We’re sorry, this site is currently experiencing technical difficulties. Please try again in a few moments. Exception: request blocked
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"

Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
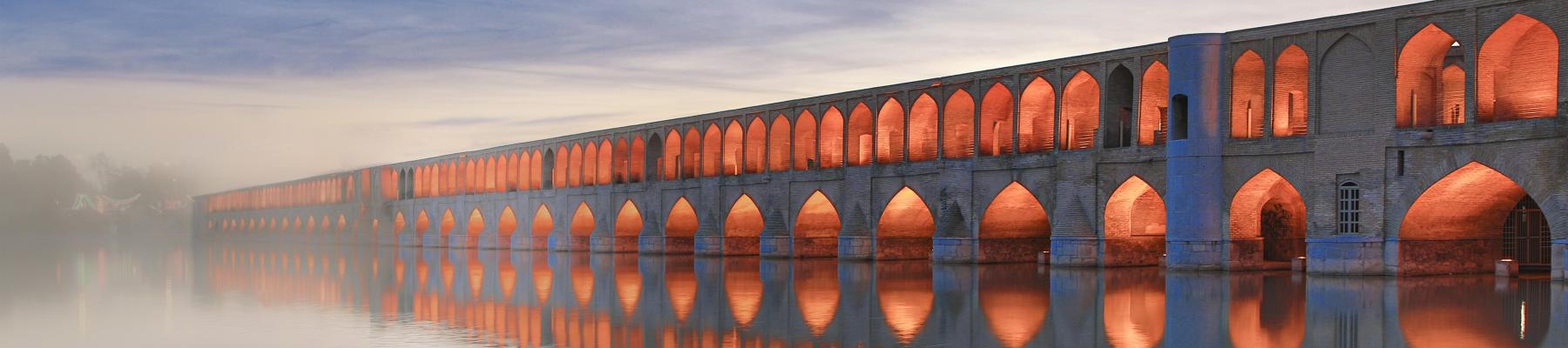
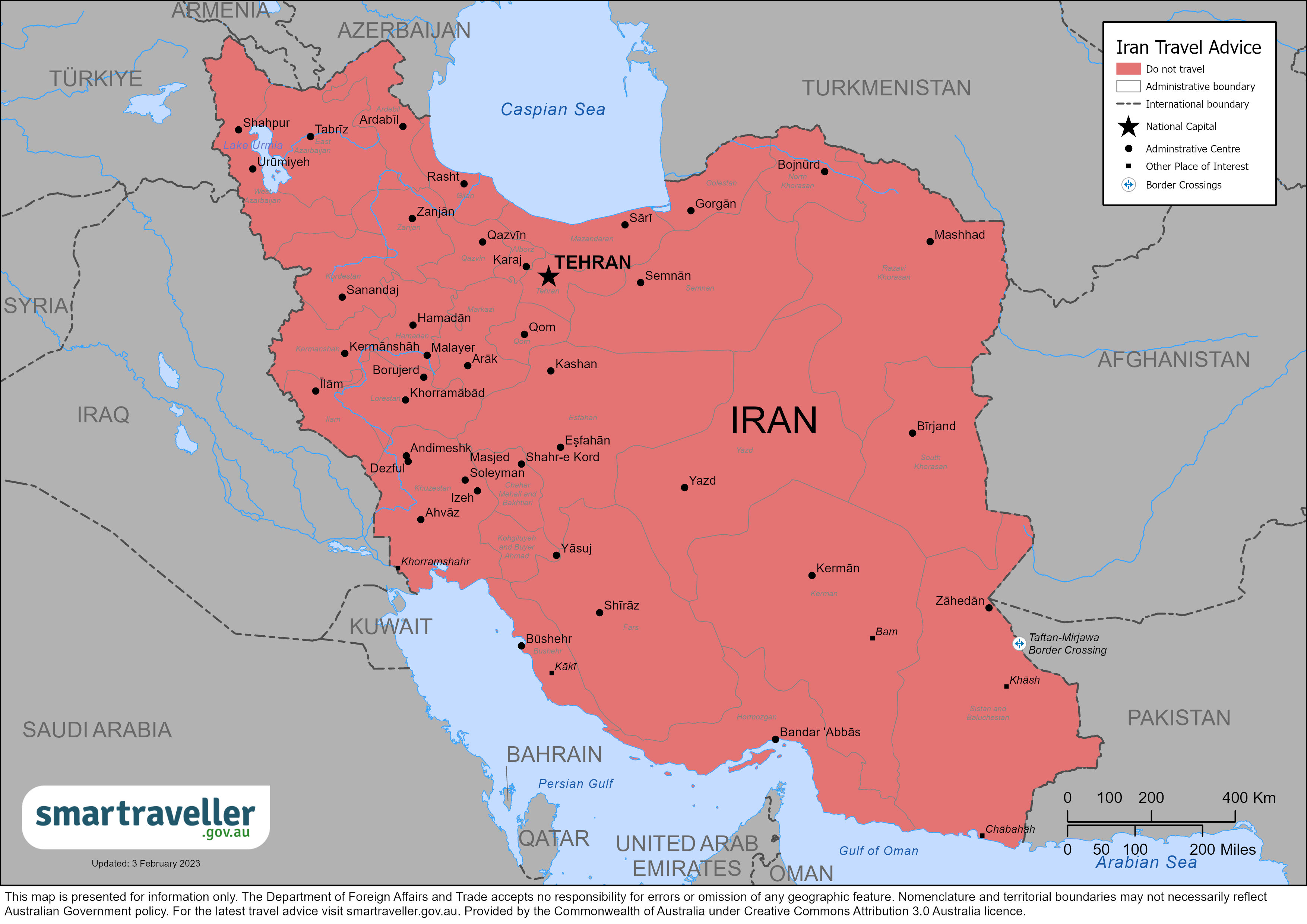
Iran travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: August 7, 2024 15:39 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, iran - avoid all travel.
You should leave by commercial means if you can do so safely. Our ability to provide consular services in Iran is extremely limited.
Back to top
In the context of recent developments between Canada and Iran, Iranian authorities could take retaliatory measures that could pose a risk to the safety and security of Canadians, including Canadian-Iranians.
Canadians in Iran are likely to be subject to increased surveillance by Iranian authorities for activities and behaviours that would be considered innocuous in Canada, including:
- taking photographs in public places
- travelling to remote areas not usually frequented by tourists
- interacting with the local population
Keep a low profile and don’t share your personal information with strangers.
There is no resident Canadian government office in Iran. The ability of Canadian officials to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
Demonstrations
Political demonstrations and gatherings may occur.
Large-scale and violent protests took place across Iran in the Fall of 2022 following the strict enforcement of the hijab law by the Iranian authorities. Security forces strongly repressed demonstrators resulting in numerous arrests, injuries and casualties. In some cases, arrested individuals were sentenced to death for charges arising from their participation in the demonstrations.
The situation remains highly volatile and could escalate without notice. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. Security forces could use excessive and lethal force to disperse crowds. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Disruptions to telecommunications services, including mobile internet access, may occur during large-scale demonstrations.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Monitor local and international media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Border areas
Pakistan and afghanistan.
Bandits in border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan are usually involved in drug trafficking and use kidnapping to secure the release of group members from prison.
Sistan-Baluchistan, which borders Pakistan, is regularly affected by ethnic conflicts and is also a known route for smugglers. Foreign nationals have been the target of kidnappings.
Terrorist attacks may also occur in this province.
If you decide to travel overland to Pakistan and Afghanistan despite this warning:
- travel only on main roads
- travel in organized groups
- avoid travel after dark
The province of Khuzestan borders Iraq. It is regularly affected by ethnic conflicts. Foreign nationals have been the target of kidnappings.
Border with Iraq is usually closed. It can be opened on a case-by-case basis to allow the passage of certain foreigners or to give refugees access to containment camps located on the Iranian side of the border.
Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan
The borders with Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan are open only to citizens of those countries.
Foreigners travelling in the vicinity of these sensitive borders often attract the attention of local security forces, which can result in short periods of detention.
There is an increased threat of attacks against Western interests and of terrorist attacks in general. The security situation could worsen rapidly and with little warning.
Attacks have targeted:
- foreign interests
- Iranian military and government establishments
- tourist attractions and popular public places
- nightclubs and entertainment venues
- public transportation
Further attacks may occur, and terrorists may also target:
- crowded places
- places with high pedestrian traffic where foreigners may gather
- commercial establishments
- local government offices
- public transit stations
- busy streets
- places of worship
Exercise a high degree of caution at all times.
Kidnapping for ransom can occur, especially in Baluchistan and in the border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan. Foreign nationals have also been the target of kidnapping.
Use varied and unpredictable routes and schedules when moving from one place to another.
Petty crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, occurs. Violent crime affects both Iranians and foreigners.
Thieves often target four-wheel-drive vehicles.
Plainclothes individuals may pose as police officers and ask to see foreign currency and passports. If you are approached, you should politely decline to cooperate but offer to go to the nearest police station.
- Avoid showing signs of affluence, such as flashy jewellery
- Ensure personal belongings, including your passports and other travel documents, are secure at all times
- Carry a photocopy of your passport’s identification page at all times and leave a photocopy with a relative
- Don’t surrender any documents or cash
- Stay in touch with family and friends, especially if you’re travelling alone
- Avoid walking after dark
Women's safety
Women may be subject to some forms of harassment and verbal abuse. Gender-based violence is common in Iran.
Some Canadian and Canadian-Iranian women have been stranded in Iran or mistreated by an Iranian husband or a male relative. Local authorities consider domestic violence to be a private matter and rarely discuss it in public.
Women and children require the permission of the husband, or an Iranian male head of household, to obtain a passport or travel document. They also require permission to leave the country.
The dress code is strictly enforced in Iran. Women must wear a headscarf and a long jacket that covers the arms and upper legs while in public.
Advice for women travellers
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety can vary greatly throughout the country, and city streets are poorly lit. The highway system is relatively well developed.
Trucks run mostly at night, often without headlights. Motorists are reckless and don’t respect traffic laws. They almost never give way to pedestrians at designated crossing points. Parked cars may obstruct sidewalks on main roads in urban areas. Sidewalks are rare in residential areas.
Expect roadblocks and checkpoints.
- Avoid travelling at night
- Consider hiring a personal driver who’s familiar with local conditions
- If you are involved in an accident, remain at the scene until authorities arrive
Public transportation
Most taxis don’t have meters. Drivers often overcharge foreigners.
- Only hire official taxis from agencies or hotel-based companies
- Take pre-booked official taxis, which are safer than those hailed from the street
- Negotiate fares in advance, or insist that the driver use the meter
- Never enter a cab if it already has one or more passengers
- Note the licence plate number and name of the driver when you travel
- Immediately communicate this information to family or friends
Railway transport
Trains are comfortable and punctual, but service is limited and slow.
Iran and the United Arab Emirates both claim sovereignty over the islands in the Gulf and the military patrols the waters. Foreigners navigating Iranian waters have been arrested and detained. In September 2019, Iranian authorities specifically called for the seizure of Canadian assets and vessels.
Exercise caution if travelling by sea, including for recreational purposes, particularly around the disputed islands of Abu Musa and Tunb.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Iranian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Canadians can verify this information with the Interests Section of the Islamic Republic of Iran of the Embassy of Pakistan in Washington, D.C.
- Interests Section of the Islamic Republic of Iran – Embassy of Pakistan in Washington, D.C.
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months beyond the date you expect to leave Iran.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Tourist visa: required Business visa: required Student visa: required Pilgrimage visa: required Press visa: required Transit visa: required
Overstaying your visa period may lead to detention, imprisonment and fines. You will be required to remain in Iran until the situation has been resolved.
- E-Visa Portal – Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Government of Iran
Transit pass
If you enter Iran with a transit pass issued by an Iranian embassy or consulate abroad, you may have to obtain an Iranian passport to exit the country.
Regional travel
Canadians have been denied entry into Iran because their passports bore an Israeli visa, an Israeli border stamp or an Egyptian or Jordanian border stamp issued by an office bordering Israel. Such a stamp would indicate the traveller entered from Israel.
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
In this destination, rabies is commonly carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by a dog or other animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. In this destination, rabies treatment may be limited or may not be available, therefore you may need to return to Canada for treatment.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The level of risk may vary by:
The virus that causes chikungunya is spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times.
Learn more:
Insect bite and pest prevention Chikungunya
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever is a viral disease that can cause fever, pain and bleeding under the skin. In some cases, it can be fatal. It spreads to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, or from the bite of an infected tick. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Celebrations which include the slaughtering of animals and contact with their blood and/ or tissues may increase the risk of exposure to the virus.
Protect yourself from tick bites and wear gloves or other protective clothing if you are in contact with the blood and tissues of animals, particularly livestock. There is no vaccine available for Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.
- In this country, risk of dengue is sporadic. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue fever.
Cutaneous and mucosal leishmaniasis causes skin sores and ulcers. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly.
Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
Cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) have been reported in this destination. The risk to travellers is low; MERS is primarily spread through contact with camels or camel-based products (raw milk, meat, urine). It can also spread through close contact, such as when caring for an infected person.
Avoid contact with animals (especially camels), camel-based products, and wash your hands frequently.
Prevention of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
MERS symptoms range from mild and flu-like to more severe pneumonia-like symptoms, and can result in death.
There is no vaccine or medication that protects against MERS.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Air quality
Air pollution can be severe in major cities. It may affect people suffering from respiratory ailments.
During periods of high pollution:
- consult your doctor before traveling to see if the situation could affect you
- limit your activities outdoors
- monitor local media
- follow the instructions of local authorities
Medical services and facilities
Good health care is limited in availability. Quality of care varies greatly throughout the country.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Health and safety outside Canada
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Iran is under international and Canadian sanctions . While these sanctions don’t prohibit travel to Iran, they could be relevant to your travel.
Legal system
The Iranian legal system differs from the one in Canada.
You may be held for lengthy periods without access to legal counsel or consular officials if you are suspected of or witness to offences.
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs and alcohol are severe. Convicted offenders can expect severe penalties, including the death penalty.
Drugs, alcohol and travel
Iran is an Islamic theocratic republic. A conservative interpretation of Islamic practices and beliefs is closely adhered to in the country’s customs, laws, and regulations.
Islamic law is strictly enforced. Breach of public morality, non-compliance with dress-code and making disparaging remarks about Islam, the clergy and religious symbols, including on social networks, are considered serious offences. They are punished severely.
Former Muslims who have converted to other religions have been subject to arrest and prosecution.
- Respect local traditions, customs, laws and religion at all times
- Be aware of your actions and behaviour
In 2024, the lunar month of Ramadan is expected to begin on or around March 10.
In public, between sunrise and sunset, refrain from:
Dress and behaviour
Iranian customs, laws and regulations reflect the conservative interpretation of traditional and Islamic practices and beliefs adhered to by the Iranian authorities.
To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- dress conservatively
- behave discreetly
- respect religious and social traditions
Shorts are considered inappropriate attire for both men and women.
Women should carry a headscarf to cover their head at all times while travelling in Iran.
There are reports indicating that the police are using surveillance cameras to identify and monitor women who don’t wear the hijab in public places, as required by Iranian law. Employers and owners of businesses such as stores, restaurants, cafés and shopping malls face closure and prosecution if they don’t enforce the hijab law.
If you promote unveiling while you are in Iran, you could face criminal charges.
Women who fail to comply with the law may face:
- arrest and detention
- jail sentences
- restricted access to public institutions such as hospitals, schools, airports and other social services.
- restricted access to mobile phones and Internet
Intimate and extramarital relations
Public displays of affection between two people of the opposite sex, especially between a non-Muslim man and a Muslim woman, is not well socially accepted.
If you engage in extramarital relationships, you may be subject to severe penalties, including the death penalty.
Canadian women who register their marriage with the Iranian authorities automatically become Iranian citizens. They are treated as such by Iranian law.
Marriage between an Iranian and a foreigner is subject to the rules of conduct and Islamic laws. As such, an Iranian husband may prevent his wife and children from leaving Iran, even if they are of foreign nationality.
Marriage Overseas
Iranian and Canadian family law systems are significantly different.
Iran doesn’t automatically recognize the orders of Canadian courts in matters of family law.
A Canadian divorce certificate is not automatically recognized in Iran.
You must get the Canadian divorce certificate authenticated by a Canadian Embassy prior to have it sanctioned by an Iranian Court for it to be recognized under Iranian law.
If an Iranian court doesn’t sanction your divorce, and you return to Iran as a woman, your ex-husband may request the Iranian authorities to confiscate your passport. As a husband, authorities may not allow you to leave Iran if you have not paid the dowry to your wife after divorce.
Children custody
Iran isn’t a signatory to The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction.
Children of a male Iranian national, including Canadian-Iranian citizens, are in the sole custody of their father. They require their father’s permission to leave Iran.
To avoid any difficulties in Iran, consult a Canadian and an Iranian lawyer before travelling. If you're involved in local legal proceedings such as divorce or custody, seek legal advice regarding your rights and responsibilities.
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and Iran.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in Iran by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in Iran to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
2SLGBTQI+ persons
Iranian law criminalizes sexual acts and relationships between persons of the same sex.
2SLGBTQI+ persons could also be discriminated against or detained based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, or sex characteristics.
If you are convicted, you could face corporal punishment, imprisonment or the death penalty.
2SLGBTQI+ persons should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Iran.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship
Iran doesn’t legally recognize dual citizenship.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of Iran, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
If you're a Canadian-Iranian citizen, you must enter and exit Iran using your Iranian passport. You may also not be able to leave Iran unless you meet certain conditions.
Canadians, particularly dual Canadian-Iranian citizens, are at risk of:
- being arbitrarily questioned, arrested or detained
- having their passport confiscated
Canadian-Iranian dual citizens should carefully consider the risks of travelling to Iran.
Dual citizens
Mandatory military service
Military service is mandatory for male Iranian citizens aged 18 to 34, unless exempt. This also applies to dual Canadian-Iranian citizens, even those born in Canada.
If you are a Canadian-Iranian citizen older than 17 years, and planning to visit Iran, check your military service obligation prior to your travel. You may not be allowed to leave Iran without first having completed your military service.
Communications and political activities
Communications are closely scrutinized by local authorities. You may face severe consequences if you discuss, share or publish information on the political situation or criticize the regime in place, including on social media.
Photography
It is prohibited to photograph (including with drones);
- government buildings
- security forces, military and police installations and vehicles
- public buildings, including airports, ports, bridges, embassies and power plants
Such sites are not always well identified. In doubt, seek permission, or refrain from taking the photo.
Always ask permission before taking photographs of local residents.
All luggage may be subject to search upon arrival and departure.
Customs officials may screen your electronic device.
Prohibited items
Possession of prohibited items is forbidden and may result in detention and or imprisonment. Such items include:
- Magazines and DVDs with sexual or explicit content
- Satellite dishes
- Western CDs and film
Pork Products
It’s prohibited to import and consume pork-based products.
The workweek runs from Sunday to Thursday.
You must carry an International Driving Permit.
International Driving Permit
The currency in Iran is the Iranian rial (IRR).
The economy is exclusively cash-based. Credit cards aren’t accepted in Iran. ATMs exist only for local banking, for the use of Iranians. Due to international sanctions, it’s not possible to transfer funds to Iran using commercial banking system or money transfer company.
- Bring sufficient cash, preferably in U.S. dollars or euros
- Note that U.S. banknotes used must be in crisp condition
Seismic activity
Iran is located in an active seismic zone. Earthquakes occur.
Severe weather
Dust storms.
The weather is very dry and hot from May to October. Dust storms and sand storms may occur during the summer months.
Sand-laden winds can blow at high speeds for days, creating difficult driving conditions. Poor visibility can also affect flights. These storms can also cause respiratory problems, which can be fatal in some individuals.
If a dust storm is occurring:
- stay indoors
- keep windows closed
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- monitor local media for up-to-date information on the situation
Rainy season
The rainy season extends from November to March. During the rainy season, flooding, including flash flooding, can occur.
Seasonal flooding can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable, due to mudslides and landslides. Bridges, buildings and infrastructure may be damaged.
- Monitor local media for the latest updates, including those on road conditions
- Stay away from flooded areas
- Monitor local news and weather reports
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 110
- medical assistance: 115
- firefighters: 125 / 123
Consular assistance
There is no resident Canadian government office in Iran. The Embassy of Canada to Türkiye in Ankara has consular responsibility for Iran.
Azerbaijan, Georgia. Offering consular services to Canadians in Iran.
For emergency consular assistance, call the Embassy of Canada to Türkiye in Ankara and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
We continue to advise:
Do not travel to Iran as there's a high risk you could be arbitrarily detained or arrested.
Iran (PDF 927.2 KB)
The Middle East (PDF 1.45 MB)
Local emergency contacts
Fire and rescue services, medical emergencies.
Call 115 or go direct to the hospital.
Mountaineers can also contact the Red Crescent on 112 for help.
Call 110 or visit the nearest police station.
Advice levels
Do not travel to Iran.
Do not travel to Iran as there's a high risk you could be arbitrarily detained or arrested.
- Terrorist attacks could happen anywhere in Iran, including Tehran or other locations frequented by foreigners and tourists. They could occur at any time with little or no warning. Avoid possible targets and areas with a low level of security. Possible targets for attacks include embassies, hotels, places of worship, tourist sites, government interests, military parades and locations, Western businesses and other interests. Take official warnings seriously.
- An increased threat of military and terrorist attacks against Israel and Israeli interests across the region and ongoing military action in the Occupied Palestinian Territories could lead to increased tensions in other locations in the Middle East.
- Regional tensions are high, and the security environment could deteriorate with little or no notice. In an attack or other armed conflict, you should follow the advice of local authorities. See our general advice on protecting your safety ( There’s an armed conflict ).
- Increased tensions in the Middle East may result in airspace closures, flight cancellations and diversions and other travel disruptions.
- Dependants of Australian officials in Iran have been offered voluntary departure to return to Australia.
- Demonstrations and protests are expected. Small, localised protests continue in parts of Iran. Previously, security forces' response to protests has been severe, and many protesters and bystanders have been injured, killed or detained. There has been an increase in the number of foreign nationals arrested during previous protests. Avoid all demonstrations and protests.
- Australians, including dual nationals, should strongly consider leaving Iran as soon as possible. Foreigners in Iran, including Australians, are at a high risk of arbitrary detention or arrest. Foreign and dual nationals have been detained without due process of law. Iran does not recognise dual nationality. Our ability to provide consular support to dual Australian-Iranian nationals is extremely limited. We can't guarantee access to consular services or legal representation if you're detained or arrested.
- There are ongoing disruptions to telecommunications services, including mobile internet access.
- Regional tensions are high and could escalate rapidly. There is ongoing hostility between Iran and Israel, and military tensions between Iran, the US and other countries in the Middle East. The Iran-Iraq, Iran-Afghanistan, and Iran-Pakistan border areas are extremely dangerous.
- Regional and international politics can trigger protests. These may target Western or UN diplomatic missions. Avoid vigils, marches, demonstrations and large public gatherings, as they can turn violent without warning.
- Kidnapping for ransom can occur. Foreign nationals have also been the target of kidnapping. Terrorist groups, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in the Afghanistan and Pakistan border areas. They often clash violently with security forces. Bombings and shootings occur. Be alert to your surroundings, especially at night. Outside these areas, the level of violent crime is low.
- Women can face unwanted attention and harassment. If you're a woman, take care when travelling alone, particularly at night.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Outbreaks of insect borne diseases such as malaria, tick-borne encephalitis and leishmaniasis occur. Use insect and mosquito repellent.
- HIV/AIDS is a risk. Take precautions if you engage in high-risk activities.
- Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur. These include cholera, typhoid and hepatitis. Drink only boiled or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- Significant air pollution occurs in major cities. Sandstorms and dust storms happen often. Get medical advice if you have allergies or breathing difficulties.
Full travel advice: Health
- Don't use, carry or import illegal drugs. Punishments for drug offences are severe. They include the death penalty.
- Get professional advice if you're involved in local legal proceedings. In particular, seek advice on matters of family law, such as divorce, child custody and child support.
- Same-sex relations are illegal for both men and women. Penalties include corporal punishment and death.
- Iran has strict codes of dress and behaviour. Women are required by law to wear a headscarf and loose-fitting clothing covering their arms and legs. Men face fewer clothing restrictions but should avoid shorts and sleeveless t-shirts. Close contact between unmarried men and women is illegal, as is being in a de facto relationship. This is particularly the case for interactions between Muslims and non-Muslims. It's against the law to behave in a way that offends Islam, such as encouraging a Muslim to convert.
- Be careful when taking photos. It's illegal to photograph military or government sites, critical civil infrastructure and public protests. It's illegal to use drones without authorisation.
- Iran has strict importation laws. You can't import alcohol, pornography, pork products or short-wave radios. It's also illegal to import printed or recorded Western materials, including religious material. You'll need to get permission to bring in certain types of electronic equipment, such as satellite phones, GPS trackers and walkie-talkies.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- We advise Australians not to travel to Iran. If you're in Iran, you should strongly consider leaving as soon as possible. If despite our advice you travel to Iran, you'll need a visa to enter and you'll need to get it before you travel. Contact your nearest Iranian embassy for details.
- Airlines may cancel or reduce their operations into and out of Iran at short notice.
- Some countries have restrictions on travellers coming out of Iran.
- If your passport contains Israeli stamps or visas, Iranian authorities will refuse your entry.
- If you overstay your visa in Iran for any reason, even one beyond your control, you'll incur a fine. The Australian Government cannot pay this fine for you. You must also apply for an exit visa. You can get more information on Iranian visa and exit permit requirements from the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Bureau for Aliens and Foreign Immigrant Affairs.
- Most Australian travel insurance policies won't cover you for travel to Iran. You'll need a specialised policy.
- The local currency is the Iranian Rial (IRR). Declare any foreign currency you have when you arrive in Iran or authorities may confiscate it when you leave. You can exchange major currencies in all big cities. You can't use international credit or bank cards. You can't transfer money using commercial banks or money transfer companies. Bring enough cash in Euros or US Dollars to cover your stay.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Tehran . The Embassy's working week is from Sunday to Thursday.
- Our ability to provide consular support to dual Australian-Iranian nationals is extremely limited.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Security situation.
Regional tensions are high, and the security situation could deteriorate quickly with little or no notice. This may also result in airspace closures, flight cancellations, flight diversions, and other travel disruptions.
The security situation in Iran remains volatile. Tensions in the region are high and may escalate further, due to ongoing hostility between Iran and Israel, and military tensions between Iran, the US, and other countries in the Middle East.
If despite our advice you go to Iran, or decide to stay there, monitor media for possible threats and take extra precautions for your safety:
- keep a low profile.
- keep in contact with family and friends
- don't travel alone or at night
- check routes before you travel
- don't put your travel or other plans on social media
- work with only reliable, registered and authorised organisations and travel agencies
- don't carry large amounts of cash
Airlines may cancel or reduce their operations to and from Iran at short notice. If tensions escalate, your options to leave may be limited. The Australian Government may not be able to assist with your departure. Check the latest flight status with your airline or travel provider and make arrangements in case you can’t leave. Share those plans with family and friends.
Iranian authorities are active in and closely monitor border areas with Iraq, Afghanistan and Pakistan. The security situation within 10km of the Iran-Iraq border is extremely dangerous.
Do not visit military or nuclear sites; these are not always clearly marked. Follow the advice of local authorities and monitor the media.
Civil unrest and political tension
Political developments in the region and local political tensions can trigger protests, demonstrations and vigils with little notice. Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can potentially turn violent.
Australian embassy staff and their families in Tehran have been advised to monitor their surroundings and avoid protest areas.
Some airlines may cancel flights at short notice in response to security developments - check with your airline.
In late 2022 and early 2023, there were widespread protests across many cities and towns in Iran. Previously, security forces' response to protests has been severe, and many protesters and bystanders have been injured, killed or detained. During past protest periods, there have been increases in the number of foreign nationals arrested. You should avoid all protest activity.
Iranians sometimes protest against some Western and Middle East embassies and UN missions.
To protect yourself during periods of unrest:
- avoid demonstrations, protests, large crowds and vigils
- do not photograph demonstrations, protests, large crowds or vigils
- monitor media for possible threats
- plan activities to avoid disruption on national or commemorative days
- follow the advice of local authorities
- share your itinerary with family and friends and keep in close contact so they know where you are.
Be prepared to change your plans in case of disruptions.
If civil unrest disrupts transport, ask your airline, travel agent or insurer for help.
More information:
- Demonstrations and civil unrest
Risk of arbitrary detention or arrest
Travellers in Iran, including Australians, are at a high risk of arbitrary detention or arrest. A number of Australians, including dual nationals, have been detained in Iran without due process of law.
There's been an increase in the number of foreign nationals being arrested or detained in Iran.
You may be at greater risk of detention if authorities are suspicious of your activities or background. You could attract the attention of authorities if you:
- study or do other academic activity
- travel outside tourist areas
- are near crowds, demonstrations or sensitive sites
- take photos, except in major tourist sites
- have contact with Iranians who are of interest to authorities
- behave or express views perceived as anti-Iranian, anti-Iranian Government, or that could cause religious offence
- are affiliated with, or have links to, Iranian opposition or other political groups.
Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you're a dual Australian-Iranian national and are detained in Iran, our ability to provide consular support is extremely limited.
The Australian Government may not be notified if you're detained. We can't guarantee consular access to any Australian detained or arrested. We also can't guarantee access to legal representation.
If you're in Iran, you should leave immediately.
- Advice for dual nationals
- Fact sheet: Arrested or jailed overseas
A terrorist attack could happen anywhere in Iran at any time, including in Tehran.
In January 2024, at least 84 people were killed and more than 200 wounded in suicide bombing attacks in Kerman, southern Iran, carried out by Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISKP).
On 26 October 2022, a terrorist attack on the Shah Cheragh Shrine in Shiraz killed at least 14 people and injured 40 others.
Possible targets for attacks include:
- places of worship
- tourist sites
- government interests
- military parades and locations
- Western businesses and other interests
To stay safe from terrorist risks:
- be alert to possible threats throughout the country
- avoid places where there is a low level of security and possible target areas
- monitor the media for new threats
- report suspicious activity or items to police
- take official warnings seriously
- follow the instructions of local authorities
If there's an attack:
- leave the area as soon as it's safe
- avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks
Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
Kidnapping for ransom is a risk in Iran. Foreign nationals have been targeted. The kidnapping risk is heightened in the border areas with Afghanistan and Pakistan, including in the area east of Bam, Jask, and the Sistan and Baluchestan provinces. Terrorists, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in these regions.
Kidnapping happens with political, ideological and criminal motives.
To reduce the risk of being kidnapped:
- always be alert to your personal security and surroundings
- get professional security advice for travel in locations with a heightened kidnap risk
- check your accommodation has appropriate security measures
- vary your movements and don't set patterns
- avoid isolated locations, particularly when travelling alone
- notify family or friends of planned travel and share your location
- avoid talking about your money or business affairs
- use ATMs in public places and during daylight hours
- avoid giving personal details to strangers online or over the phone
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers.
Ransom payments to kidnappers have funded further terrorist attacks and criminal activity. Paying a ransom to terrorist groups will likely break Australian counter-terrorism financing laws.

Violent crime
The level of violent crime in Iran is generally low, but petty crime is increasing due to the worsening economic situation.
Terrorists, drug traffickers, smugglers and bandits are active in the border areas near Afghanistan and Pakistan. This includes:
- Sistan and Baluchestan province
- east of the city of Bam in Kerman province
Violent incidents often occur in these areas, such as:
- clashes between security forces and smugglers
Travel at night in these areas is particularly dangerous.
Be alert to your surroundings, especially at night. Don't draw unwanted attention to yourself.
Petty crime
There have been increasing reports of thieves in passing vehicles and on motor bikes snatching bags from pedestrians, home break-ins and robberies.
Women can face unwanted attention and harassment. Women should take care travelling alone, particularly at night.
Scams and fraud
Men may approach foreigners and claim to be plain-clothes police. They say they're looking for foreign drug dealers and ask to see wallets and ID.
If this happens, it could be a scam . Ask a uniformed police officer for help.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you’re connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or to Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations where there are social or political tensions, or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
Cyber security when travelling overseas
Climate and natural disasters
Earthquakes and severe weather occur in Iran.
If a natural disaster happens:
- secure your passport in a safe, waterproof location
- monitor local media
- follow the advice of local authorities
- keep in contact with your friends and family
Earthquakes
Iran is in an active seismic zone and experiences frequent earthquakes . There have been several major earthquakes in recent years.
Aftershocks often follow a major earthquake. They can cause further damage to already weakened structures.
Register with the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System to receive alerts on major disasters.
Severe weather
Iran experiences extremely high temperatures.
The temperature in some areas can reach over 50˚C in July and August, the hottest months of the year.
Some regions have heavy snowfall during winter.
Sandstorms and dust storms occur regularly.
Flash flooding can occur, particularly in Spring.
Travel insurance
If despite our advice you plan to travel to Iran, you'll need a specialised travel insurance policy that covers travel to high-risk destinations. Most Australian policies won't cover you for travel to Iran. Check that Iran is not excluded from your cover because of sanctions or its travel advice level of 'do not travel'.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care. The Australian Government won't pay for any costs or organise evacuation.
If you can't get or afford travel insurance , you should not travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
Some specialised medicines are in short supply in Iran.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in Iran. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medicine is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Medical evacuation may be difficult.
Insect-borne diseases
Malaria is endemic outside the major towns in Iran's south and west.
Other insect-borne diseases are common, including:
- leishmaniasis
- tick-borne encephalitis
Ticks are most active in spring, summer and autumn.
To protect yourself from disease:
- ensure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Get medical advice if you have a fever, muscle pain, rash or severe headache.
Infectious diseases
HIV/AIDS is a risk.
Take precautions if you engage in activities that may expose you to the virus.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases occur, such as:
- tuberculosis
Serious outbreaks sometimes occur.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink boiled water or bottled water with sealed lids
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food, such as salads
Get medical help if you have a fever or diarrhoea.
Air pollution
Significant air pollution occurs in major cities. Sandstorms and dust storms occur regularly.
Get medical advice if you have allergies or breathing difficulties.
Medical care
Medical facilities.
The standard of medical facilities varies. Facilities in remote areas are extremely limited.
If you become seriously ill or injured, you'll need to be evacuated to a place with better facilities, such as London or Dubai. Medical evacuation can be very expensive and may not be possible.
Medical tourism
Medical tourism including for cosmetic operations is common in Iran. The standard of medical service providers can vary. If you're considering getting medical treatment in Iran, you should research and choose your medical service providers carefully. Serious post-surgery complications and deaths have occurred.
You should discuss your plans with your Australian doctor or specialist before committing to getting procedures done in Iran.
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you're an Australian citizen with Iranian nationality, our ability to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
The Australian Government may not be notified if you're detained. We can't guarantee consular access to any Australian detained or arrested. We also can't guarantee access to legal representation of your choice.
Penalties for importing and possessing drugs are severe and include the death penalty.
Authorities have executed foreigners for drug-related offences in recent years.
Carrying or using drugs
Get professional advice if you're involved in local legal proceedings. In particular, seek advice on matters of family law, such as:
- child custody
- child support
Know your rights and responsibilities.
Penalties for serious offences include death and corporal punishment. Same-sex relations are considered serious offences.
These activities are illegal in Iran:
- homosexual acts for both men and women
- close contact between unmarried men and women
- being in a de facto relationship
- failing to meet the legal dress code
- importing alcohol, pornography, pork products or short-wave radios
- importing printed or recorded Western material, including those with a religious theme
Local authorities consider domestic violence to be a private family matter. Iranian law does not prohibit domestic violence.
Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
Dress and behaviour
Iran has strict Islamic codes of dress and behaviour.
It's illegal to behave in a way considered to offend Islam. For example, you must not encourage Muslims to convert to another religion.
In public women are required by law to wear:
- loose-fitting clothing to cover arms and legs
- a long coat
- a headscarf
If you fail to follow these dress requirements, you may be detained, fined or denied access to government and other services.
In public men should not wear shorts or sleeveless T-shirts.
Photography
You cannot photograph sensitive sites or events, including:
- military and nuclear sites
- government buildings and installations
- critical civil infrastructure
- public demonstrations
Electronic equipment
It's illegal to use drones without authorisation.
You will need permission to bring in a range of electronic equipment, including:
- satellite phones
- GPS trackers
- walkie-talkies
Unauthorised use may result in arrest or detention. Tracking software installed on mobile phones, tablets or other computer equipment may attract the attention of authorities.
For advice, contact your nearest Iranian embassy or consulate .
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law and respecting customs
Dual citizenship
Iran doesn't recognise dual nationality.
If you're a dual national, you may be at greater risk of arbitrary arrest or detention. Our ability to provide consular assistance is extremely limited.
If you're arrested or detained, it's highly unlikely the Government of Iran would:
- allow us to give you consular services
- notify the Australian Embassy that you've been arrested or detained.
Under Iranian law, Iranian dual nationals must enter and exit Iran on their Iranian passport. Iranian immigration officials routinely confiscate the foreign and Iranian passports of dual nationals. D ual nationals will not be able to depart Iran without their Iranian passport.
If you're an Australian-Iranian dual national, authorities may not allow you to leave Iran if:
- you're male and you haven't completed military service
- you're female and you don't have permission from your husband or a senior male relative to leave Iran
- you're male and have not paid back the dowry to your wife after divorce
We advise you not to travel to Iran if you are dual Australian-US or Australian-Israeli citizen, in line with those countries' advice to their citizens. For other nationalities, you should check with the relevant country’s travel advice for advice about your risks.
- Dual nationals
- US travel advice for Iran
- UK Government travel advice for Iran
Local customs
The Islamic holy month of Ramadan is observed in Iran. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws during this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during the day. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Visitor visa
If despite our advice you decide to travel to Iran, you'll need a visa to enter. You must apply for a visa before you travel. Contact Iranian embassy in Australia to apply.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the embassy of Iran for details about visas, currency, customs and other travel requirements.
The Government of Iran issues Iranian visas. The Australian Embassy can't intervene in visa matters, including visas on arrival.
If you overstay your visa in Iran for any reason, even one beyond your control, you'll incur a fine. The Australian Government cannot pay this fine for you. You must also apply for an exit visa. You can get more information on Iranian visa and exit permit requirements from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Bureau for Aliens and Foreign Immigrant Affairs.
- Embassies and Consulates of Iran
Other formalities
If your passport has evidence you've travelled to Israel, such as an Israeli exit or entry stamp, authorities will refuse you entry to Iran.
Strict import restrictions apply.
If you're a dual national, you may not be able to leave Iran unless you meet certain conditions.
Some countries won't let you enter unless your passport is valid for 6 months after you plan to leave that country. This can apply even if you're just transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
You can end up stranded if your passport isn't valid for more than 6 months.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible.
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with ‘X’ gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can’t guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
The local currency is the Iranian Rial (IRR).
Declare any foreign currency you have when you arrive in Iran. If you don't, authorities may confiscate it when you leave.
You can change major foreign currencies in all major cities. However, recent government action has made it harder to change money in exchange bureaus.
You can't use international credit or bank cards.
You can't transfer funds into Iran using:
- the commercial banking system
- a money transfer company
Bring enough cash in Euros or US Dollars to cover your stay.
Local travel
Driving permit.
To drive in Iran you need both:
- a valid Australian driver's licence
- an International Driving Permit (IDP)
Get an IDP before leaving Australia.
Road travel
Iran has one of the highest rates of road accidents in the world.
You're more likely to die in a motor vehicle accident in Iran than in Australia. Road accidents are a common cause of death and injury.
Hazards include bad roads and poor driving standards.
If you plan to drive:
- check you have enough insurance cover
- ensure you understand local traffic laws and practices
- don't drink and drive
Pedestrians should exercise extreme caution when crossing roads, as traffic can be very congested and road-users unpredictable or undisciplined.
Driving or riding
Motorcycles
Check if your travel insurance policy covers you for using a motorbike, quad bike or similar vehicle.
Always wear a helmet.
Only use registered taxis and limousines. Book them through your hotel.
Public transport
Iran is serviced by extensive bus and rail options. Road conditions and road safety vary across the country. Rail services are more limited and slower. Public transport in the main cities is often very crowded.
The Gulf has many areas with security issues and territorial disputes. Authorities may inspect, detain and arrest vessels. Foreigners navigating Iranian waters have been arrested and detained.
Piracy occurs in the Gulf.
Check the International Maritime Bureau's piracy report .
The International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) hasn't audited air safety authorities in Iran.
The EU has operational restrictions in place for some of Iran Air's fleet. The airline hasn't met the EU's international safety standards.
Ageing planes on many of Iran's domestic air services create serious safety concerns.
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check Iran's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network .
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
English speakers are generally not available.
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact the Australian Embassy in Tehran.
Australian Embassy
No.11, Yekta Street Bahar Street, Shahid Fallahi Street Valie Asr Avenue Tehran, Iran
Phone: +98 21 7206 8666 Fax: +98 21 7206 8777 Website: iran.embassy.gov.au Facebook: Australia in Iran Instagram: @AustraliaInIran
The Embassy's working week is from Sunday to Thursday.
Check the Embassy website for details about opening hours, scheduled Embassy holidays and any temporary closures.
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
+61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to Iran?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Share this page:
Learn about your destination
Take 90 seconds for safer travel.
Travel Advisory Levels
Enroll in step.

Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad.
Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Passports, travel and living abroad
- Travel abroad
- Foreign travel advice
Entry requirements
This information is for people travelling on a full ‘British citizen’ passport from the UK who choose to travel against FCDO advice. It is based on the UK government’s understanding of Iran’s current rules for the most common types of travel.
The authorities in Iran set and enforce entry rules. If you’re not sure how these requirements apply to you, contact the Iranian Embassy in the UK .
You are at risk of arrest, detention and a death sentence if you travel to Iran.
British nationals are at increased risk of questioning and detention by the Iranian authorities. See Safety and security .
COVID-19 rules
There are no COVID-19 testing or vaccination requirements for travellers entering Iran.
Passport validity requirements
If you choose to enter Iran against FCDO advice, your passport must have an ‘expiry date’ at least 6 months after the date you arrive. It’s not possible to apply for a British passport from Iran.
Check with your travel provider that your passport and other travel documents meet requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.
You will be denied entry if you do not have a valid travel document or try to use a passport that has been reported lost or stolen.
Dual nationality
Iran does not recognise dual nationality. If you are a dual national, the Iranian authorities will consider you to be an Iranian national. They are highly unlikely to accept any requests made by the UK government on your behalf.
All Iranian nationals must enter and leave Iran using an Iranian passport. If you want to travel to the UK from Iran, you may also need to prove to the Iranian authorities that you have the right to enter the UK. You must be able to produce your British passport or a valid UK visa in your Iranian passport on request. You may face increased scrutiny, questioning or detention because of your connection to the UK.
Recent media reports suggest Iran is willing to detain people who have been visiting relatives inside Iran. Having travelled to and from Iran previously without issue does not guarantee your safety. See Safety and security for more information about the risks British nationals face in Iran.
Being considered an Iranian national
Even if you do not consider yourself Iranian, the Iranian authorities may see you as an Iranian national. For example, if your father is Iranian, or if you’re married to an Iranian man.
Previous travel to Israel
If your passport has stamps from Israel or other countries’ border crossing points with Israel, you may be refused entry to Iran.
Overseas British passport applications
You cannot apply for a British passport from Iran.
You can apply in a neighbouring country . Choose from the list of countries and follow the application process for that country.
For help with your passport application, contact HM Passport Office .
Visa requirements
You must have a visa to visit Iran unless you hold an Iranian passport.
Check the expiry date of your visa before travelling. If you overstay your visa, you may have to stay in Iran until this is resolved and you may be detained.
If you’re travelling through an Iranian airport, check visa requirements with your airline and the Iranian Embassy in the UK .
Applying for a visa
If you choose to travel to Iran against FCDO advice, apply for a visa well in advance of your travel. The application process for an Iranian visa can be long and unpredictable.
If you want to travel to Iran with a British passport, the Iranian Embassy has told FCDO you must either apply as part of an organised tour or have a sponsor in Iran to get a visa. Check with the Iranian Embassy in the UK for more information.
Your passport must be valid for at least 6 months from the date you submit your visa application.
Women and girls aged 10 or over should wear a headscarf in their visa application photos.
Some British nationals have had problems getting visas from private online visa agencies.
Vaccine requirements
To enter Iran, you must have certificates to prove you’ve had:
a yellow fever vaccination if you’re coming from a country listed as a transmission risk
a polio vaccine if you’re coming from a polio-affected country
For full details about medical entry requirements and recommended vaccinations, see TravelHealthPro’s Iran guide .
Customs rules
There are strict rules about goods that you can take into or out of Iran. You must declare anything that may be prohibited or subject to tax or duty.
Pork products
Importing pork products is illegal.
Children travelling without a male parent
In Iran, a female parent travelling with her children must have the father’s permission, usually verbal, to take them out of Iran. Iranian immigration authorities will usually assume you have permission unless the father has petitioned the court, or the court has ruled to prevent the children travelling. For more information, contact the Iranian Embassy in the UK .
Kish Island
To enter Kish Island, you must arrange your visit through an Iranian travel agency. The agency must:
- inform the Iranian Ministry of Foreign Affairs about your visit at least 2 weeks before you travel
- have received confirmation that a visa will be issued on arrival
The nearest Iranian embassy or consulate can give you advice and a list of registered travel agents.
You must also have a hotel reservation before you travel. Your guide must:
- pass a copy of the hotel reservation confirmation to the immigration office at Kish Airport at least 48 hours before you arrive
- meet you at the airport when you arrive
Travellers have occasionally been denied entry to Kish without explanation. If you’re denied entry, follow the advice of your airline or travel agent.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Do not travel to Iran due to the risk of terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping, arbitrary arrest of U.S. citizens and wrongful detentions. Country Summary: U.S. citizens should not travel to Iran for any reason.
Do not travel to Iran due to the risk of kidnapping and the arbitrary arrest and detention of U.S. citizens. Exercise increased caution due to wrongful detentions. Country Summary: U.S. citizens visiting or residing in Iran have been kidnapped, arrested, and detained on spurious charges.
The Travel Advisory for Iran is Level 4, Do Not Travel. The Department of State recommends U.S. citizens do not travel to Iran due to the risk of terrorism, civil unrest, kidnapping and the arbitrary arrest of U.S. citizens.
Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
We advise Australians not to travel to Iran. If you're in Iran, you should strongly consider leaving as soon as possible. If despite our advice you travel to Iran, you'll need a visa to enter and you'll need to get it before you travel. Contact your nearest Iranian embassy for details.
FCDO travel advice for Iran. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
Learn about your destination. 1 2 3 4 5. Take 90 Seconds for Safer Travel. Travel Advisories and Alerts for U.S. Citizens. Travel Advisory Levels. Subscribe to get up-to-date safety and security information and help us reach you in an emergency abroad. Recommended Web Browsers: Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome.
FCDO travel advice for Iran. Includes safety and security, insurance, entry requirements and legal differences.
All Iranian nationals must enter and leave Iran using an Iranian passport. If you want to travel to the UK from Iran, you may also need to prove to the Iranian authorities that you have the...
If you’re travelling to Iran, our up-to-date travel advice gives you practical tips on emergency contacts, security, climate and other essential information.