about 340,000, that would have a far bigger impact than the same number dying in the United States, with its population of 331 million. 1 This difference in impact is clear when comparing deaths per million people of each country’s population – in this example it would be roughly 3 deaths/million people in the US compared to a staggering 2,941 deaths/million people in Iceland.
Bolivia: What is the cumulative number of confirmed deaths?
Which world regions have the most cumulative confirmed deaths?
The previous charts looked at the number of confirmed deaths per day – this chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed deaths since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Bolivia: Cumulative confirmed deaths: how do they compare to other countries?
This chart shows the cumulative number of confirmed deaths per million people.
Bolivia: Biweekly deaths : where are confirmed deaths increasing or falling?
Why is it useful to look at biweekly changes in deaths.
For all global data sources on the pandemic, daily data does not necessarily refer to deaths on that day – but to the deaths reported on that day.
Since reporting can vary significantly from day to day – irrespectively of any actual variation of deaths – it is helpful to look at a longer time span that is less affected by the daily variation in reporting. This provides a clearer picture of where the pandemic is accelerating, staying the same, or reducing.
The first map here provides figures on the number of confirmed deaths in the last two weeks. To enable comparisons across countries it is expressed per million people of the population.
And the second map shows the percentage change (growth rate) over this period: blue are all those countries in which the death count in the last two weeks was lower than in the two weeks before. In red countries the death count has increased.
What is the weekly number of confirmed deaths?
What is the weekly change (growth rate) in confirmed deaths?
Bolivia: Global deaths in comparison: how are deaths changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 deaths , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in deaths compare across the world.
- How many COVID-19 vaccine doses are administered daily ?
- How many COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in total ?
- What share of the population has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine?
- What share of the population has completed the initial vaccination protocol ?
- Global vaccinations in comparison: which countries are vaccinating most rapidly?
Bolivia: How many COVID-19 vaccine doses are administered daily ?
How many vaccine doses are administered each day (not population adjusted)?
This chart shows the daily number of COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people in a given population . This is shown as the rolling seven-day average. Note that this is counted as a single dose, and may not equal the total number of people vaccinated, depending on the specific dose regime (e.g., people receive multiple doses).
Bolivia: How many COVID-19 vaccine doses have been administered in total ?
How many vaccine doses have been administered in total (not population adjusted)?
This chart shows the total number of COVID-19 vaccine doses administered per 100 people within a given population. Note that this is counted as a single dose, and may not equal the total number of people vaccinated, depending on the specific dose regime as several available COVID vaccines require multiple doses.
Bolivia: What share of the population has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine?
How many people have received at least one vaccine dose?
This chart shows the share of the total population that has received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. This may not equal the share with a complete initial protocol if the vaccine requires two doses. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric goes up by 1. If they receive the second dose, the metric stays the same.
Bolivia: What share of the population has completed the initial vaccination protocol ?
How many people have completed the initial vaccination protocol?
The following chart shows the share of the total population that has completed the initial vaccination protocol. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric stays the same. If they receive the second dose, the metric goes up by 1.
This data is only available for countries which report the breakdown of doses administered by first and second doses.
Bolivia: Global vaccinations in comparison: which countries are vaccinating most rapidly?
In our page on COVID-19 vaccinations, we provide maps and charts on how the number of people vaccinated compares across the world.
Testing for COVID-19
- The positive rate
- The scale of testing compared to the scale of the outbreak
- How many tests are performed each day ?
- Global testing in comparison: how is testing changing across the world?
Bolivia: The positive rate
Here we show the share of reported tests returning a positive result – known as the positive rate.
The positive rate can be a good metric for how adequately countries are testing because it can indicate the level of testing relative to the size of the outbreak. To be able to properly monitor and control the spread of the virus, countries with more widespread outbreaks need to do more testing.
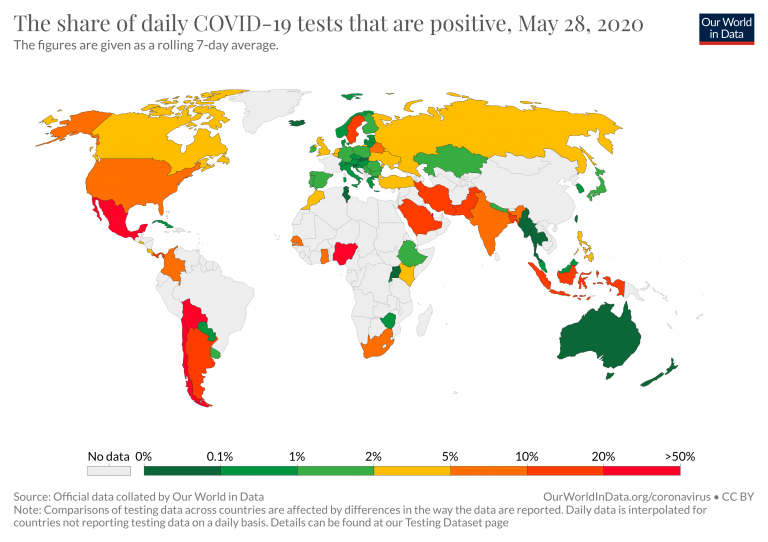
It can also be helpful to think of the positive rate the other way around:
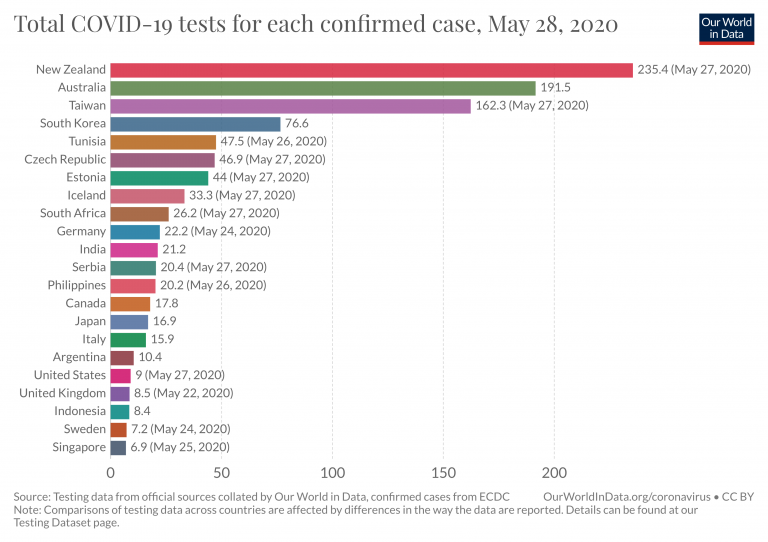
How many tests have countries done for each confirmed case in total across the outbreak?
Bolivia: The scale of testing compared to the scale of the outbreak
How do daily tests and daily new confirmed cases compare when not adjusted for population ?
This scatter chart provides another way of seeing the extent of testing relative to the scale of the outbreak in different countries.
The chart shows the daily number of tests (vertical axis) against the daily number of new confirmed cases (horizontal axis), both per million people.
Bolivia: How many tests are performed each day ?
This chart shows the number of daily tests per thousand people. Because the number of tests is often volatile from day to day, we show the figures as a seven-day rolling average.
What is counted as a test?
The number of tests does not refer to the same thing in each country – one difference is that some countries report the number of people tested, while others report the number of tests (which can be higher if the same person is tested more than once). And other countries report their testing data in a way that leaves it unclear what the test count refers to exactly.
We indicate the differences in the chart and explain them in detail in our accompanying source descriptions .
Bolivia: Global testing in comparison: how is testing changing across the world?
In our page on COVID-19 testing , we provide charts and maps on how the number and change in tests compare across the world.
Case fatality rate
- What does the data on deaths and cases tell us about the mortality risk of COVID-19?
- The case fatality rate
- Learn in more detail about the mortality risk of COVID-19
Bolivia: What does the data on deaths and cases tell us about the mortality risk of COVID-19?
To understand the risks and respond appropriately we would also want to know the mortality risk of COVID-19 – the likelihood that someone who is infected with the disease will die from it.
We look into this question in more detail on our page about the mortality risk of COVID-19 , where we explain that this requires us to know – or estimate – the number of total cases and the final number of deaths for a given infected population.
Because these are not known , we discuss what the current data on confirmed deaths and cases can and can not tell us about the risk of death. This chart shows both those metrics.
Bolivia: The case fatality rate
Related chart:.
How do the cumulative number of confirmed deaths and cases compare?
The case fatality rate is simply the ratio of the two metrics shown in the chart above.
The case fatality rate is the number of confirmed deaths divided by the number of confirmed cases.
This chart here plots the CFR calculated in just that way.
During an outbreak – and especially when the total number of cases is not known – one has to be very careful in interpreting the CFR . We wrote a detailed explainer on what can and can not be said based on current CFR figures.
Bolivia: Learn in more detail about the mortality risk of COVID-19
Learn what we know about the mortality risk of COVID-19 and explore the data used to calculate it.
Government Responses
- Government Stringency Index
To understand how governments have responded to the pandemic, we rely on data from the Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker (OxCGRT), which is published and managed by researchers at the Blavatnik School of Government at the University of Oxford.
This tracker collects publicly available information on 17 indicators of government responses, spanning containment and closure policies (such as school closures and restrictions in movement); economic policies; and health system policies (such as testing regimes).
How have countries responded to the pandemic?
Travel bans, stay-at-home restrictions, school closures – how have countries responded to the pandemic? Explore the data on all policy measures.
Bolivia: Government Stringency Index
The chart here shows how governmental response has changed over time. It shows the Government Stringency Index – a composite measure of the strictness of policy responses.
The index on any given day is calculated as the mean score of nine policy measures, each taking a value between 0 and 100. See the authors’ full description of how this index is calculated.
A higher score indicates a stricter government response (i.e. 100 = strictest response).
The OxCGRT project calculates this index using nine specific measures, including:
- school and workplace closures;
- restrictions on public gatherings;
- transport restrictions;
- and stay-at-home requirements.
You can see all of these separately on our page on policy responses . There you can also compare these responses in countries across the world.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Routine Vaccines
It’s important to be up to date on recommended routine vaccines prior to travel, including Flu, RSV and COVID-19.

Find a Clinic
Advice for Travelers
Personalized Health Information Tool for Global Travel
Disease Directory
Frequently Asked Questions
CDC Yellow Book
Pre-travel Rapid Evaluation Portal for Patients
Clinician Resources
Research and Surveillance
- Medical Tourism
- Cholera Information for Health Care Professionals
- COVID-19 Travel Information
- Travel Industry Resources
Learn about CDC’s Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country.
Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips.
See the full list of Travel Health Notices , including:
Level 2 - Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Updated Global Polio April 26, 2024
- Diphtheria in Guinea April 23, 2024
- Chikungunya in Timor-Leste April 05, 2024
Level 1 - Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Global Measles April 26, 2024
- Updated Oropouche Fever in South America April 24, 2024
- Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands April 18, 2024
There are no Warning , Alert, Watch, COVID-19 Very High, COVID-19 High, COVID-19 Moderate, COVID-19 Low, COVID-19 Unknown, Level 4, or Level 3 notices currently in effect.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in Bolivia due to the threat of violent crime and the risk of civil unrest.
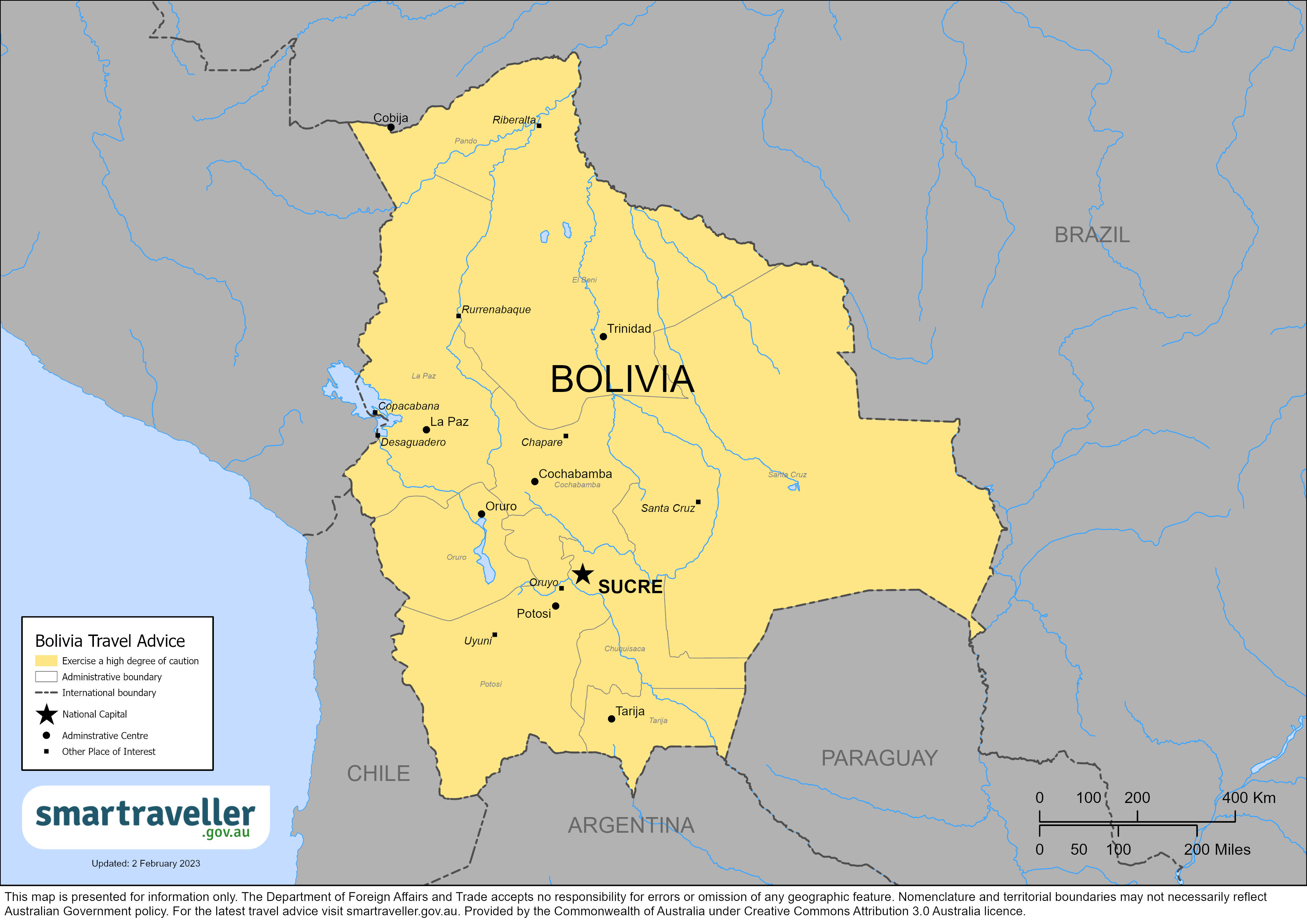
Bolivia (PDF 807.61 KB)
Americas (PDF 3.25 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 118 or go to the hospital.
Call 222 5016 for English-speaking tourist police.
Call 110 or contact the nearest police station.
Advice levels
Exercise a high degree of caution in Bolivia
- Civil unrest is common in Bolivia. Roadblocks, demonstrations, protests (some violent), and strikes could occur at any time. Don't cross roadblocks set up by protesters. Avoid crowds as they can become violent.
- Violent crime, associated with drug trafficking, poses a risk in some parts of the country, particularly Chapare and the Yungas regions. Take care in these areas. Travellers can be victims of drug-related crime near the Brazil border. Take extra precautions in this area.
- Petty theft is common in tourist areas and bus stations. Be alert to attempts to distract your attention from your luggage. Violent crime against foreigners has increased, including armed robbery, assault, and food and drink spiking. Don't leave your food or drink unattended.
- Criminals can pose as taxi drivers. Use only well-known radio taxi companies with the phone number displayed on the vehicle's roof. Don't hail taxis off the streets.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Yellow fever is a risk. Get vaccinated before you travel.
- Zika virus is also a risk. If you're pregnant, discuss your travel plans with your doctor before you leave.
- In areas below 2500m, there's a risk of malaria and dengue. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof. Use insect repellent. Consider taking anti-malaria medication.
- Many parts of Bolivia are at high altitudes. You can suffer altitude sickness above 2500m. If you plan to travel to these areas, consult your doctor before you leave. Get travel insurance to cover emergency evacuation from altitude and related medical costs.
Full travel advice: Health
- You must register your accommodation or hotel address online with Bolivian migration authorities. Failing to comply can result in fines when you leave the country.
- You must carry photo identification. This can be a photocopy of your passport.
- Dual national males older than 18 must complete military service upon arrival. Contact an embassy or consulate of Bolivia for details.
- Photography may upset locals. Ask permission before taking photos, particularly of children and in remote areas.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You don't need a visa to visit Bolivia for tourism. The length of stay permitted on entry is 30 days, which can be extended to 90 days, the maximum stay per year.
- You may need to show proof of onward travel on entry to Bolivia (a plane or bus ticket).
- Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate of Bolivia for the latest details.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- Australia has a consulate in La Paz. It provides limited consular assistance and can't issue passports.
- For full consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Peru .
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the Embassy's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Civil unrest and political tension.
Political and civil tensions are ongoing, and events can be unpredictable. Large-scale political demonstrations could occur with little warning and may result in violence. Pay close attention to your personal security at all times.
Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent.
You could encounter:
- demonstrations
Authorities may use tear gas and force to control protests.
Strikes and demonstrations may disrupt:
- local travel to Oruro, Uyuni and Santa Cruz
- international travel
Don't cross roadblocks set up by protesters, even if they appear unattended. Doing so may lead to violence. Check the Bolivian road authority website (Spanish only) for up-to-date information on which roads are blocked.
Anti-narcotics activities can lead to conflict between authorities and their targets in coca-growing regions:
- Chapare region between Santa Cruz and Cochabamba
- the Yungas region, north-east of La Paz
Bystanders can be affected.
During periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, protests and large public gatherings
- monitor local media and other sources
- follow the advice of local authorities
- take particular care to avoid conflicts in Chapare and the Yungas regions
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Criminals sometimes pose as police officers. Under Bolivian law, police need a written order or warrant to detain or search a suspect. If a police officer approaches you, ask to see a written order or warrant.
Petty crime
Theft is common:
- in tourist areas, including the Uyuni salt flats
- in bus stations
Thieves work in teams using various forms of distraction.
Violent crime
Violent crime against foreigners, including armed robbery and assault , has increased.
Violent crime can happen in the cities of La Paz and Santa Cruz, particularly:
- in tourist areas
- on public transport
Assaults and robberies are becoming more common, especially:
- in shared, unmarked and radio taxis
- in Coronilla Hill, located behind the main bus terminal in Cochabamba
- among hikers travelling without a guide on the Inca trails and in Rurrenabaque
Use an experienced, reputable tour guide to reduce risks when hiking.
Express kidnappings are a high risk at overland border points with Chile and Peru, such as Copacabana and Desaguadero. Victims are forced to withdraw money from ATMs to secure their release.
Travellers in Bolivia can also be victims of:
- food and drink spiking, followed by robbery or assault
- drug traffickers and other criminals in the Bolivian-Brazilian border region
To protect yourself from violent crime:
- don't leave food or drinks unattended
- don't accept drinks, food, gum or cigarettes from strangers or people you have just met
- use experienced, reputable tour guides for hiking or adventure trips
- take extra precautions in the Bolivia-Brazil border region
Use only well-known radio taxi companies with the phone number displayed on the vehicle's roof or ride-sharing applications. Don't hail taxis off the street.
Note the taxi's registration number and phone number.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
More information:
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Climate and natural disasters
Bolivia experiences severe weather , including landslides and flooding.
The rainy season is from November to March. Landslides, blocked roads and flooding are common.
Severe flooding and landslides can:
- disrupt transport services
- close airports
- make road travel difficult
If you plan to travel in the rainy season, confirm arrangements before you leave and check local weather reports.
In case of a natural disaster :
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- keep in contact with friends and family
- Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
- Bolivian road authority website (Spanish only)
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you leave.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Bolivia. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Insect-borne diseases
Yellow fever is a risk in Bolivia. Yellow fever is a potentially fatal virus spread by mosquitoes. It's prevented by vaccination. Get vaccinated before you travel.
Zika virus is widespread in Bolivia. If you're pregnant, the Australian Department of Health recommends you:
- discuss any travel plans with your doctor
- consider deferring non-essential travel to affected areas
In areas below 2500m, travellers are at risk from:
- Chagas disease
To protect yourself from illness:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
Consult your doctor about how to prevent malaria.
Seek medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
- Infectious diseases
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic, and other infectious diseases are common. These include:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
- avoid contact with dogs and other mammals
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, get medical help straight away.
Seek medical advice if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Altitude sickness
You're at risk of altitude sickness if you travel above 2500m.
Altitude sickness can be life-threatening and affect anyone, even if you're healthy.
You're more at risk if you:
- ascend quickly
- have had altitude sickness before
- exercise or drink alcohol before you get used to the altitude
- have health problems that affect breathing
Many areas of Bolivia are above 2500m, including:
- La Paz — 3660m
- Salar de Uyuni — 3650m
- Lake Titicaca — 3820m
- Potosi – 4090m
- Sucre – 2810m
See your doctor for specific advice to minimise the risk of altitude sickness.
Check if your insurance covers emergency evacuation from altitude and related medical costs.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
Private hospital facilities in Bolivia's major cities are reasonable. Outside of major cities, facilities are limited.
Treatment at private clinics and hospitals is expensive.
Hospitals often need payment or proof of medical insurance before they will treat you, even in an emergency.
You could need treatment at a more suitable place if you become seriously ill or injured.
Medical evacuation from Bolivia can be difficult and very expensive. Many air ambulance services can't fly into La Paz due to the high altitude.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
You must register your home or hotel address online with Bolivian migration authorities. If you don't register, you can receive a fine when you depart from the country. Consult your accommodation provider for more information or access the registration system online (Spanish).
Penalties for drug offences are severe. They include long prison sentences in local jails.
- Carrying or using drugs
Proof of identity
You must always carry photo identification in Bolivia. This can be a photocopy of your passport.
It's illegal to remove national treasures, including:
- pre-Columbian artefacts
- certain historical paintings
- items of Spanish colonial architecture and history
- some native textiles
- certain flora, fauna and fossils
It's illegal to excavate or collect fossils without written approval.
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
Bolivia has compulsory military service. Dual national males older than 18 must complete military service upon arrival in Bolivia.
Children who are dual citizens travelling alone or with only one parent or legal guardian must follow strict entry and exit rules. See Travel
- Dual nationals
- Embassy or consulate of Bolivia
Local customs
Ask permission before taking photos of people, particularly children and in remote areas.
- LGBTI travellers
Same-sex relationships are legal, but they aren't widely accepted.
- Advice for LGBTI travellers
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Visa-free short stays
You don’t need a visa to visit Bolivia for tourism. The length of stay permitted upon entry is 30 days. You can request an extension of your stay at an immigration office in Bolivia. The maximum visa-free stay length is 90 days during one calendar year.
Ensure you get an entry stamp when you arrive in Bolivia. Otherwise, you'll have to pay a fine when you leave. You should also make sure to get an exit stamp, especially when you are crossing a land border.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the nearest embassy or consulate for details about visas, currency, customs and other travel requirements.
Travel via the United States
If you're travelling through the US, you must meet US entry or transit requirements.
Check your visa requirements with a US embassy or consulate well in advance of your travel.
- Travel advice for the US
Travel via Chile
If you’re travelling via Chile, ensure you meet all current entry or transit requirements.
- Travel advice for Chile
Border measures
Visitors may be asked to show proof of onward travel on entry to Bolivia (a plane or bus ticket).
Yellow fever vaccination
You'll need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter Bolivia. Some airlines may want to see one when you leave.
Find out about returning to Australia after exposure to yellow fever .
- Countries with a risk of yellow fever
Other formalities
Travel with dual-national children.
Unless travelling with both parents, dual nationals under the age of 18 years must:
- provide their birth certificate and written consent to travel from both parents, translated into Spanish and certified by a Bolivian embassy or consulate on arrival
- provide a travel permit from the Children's Court on exit
Bolivian Immigration Service Avenida Camacho entre Calles Loayza y Bueno La Paz, Bolivia Phone: (+591 2) 211 0960
- Advice for people travelling with children
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport is not valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with X gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country.
Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
The currency is the Boliviano (BOB).
Declare all amounts more than $US10,000 on arrival. This covers all forms of currency, not only cash.
US dollars are the most easily exchangeable foreign currency.
ATMs are available in cities throughout Bolivia.
Many businesses accept international credit cards.
Local travel
Tours and adventure activities
Transport and tour operators don't always follow recommended safety precautions or maintenance standards. They may not provide safety equipment, such as life jackets and seatbelts.
This includes adventure activities, such as "Death Road" mountain biking tours, tours to the Uyuni salt plains, and mine tours in Potosi.
If you plan to take part, do a tour or adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Uyuni salt plains
Choose a tour operator that has a CB radio or satellite phone. Mobile phone coverage is limited.
Be prepared for delays from melting snow and snowfalls.
Driving permit
To drive in Bolivia, you need both:
- a valid Australian driver's licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Get your IDP before you leave.
Road travel
Driving in rural areas is dangerous. Hazards include:
- poorly maintained roads and vehicles
- poor street signs and lighting
- pedestrians and livestock on roads
- heavy snowfalls and melting snow
During the wet season, November to March, the road to the Yungas and Beni may experience flooding and landslides.
It's illegal to drive with a blood alcohol reading above 0%.
If driving:
- check local traffic laws and practices
- be alert to possible hazards, especially at night and in rural areas
Allow extra time and be prepared to change your plans if travelling to:
- the Uyuni salt plains during winter or early spring
- the Yungas or Beni during the wet season
- Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check with your travel insurer whether your policy covers you when using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet.
Book registered taxis through your hotel or ride-share apps.
Be aware of criminals and scams targeting taxi passengers.
Public transport
Public transport can be unsafe due to poor roads, driving and vehicle maintenance standards.
Boat travel
Tourist boats used on Lake Titicaca and for river excursions in jungle areas are often basic.
Always wear a life jacket, even if others don't.
- Travelling by boat
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Bolivia's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Call 800-14-0081 for English-speaking tourist police.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
Australia has a consulate in La Paz. It provides limited consular assistance and can't issue Australian passports.
Australian Consulate, La Paz
Centro Empresarial del Sur Av Arequipa No 8221 2nd floor, office 16
Phone/Whatsapp: (+591) 706 10626 Email: [email protected]
Opening hours: 9am-12pm, Monday to Friday You can also contact the Consul via email, phone or WhatsApp to discuss your needs.
Australian Embassy in Peru
The Australian Embassy in Peru also offers consular assistance.
Avenida La Paz 1049, 10th Floor Miraflores, Lima, 18 Peru
Phone: +51 1 630 0500 Email: [email protected] Website: peru.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australia en Perú y Bolivia Instagram: @embauslima X: @embauslima
Opening hours: 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
- +61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
- 1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Bolivia?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This advice reflects the UK government’s understanding of current rules for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport , for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Bolivia set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Bolivian Embassy in the UK (in Spanish).
Passport validity requirements
To enter Bolivia, your passport should have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Checks at border control
You may need to show proof of your accommodation, for example, a hotel or hostel booking and its address, at least for your first night in Bolivia.
Make sure you get your passport stamped.
Make sure you get an entry stamp when you arrive in Bolivia, otherwise you’ll have to pay a fine when you leave.
If you enter Bolivia overland, make sure you get your passport stamped on both sides of the border, with an exit stamp from the country you are leaving and an entry stamp on the Bolivian side.
Bolivia no longer stamps passports on the border with Argentina, but you must register your exit with Argentina’s immigration authorities (in Spanish) who pass the information to Bolivian immigration.
The British Embassy cannot intervene in immigration issues.
Visa requirements
You can visit Bolivia for up to 90 days without a visa. Border officials issue 30-day stamps, but you can apply for 90 days in person at your nearest immigration office in Bolivia (in Spanish).
As a tourist, you get 90 days of visa-free travel in a one-year period. If you want to stay longer, check with the Bolivian Embassy in the UK (in Spanish) or the Department of Immigration (in Spanish).
To work, study, travel for business or for other reasons, you must meet the Bolivian government’s entry requirements (in Spanish). Requirements include a police criminal record certificate from the UK, which you can get from the ACRO Criminal Records Office . If you need any documents from the UK, get them translated into Spanish and legalised by the Legalisation Office .
Travelling with children
If only one parent or legal guardian is travelling with a child, you cannot visit Bolivia for longer than 90 days. If you stay for more than 90 days, the child will need a judicial permit to leave Bolivia with only one parent.
Vaccination requirements
At least 8 weeks before your trip, check the vaccinations and certificates you need in TravelHealthPro’s Bolivia guide .
Depending on your circumstances, this may include a yellow fever vaccination certificate.
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods you can take into or out of Bolivia (in Spanish). You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
- Coronavirus
Bolivia
Coronavirus cases:, total coronavirus cases in bolivia.
- logarithmic
Daily New Cases in Bolivia
Active cases in bolivia, total coronavirus deaths in bolivia, daily new deaths in bolivia.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
COVID-19 Testing: Numerous private and public clinics throughout Bolivia offer COVID-19 testing. For a comprehensive list of COVID-19 testing centers, please visit our medical assistance page. The designated government agency regulating COVID-19 testing in Bolivia is the Servicio Departamental de Salud (SEDES).
Read the country information page for additional information on travel to Bolivia. If you decide to travel to Bolivia: Read the Department of State's COVID-19 page before planning any international travel, and read the Embassy COVID-19 page for country-specific COVID-19 information. Monitor local media for breaking events and be prepared to ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Bolivia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements. ... Do I need a COVID test to enter Bolivia? Visitors from the United States are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Bolivia.
COVID-19: All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information. COVID-19 vaccine. ... Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for Bolivia for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Read the entire Travel Advisory. Do not travel to: Chapare region due to crime. Reconsider travel to: Yungas region due to crime. Country Summary: Demonstrations, strikes, and roadblocks can occur at any time in Bolivia. Demonstrations can result in violence. Roadblocks and strikes may cut off traffic and restrict the flow of goods and services ...
Children and travel. Bolivia has strict requirements for the entry and exit of persons under the age of 18, including special documentation. ... COVID-19. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Detailed Travel Advisory. Published 26.11.2021 1. Passengers must have a negative COVID-19 RT-PCR test taken at most 72 hours before departure from the first embarkation point. - This does not apply to passengers who are 5 years or younger. 2. A completed "Declaracion Jurada del viajero para el seguimiento COVID-19" must be presented upon ...
Show More. Johns Hopkins experts in global public health, infectious disease, and emergency preparedness have been at the forefront of the international response to COVID-19. This Project is supported by Bloomberg Philanthropies and the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF). Bolivia - COVID New Cases, Deaths, Testing Data - Johns Hopkins ...
There have been 952,456 infections and 21,973 coronavirus-related deaths reported in the country since the pandemic began. Daily reported trends How Bolivia compares
The COVID-19 pandemic in Bolivia was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).The virus was confirmed to have spread to Bolivia on 10 March 2020, when its first two cases were confirmed in the departments of Oruro and Santa Cruz.. On 12 March, Bolivia suspended all public school sessions until ...
Also remember to check other immigration and sanitary requirements for your trip, such as: passport, visas, tourist cards, yellow fever vaccine and any additional or special document required by the legal provisions of the countries of departure, transit and destination. Visit the Required Immigration Documents section. Let's find your travel ...
Object moved to here.
Visit the Embassy of Bolivia website for the most current visa information. Entry requirements: Valid U.S. passport with at least 6 months validity remaining. International Certificate of Yellow Fever Vaccination. With a visitor visa, you may stay 30 days per trip, not to exceed 90 days per year. A Bolivian visitor visa costs $160 US and can be ...
Travel and sale of alcohol ban 22-23 March. There is a national travel ban on 23 March, seek local advice about travel to the airport if you have a flight. The sale of alcohol will also be banned ...
Find continuously updated travel restrictions for Bolivia such as border, vaccination, COVID-19 testing, and quarantine requirements. ... Do I need a COVID test to enter Bolivia? Visitors from Canada are not required to present a negative COVID-19 PCR test or antigen result upon entering Bolivia.
Find out where you can travel and COVID-19 policies. Select origin country, search destination or select a country on the map to see travel restrictions. Updated Monday, September 11, 2023 ... regardless of vaccination status, can enter Bolivia. Show more. Open. Bosnia and Herzegovina. Most visitors from the United States, regardless of ...
The actual death toll from COVID-19 is likely to be higher than the number of confirmed deaths - this is due to limited testing and challenges in the attribution of the cause of death. The difference between confirmed deaths and actual deaths varies by country. How COVID-19 deaths are determined and recorded may differ between countries.
More. Learn about CDC's Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country. Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips. CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide ...
Zika virus is also a risk. If you're pregnant, discuss your travel plans with your doctor before you leave. In areas below 2500m, there's a risk of malaria and dengue. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof. Use insect repellent. Consider taking anti-malaria medication. Many parts of Bolivia are at high altitudes.
Passport validity requirements. To enter Bolivia, your passport should have an 'expiry date' at least 6 months after the date you arrive. Check with your travel provider that your passport and ...
1,177,145. Daily Cases Graph - Daily Deaths Graph. Learn more about Worldometer's COVID-19 data. Bolivia Coronavirus update with statistics and graphs: total and new cases, deaths per day, mortality and recovery rates, current active cases, recoveries, trends and timeline.
LATEST BOLIVIA COVID-19 NEWS: 29th April 2022 - Bolivia no longer requires unvaccinated travellers to quarantine upon arrival. From 26th January 2022, vaccination certificates (or negative PCR test results taken within the last 48 hours) will be required to enter any public building (including banks, bars and supermarkets), buses and internal ...
All land border crossings between Chile and Bolivia are open perMay 1, 2022. As of 9 May 2023, no Covid-19 related restrictions or requirements apply to travelers entering Chile. No COVID-related entry requirements. No COVID-19 test (PCR and/or serology) required for entry. No health screening procedures in place at airports and other ports of ...