- Government of india
- Skip to main content

COVID-19 Travel Advisory
Please visit : https://incredibleindia.org/content/incredible-india-v2/en/covid-19-travel-advisory.html

- GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
- Skip to main content


Search form

स्वास्थ्य एवं परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय Ministry of Health & Family Welfare स्वास्थ्य एवं परिवार कल्याण विभाग Department of Health & Family Welfare

About the Ministry
- Who's Who
- Minister of State
- Social Media Update
- Contact Details
- Organisational Chart
- Work Allocation
- Constitutional Provisions
- Departments of Health and Family Welfare
- Department of Health Research
- Central International Health Division
- Autonomous Bodies
- State Health Departments
- State Health Societies
- Teaching Institutions
- Research Institutions
- National Health Mission
- Department of AIDS Control
- Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP)
- National Center for Vector Borne Diseases Control (NCVBDC)
- National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme (NTEP)
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program (NVHCP)
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP)
- National Programme for Health Care of the Elderly(NPHCE)
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Deafness (NPPCD)
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS)
- Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme under NHM
- National programme for Prevention & Management of Trauma & Burn Injuries (NPPMT&BI)
- Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana - PMSSY
- Poor Patients-Financial Support
- Infrastructure Maintenance
- Other National Health Programmes
- Health Melas
- PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)
- Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)
- Pulse Polio Programme
- Result Framework Document (RFD)
- Expenditure Budget
- Outcome Budget
- Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA)
- Publications
- Central Health Services (CHS)
- Hospital-II
- PH Division
- Recruitment Rules
- Program Guidelines
- 1st Quarterly Review Meeting With States/ Union Territories 19 & 20 September 2019
- Implementation of AB-HWCs in the States/UTs
- Vision, Mission and Objective Statement for MoHFW
- WHO Regional Committee session 2018
- Digital Payment
- National Institute of Cancer Prevention and Research (NICPR)
- Advanced Clinical Oncology
- Basic of Clinical Oncology
- Medical Education & Counselling
- e-Clearance for Afterlife Remains (eCARe)
- Citizen's Charter
- CS(MA) Central Services Medical Attendant
- Notifications
- Standards for Health Sector
- Public Grievances
- Photo Gallery
- News and Highlights
- Events/Announcements
- Disease Alerts
- Key Developments
- Major Achievements
- Rajya Sabha
- Directory of DoHFW
- Web Information Manager
- National AIDS Control Organisation
- Directorate General of Health Services
- STATES/UTS OFFICIAL
- Public Grievance Officer Details
- Name and address of organisation
- Nodal Officer under provision of Information Technology (procedures and safeguards for blocking of access of information by Public) Rules, 2009
- International Day of Yoga 2023
- Most Searched

Initially the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare had two Departments, Each of these Departments was headed by the Secretary to the Government of India:-Department of Health & Family Welfare and Department of Health Research. On August 7, 2014 vide extraordinary Gazette notification Part II Section-3, Sub Section(ii) New Delhi Thursday August 7, 2014, Department of AIDS Control has been merged with Department of Health & Family Welfare and now be known as National AIDS Control Organization (NACO)... Read More

Hon'ble Minister of Health & Family Welfare and Chemicals & Fertilizers

Hon’ble Minister of State (Independent Charge) of Ministry of AYUSH and Minister of State of Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India

Hon'ble Minister of State for Health & Family Welfare and Chemicals and Fertilizers, Government of India

Press Releases
Releases in English
Releases in Hindi
Press Photos
Photos (English Caption)
Photos (Hindi Caption)
Niramaya-NCD Newsletter
News & Highlights
Related Links
- Hiring services of 1 consultant for the programme management unit (Trauma & Burns Unit)
- FRAMING OF RECRUITMENT RULES FOR THE POST OF ASSISTANT DIRECTOR (OFFICIAL LANGUAGE), LEVEL10 AT AIIPMR, MUMBAI
- Advertisement for the post of Deputy Director (Administration) in each AIIMS at Raebareli (Uttar Pradesh), Rajkot (Gujarat) and Madurai (Tamil Nadu)
- Advertisement for the post of Deputy Director (Administration) in each AIIMS at Vijaypur (Samba) (Jammu & Kashmir) and Guwahati (Assam)
- Relaxation under Rule 161(IV) of General Financial Rules 2017 for issuance of Global Tender Enquiry
- Guidelines on appointment of Head of Department (HoD) in three Central Govemment Hospitals and associated Medical Colleges.
- Guidelines for ethical use of leftover De-identified /Anonymous Samples for Commercial Purpose
- Poliovirus vaccination guideline for travelers from Endemics Countries
- Requirement of polio vaccination for International travellers between India and polio infected countries.
- O.M. No. W -11037 / 40/2O22-Grants(RD)( Part2) dated 18/01/2023 regarding inclusion of 06 Rare Diseases with categorization under Para 6.2 of National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD), 2021
- Special Campaign 2.0 Best Practice
- Guidelines for Management of Monkeypox Disease
- List of INSACOG WGS Laboratories with indicative State distribution
- National Sickle Cell Anaemia Elimination Mission
- Central Council of Health & Family Welfare
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
- National Health Authority (NHA)
- Ayushman Bharat - Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
- St John Ambulance

I mportant Events
- हिन्दी Hindi
- অসমীয়া Assamese
- বাংলা Bengali
- ગુજરાતી Gujarati
- ಕನ್ನಡ Kannada
- മലയാളം Malayalam
- मराठी Marathi
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ Punjabi
- தமிழ் Tamil
- తెలుగు Telugu
Home | MyGov
- White to Black
- Poll/Survey
- Andaman & Nicobar Islands
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- Jammu And Kashmir
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand
- Uttar Pradesh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Transforming India
- Self4Society
- Innovate India
- About MyGov
- Work at MyGov
- Associate with MyGov
- MyGov Media
- MyGov Tenders
- Weekly Newsletter
- Pulse Newsletter
- Website Policies
- Points & Badges
- Meity Dashboard
- Usage of Aadhaar
- Web Information Manager
- Terms & Conditions
- Public Grievance
Travel Advisories
Guidelines for international arrivals (updated on 19th july 2023) - source : mohfw.gov.in.
- Read more about Guidelines for International Arrivals (updated on 19th July 2023) - Source : mohfw.gov.in
Guidelines for International Arrivals (updated on 10th February 2023) - Source: mohfw.gov.in
- Read more about Guidelines for International Arrivals (updated on 10th February 2023) - Source: mohfw.gov.in
Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 29th December 2022)
- Read more about Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 29th December 2022)
- Log in or register to post comments
Covid-19 - Air Suvidha Guidelines
- Read more about Covid-19 - Air Suvidha Guidelines
List of Countries/Regions in respect of which primary vaccination schedule completion certificate is allowed to be considered (in context of guidelines for international arrivals updated on 2nd September 2022)
- Read more about List of Countries/Regions in respect of which primary vaccination schedule completion certificate is allowed to be considered (in context of guidelines for international arrivals updated on 2nd September 2022)
Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 21st November 2022)
- Read more about Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 21st November 2022)
Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 2nd September 2022)
- Read more about Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 2nd September 2022)
List of Countries/Regions in respect of which primary vaccination schedule completion certificate is allowed to be uploaded (in context of guidelines for international arrivals updated on 10th February 2022)
- Read more about List of Countries/Regions in respect of which primary vaccination schedule completion certificate is allowed to be uploaded (in context of guidelines for international arrivals updated on 10th February 2022)
Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 10th February 2022) - Source: mohfw.gov.in
- Read more about Guidelines for International arrivals (updated on 10th February 2022) - Source: mohfw.gov.in

Most Searched
- Birth Certificate
- Driving Licence
- Travel Advisory
India at a Glance
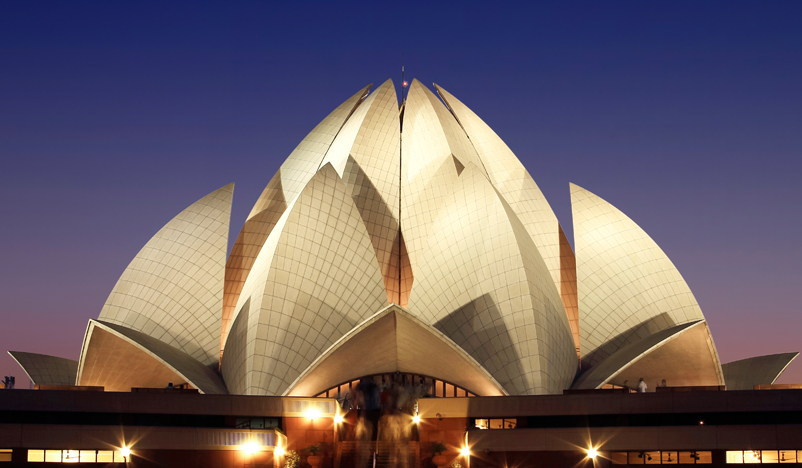

India is a land of rich cultural heritage and geographic beauty. There are many places of tourist interests in India and every year many foreign tourists from different parts of the world come to explore the eternal beauty of this Nation. Tourists come for different purposes such as tourism, business, education, family reunions, etc. Foreign nationals planning to visit India for tourism, vacations or business should check the travel advisory bulletins of their respective countries. Before finalising your plans to travel to India it is advisable to check the travel advisory notifications of your country. These travel advisories are posted with specific information regarding the health and safety for prospective travellers. For travel tips to visit India please click here .
- About India
- Visit India
- Discover India
India has a unique culture and is one of the oldest and greatest civilizations of the world. It stretches from the snow-capped Himalayas in the North to the Sun drenched coastal villages of the South. In this section, you will certainly get the best glimpse of this great country.
- States of India
- My India My Pride
- National Symbols
India is a pictorial kaleidoscope of landscapes, opulent historical and royal cities, golden beaches, misty mountain retreats, colourful people, rich cultures and festivities. A trip to India is exceptional for the tourists, as this wonderland has always offered something new.
- Where to stay
- Modes of Travel
- Travel Agents
India offers a different aspect of its personality – exotic, extravagant, elegant, and eclectic -- to each traveller to the country. With this section, we aim to help you choose that particular experience which will shape your vision of the country.
- Culture & Heritage
- People and Lifestyle
- Places to Visit
- Natural Wonders
- Biogas Application Portal
- Telephone directory of Jharkhand Commercial Tax Department
- Find information about your area tax assessment officer
- Get Key Contacts of Tamilnadu
- Website of Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL)
Most Viewed
- Information on Town and Country Planning Organisation
- Legal aid by District Courts of Haryana
- Information on Soil Conservation in Kerala
- Information on soil and water conservation in Meghalaya
- Website of Directorate of Film Festivals
Security Alert May 17, 2024
Worldwide caution.
- Travel Advisories |
- Contact Us |
- MyTravelGov |
Find U.S. Embassies & Consulates
Travel.state.gov, congressional liaison, special issuance agency, u.s. passports, international travel, intercountry adoption, international parental child abduction, records and authentications, popular links, travel advisories, mytravelgov, stay connected, legal resources, legal information, info for u.s. law enforcement, replace or certify documents.
Tourism & Visit
Study & Exchange
Other Visa Categories
U.S. Visa: Reciprocity and Civil Documents by Country
Share this page:
Reciprocity Schedule
Select a visa category below to find the visa issuance fee, number of entries, and validity period for visas issued to applicants from this country*/area of authority.
Explanation of Terms
Visa Classification: The type of nonimmigrant visa you are applying for.
Fee: The reciprocity fee, also known as the visa issuance fee, you must pay. This fee is in addition to the nonimmigrant visa application fee (MRV fee).
Number of Entries: The number of times you may seek entry into the United States with that visa. "M" means multiple times. If there is a number, such as "One", you may apply for entry one time with that visa.
Validity Period: This generally means the visa is valid, or can be used, from the date it is issued until the date it expires, for travel with that visa. If your Validity Period is 60 months, your visa will be valid for 60 months from the date it is issued.
Visa Classifications
Country specific footnotes.
▲. Maximum validity for A-1 and A-2 TDY visas is 12 months.
◼. Please check with the Visa Chief at Embassy New Delhi for Indian citizens applying for A3 visas, or A2 visas where the position is designated as "service staff member" in the diplomatic note.
Although care has been taken to ensure the accuracy, completeness and reliability of the information provided, please contact the U.S. Embassy or Consulate where you plan to apply if you believe this information is in error or if you have further questions.
Visa Category Footnotes
The validity of A-3, G-5, and NATO 7 visas may not exceed the validity of the visa issued to the person who is employing the applicant. The "employer" would have one of the following visa classifications:
- G-1 through G-4
- NATO 1 through NATO 6
An E-1 and E-2 visa may be issued only to a principal alien who is a national of a country having a treaty, or its equivalent, with the United States. E-1 and E-2 visas may not be issued to a principal alien if he/she is a stateless resident or national of a country without a treaty. *When the spouse and children of an E-1 or E-2 principal alien are accorded derivative E-1 or E-2 status and are themselves a national of a country that does not have a treaty with the United States – the reciprocity schedule, including any reciprocity fees, of the principal alien’s country of nationality should be used. **Spouse and children of an E-1 or E-2 visa principal applicant, where the spouse and children are also nationals of a country that has a treaty with the United States – the reciprocity schedule, including any reciprocity fees, of the spouse and children’s country of nationality should be used.
*Example 1: John Doe is a national of Country A that has an E-1/E-2 treaty with the U.S. however his wife and child are nationals of Country B which has no treaty with the U.S. The wife and child would, therefore, be entitled to derivative status and receive the same reciprocity as John Doe, the principal visa holder. **Example 2: Mike Doe is a national of Country Y that has an E-1/E-2 treaty with the U.S. however his wife and child are nationals of Country Z that also has a treaty with the U.S. The wife and child would, therefore, be entitled to derivative status and receive the reciprocity issued to nationals of Country Z.
The validity of H-1 through H-3, O-1 and O-2, P-1 through P-3, and Q visas may not exceed the period of validity of the approved petition or the number of months shown, whichever is less.
Under 8 CFR §214.2, H-2A and H-2B petitions may generally only be approved for nationals of countries that the Secretary of Homeland Security has designated as participating countries. The current list of eligible countries is available on USCIS's website for both H-2A and H-2B visas. Nationals of countries not on this list may be the beneficiary of an approved H-2A or H2-B petition in limited circumstances at the discretion of the Department of Homeland Security if specifically named on the petition.
Derivative H-4, L-2, O-3, and P-4 visas, issued to accompanying or following-to-join spouses and children, may not exceed the validity of the visa issued to the principal alien.
There is no reciprocity fee for the issuance of a J visa if the alien is a United States Government grantee or a participant in an exchange program sponsored by the United States Government.
Also, there is no reciprocity fee for visa issuance to an accompanying or following-to-join spouse or child (J-2) of an exchange visitor grantee or participant.
In addition, an applicant is eligible for an exemption from the MRV fee if he or she is participating in a State Department, USAID, or other federally funded educational and cultural exchange program (program serial numbers G-1, G-2, G-3 and G-7).
However, all other applicants with U.S. Government sponsorships, including other J-visa applicants, are subject to the MRV processing fee.
Under the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), Canadian and Mexican nationals coming to engage in certain types of professional employment in the United States may be admitted in a special nonimmigrant category known as the "trade NAFTA" or "TN" category. Their dependents (spouse and children) accompanying or following to join them may be admitted in the "trade dependent" or "TD" category whether or not they possess Canadian or Mexican nationality. Except as noted below, the number of entries, fees and validity for non-Canadian or non-Mexican family members of a TN status holder seeking TD visas should be based on the reciprocity schedule of the TN principal alien.
Canadian Nationals
Since Canadian nationals generally are exempt from visa requirement, a Canadian "TN' or "TD" alien does not require a visa to enter the United States. However, the non-Canadian national dependent of a Canadian "TN", unless otherwise exempt from the visa requirement, must obtain a "TD" visa before attempting to enter the United States. The standard reciprocity fee and validity period for all non-Canadian "TD"s is no fee, issued for multiple entries for a period of 36 months, or for the duration of the principal alien's visa and/or authorized period of stay, whichever is less. See 'NOTE' under Canadian reciprocity schedule regarding applicants of Iranian, Iraqi or Libyan nationality.
Mexican Nationals
Mexican nationals are not visa-exempt. Therefore, all Mexican "TN"s and both Mexican and non-Mexican national "TD"s accompanying or following to join them who are not otherwise exempt from the visa requirement (e.g., the Canadian spouse of a Mexican national "TN") must obtain nonimmigrant visas.
Applicants of Iranian, Iraqi, Libyan, Somalian, Sudanese, Syrian or Yemeni nationality, who have a permanent resident or refugee status in Canada/Mexico, may not be accorded Canadian/Mexican reciprocity, even when applying in Canada/Mexico. The reciprocity fee and period for "TD" applicants from Libya is $10.00 for one entry over a period of 3 months. The Iranian and Iraqi "TD" is no fee with one entry over a period of 3 months.
Q-2 (principal) and Q-3 (dependent) visa categories are in existence as a result of the 'Irish Peace Process Cultural and Training Program Act of 1998'. However, because the Department anticipates that virtually all applicants for this special program will be either Irish or U.K. nationals, the Q-2 and Q-3 categories have been placed only in the reciprocity schedules for those two countries. Q-2 and Q-3 visas are available only at the Embassy in Dublin and the Consulate General in Belfast.
No S visa may be issued without first obtaining the Department's authorization.
V-2 and V-3 status is limited to persons who have not yet attained their 21st birthday. Accordingly, the period of validity of a V-2 or V-3 visa must be limited to expire on or before the applicant's twenty-first birthday.
Posts may not issue a T-1 visa. A T-1 applicant must be physically present in the United States, American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands or a U.S. port of entry, where he/she will apply for an adjustment of status to that of a T-1. The following dependents of a T-1 visa holder, however, may be issued a T visa at a U.S. consular office abroad:
- T-2 (spouse)
- T-3 (child)
- T-4 (parent)
The validity of NATO-5 visas may not exceed the period of validity of the employment contract or 12 months, whichever is less.
The validity of CW-1 and CW-2 visas shall not exceed the maximum initial period of admission allowed by DHS (12 months) or the duration of the transition period ending December 31, 2014, whichever is shortest.
The validity of E-2C visas shall not exceed the maximum initial period of admission allowed by DHS (24 months) or the duration of the transition period ending December 31, 2014, whichever is shortest.
General Documents
Individuals residing outside of India may obtain documents from the state or local government entity with jurisdiction over the district of their previous residence. Indian relatives or friends may request issuance of documents on behalf of someone now living abroad. Relatives and friends should have specific written authorization from the interested party before they request official documents. Alternatively, persons in need of official documents can contact the Indian Embassy or Consulate nearest to their residence abroad to ask for assistance.
Birth, Death, Burial Certificates
Birth certificates.
Available : For persons born after April 1, 1970, birth certificates are available. For persons born prior to April 1, 1970, birth certificates are considered unavailable.
Fees: Fees vary from each Municipal authority, or any office authorized to issue birth and death certificates by the Registrar of Births & Deaths.
Document Name: Birth Certificate
Issuing Authority: Municipal Authority, or any office authorized to issue birth and death certificates by the Registrar of Births & Deaths.
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: Varies substantially from state to state.
Issuing Authority Personnel Title: There is no issuing authority personnel title.
Registration Criteria: The registration criteria varies
Procedure for Obtaining: Procedures vary from each authority.
Certified Copies Available: There are no certified copies available.
Alternate Documents: If an individual is born after April 1, 1970 and is unable to obtain a birth certificate, the individual must obtain a certificate of non-availability from the local authorities with jurisdiction over their place of birth. In addition to a non-availability certificate, the following documents can be accepted as secondary evidence:
- School-leaving Certificate (document provided to students when they cease attending a particular school, be it public or private),
- Matriculation Certificate,
- Certificate of Recognized Boards from the school last attended by the applicant (Boards are exams)
- A notarized affidavit executed by either a parent, if living, or another close relative older than the applicant. This affidavit should clearly state the relationship between the deponent and the applicant, how well the deponent knows the applicant, the date and place of the applicant's birth, the names of both parents, and any other related facts. If the applicant has no living relatives that witnessed their birth, a self-attested affidavit detailing their knowledge of the facts of their birth may be accepted.
Exceptions: None
Comments: For all births after April 1, 1970. It is mandatory under the law (as per the Registration of Births & Deaths Act, 1969) to register every birth with the concerned state or union territory.
Death Certificates
Available
Fees: Varies by authority
Document Name: Death Certificate
Issuing Authority: Appropriate state or municipal authorities.
Issuing Authority Personnel Title: There is no issuing authority personnel title
Registration Criteria: Varies for each authority.
Procedure for Obtaining: Varies for each authority.
Alternate Documents: There are no alternate documents.
Comments: It is mandatory under the law (as per the Registration of Births & Deaths Act, 1969) to register every death with the concerned state or union territory. Prior to April 1, 1970, reporting of deaths was voluntary.
Marriage, Divorce Certificates
Marriage certificates.
Fees: Varies by authority.
Document Name: Marriage Certificate.
Issuing Authority: Religious authorities and the offices of the Government Registrar of Marriages, which are located in the headquarters of each district.
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: Varies substantially.
Issuing Authority Personnel Title: Different for each state and religious authority that conducts the marriage.
Registration Criteria: Prior to 2006, marriages by Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, or Sikhs were not required to be registered, but may have been voluntarily registered under the Hindu Marriage Act of 1955. As of 2006, it is mandatory to register all marriages. In India, a marriage can either be registered under the Hindu Marriage Act of 1955 or under the Special Marriage Act of 1954. For marriages registered at government offices under the Special Marriage Act, the certificate will be issued by the Registrar only if the bride and groom personally appear before the official and pay the required fee. For other marriages that are required to be registered with government authorities under the Hindu Marriage Act of 1955, registration criteria vary by authority.
Procedure for Obtaining: Varies for each authority .
Alternate Documents: See comments section.
Comments: Hindu Marriage Act is applicable to Hindus, whereas the Special Marriage Act is applicable to all citizens of India irrespective of their religion. Please note that marriages by Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, or Sikhs may be voluntarily registered under the Hindu Marriage Act of 1955.
A marriage certificate issued by a Christian church needs to be registered in the office of The Registrar of Marriages. The registration authority varies from state to state.
If the parties are married in an Islamic religious ceremony, the certificate issued by the religious authority (such as a Nikah Nama contract issued by the mosque, or a marriage certificate issued by the Waqf Board) is sufficient proof of the marriage, and an additional registration with government authorities is not necessary/mandatory. A document known as a “Marriage Agreement” or “Deed of Marriage” to live as man and wife (under the Registration Act of 1908) is not sufficient confirmation of a marriage. Such a document does not confer legal marital status under the law. The minimum age for a marriage to be legal is 18 for females and 21 for males.
Same-sex marriages are illegal in India.
Divorce Certificates
Fees: Varies by court and authority.
Document Name: Divorce Decree. For Islamic religious authorities, it is called the Talaqnama.
Issuing Authority: Courts of jurisdiction, Muslim religious bodies.
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: Varies. Divorce decrees should include official stamps from the court of jurisdiction.
Procedure for Obtaining: Varies for each authority.
Alternate Documents: There are alternate documents
Comments: Parties filing for divorce can obtain divorce decrees from their court of jurisdiction. For marriages that took place under Islamic religious authorities, in the absence of a court divorce decree, a divorce certificate from the religious officiant, called a “Qazi,” or the head of the mosque is acceptable. Muslims can also apply for a court divorce decree.
Some Hindu communities practice divorce by mutual consent outside of the judicial system, resulting in a “divorce deed.” However, only a final “divorce decree,” obtained through a court, is proof of the final dissolution of a Hindu marriage.
Adoption Certificates
Fees: Yes ($5000 for inter-country adoptions)
Document Name: Adoption Order issued by an Indian court confirming adoption. Adoption gets concluded legally after obtaining an adoption order from the court concerned. NOC under Article 17 and Conformity Certificate under Article 23 are issued by the Central Authority of India.
Issuing Authority: Competent Indian Court. Court means civil court, which has jurisdiction in matters of adoption and guardianship and may include the District Court, Family Court or City Civil court. The Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) is the designated Central Authority of India.
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: No specific format/color; but the court order should be signed by a Judge and issued by a competent Indian court. Court order should state that adoption of the child is granted to the adoptive parents and the new name as given by the adoptive parents must be recorded along with the date of birth of the child.
Issuing Authority Personnel Title: Judge (The court may be City Civil Court or, District Court or Family court or High court).
Registration Criteria: Inter-country adoption means adoption of a child from India by nonresident Indian or by a person of Indian origin or by a foreigner. All inter-country adoption to be done as per the provisions of THE JUVENILE JUSTICE (CARE AND PROTECTION OF CHILDREN) ACT, 2015 (JJ Act) and the Adoption Regulations framed by The Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA). It extends to the whole of India. Procedure for Obtaining: Contact the attorney.
Certified Copies Available: Yes.
Alternate Documents: None.
Exceptions: None.
Comments: It should be noted that India is a member to the Hague convention. The Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) is a statutory body of Ministry of Women & Child Development, Government of India. It functions as the nodal body for adoption of Indian children and is mandated to monitor and regulate inter-country adoptions. CARA is designated as the Central Authority to deal with inter-country adoptions in accordance with the provisions of the Hague Convention on Inter-country Adoption, 1993, ratified by Government of India in 2003.
Identity Card
Fees: Varies by authority.
Document Name: Aadhar Card
Issuing Authority: Unique Identification Authority of India, Government of India
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: There are no special seal/color/formats.
Registration Criteria: Must be a resident of India.
Procedure for Obtaining: Available from Aadhaar Enrollment Centers, Aadhar Camps, and other enrollment facilities. Please see for more information: uidai.gov
Alternate Documents: For proof of address that the Indian Passport Offices will accept, please see this link: portal2.passportindia.gov.in
Comments: Residents of all states and union territories of India can obtain a National ID card, which bears a 12-digit unique identity number. Aadhar is a proof of residence, and not a proof of citizenship. Aadhaar does not itself grant any rights to domicile in India. The Aadhar number is linked to a resident’s basic demographic and biometric information such as a photograph, ten fingerprints and two iris scans, which are stored in a centralized database. The Aadhar project is also linked to some public subsidies and benefits. Aadhar enrollment is not compulsory.
Police, Court, Prison Records
Police certificates.
Document Name:
All Indian nationals aged 16 and above, residing in India - Indian Police Clearance Certificate.
Indian passport holders residing outside India – statement of no criminal record
Non-Indian applicants residing in India who are registered with the Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) – Police Clearance Certificate
Non-Indian applicants who reside in India and are not FRRO registered (such as Tibetan Identity certificate holders) - Police Clearance Certificate
Issuing Authority:
All Indian nationals aged 16 and above, residing in India - Regional Passport Office.
Indian passport holders residing outside India – The local Indian Embassy, Consulate, High Commission, or Deputy High Commission.
Non-Indian applicants residing in India who are registered with the Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) - The FRRO serving their area of residence.
Non-Indian applicants who reside in India and are not FRRO registered (such as Tibetan Identity certificate holders) - District Police Station serving their area of residence.
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: All police clearance certificates from regional passport offices have a similar format. The header bears the symbol of India’s Central government (three lions), and contains the contact information of the regional office, issuance date, file number, and applicant photograph. It is signed and stamped by the Ministry of External Affairs. Police clearance certificates issued by other authorities vary in format.
Registration Criteria: Varies by authority
Procedure for Obtaining: Varies by authority
Certified Copies Available: Applicants obtain original police clearance certificates from police authorities.
Alternate Documents: There are no alternate documents
Comments: Police certificates are only available for Indian nationals and non-Indian nationals currently living in India. Indian police certificates are not available for foreign (non-Indian) nationals applying outside India.
Court Records
Fees: Varies by authority
Document Name: Varies by authority
Issuing Authority: Varies by authority
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: Varies substantially, however, all court documents should bear some kind of official stamp.
Issuing Authority Personnel Title: Varies by authority
Registration Criteria: There are no registration criteria.
Procedure for Obtaining: Varies by authority
Comments: In all states and union territories there are 24 high courts at the state and union territory level of India, along with the Supreme Court of India at the national level. Each high court has jurisdiction over a state, a union territory or a group of states and union territories.
Prison Records
Document Name: Varies by authority
Special Seal(s) / Color / Format: Varies by authority
Registration Criteria: There are no registration criteria
Comments: A person who has been incarcerated can obtain a prison record from the State Inspector General of Police, from the Police authorities of Mumbai, Kolkata, or Chennai, or from the Superintendent of the jail in which the sentence was served.
Military Records
Unavailable
Passports & Other Travel Documents
Types Available:
- Regular Passport: (Type P). Dark blue. Most passports are valid for 10 years. Issued by the Ministry of External Affairs through the Central Passport Organization and its network of 37 Passport Offices and Passport Seva Kendras (local offices). Applicants must apply through a Passport Seva Kendra or online through Passport Seva . Indians living abroad can obtain passports at one of the 185 Indian consulates located overseas.
- Diplomatic Passports: (Type D). Maroon. Issued to Indian diplomats, top ranking government officials and diplomatic couriers. Has a validity period of 5 years or fewer, depending on the position of the passport holder and the nature of the assignment/visit. The Consular, Passport & Visa Division of the Ministry of External Affairs issues Diplomatic Passports.
- Official Passports: (Type S). White/Gray. Issued to individuals representing the Indian government on official business. Has a validity period of 5 years or fewer, depending on the position of the passport holder and the nature of the assignment/visit. The Consular, Passport & Visa Division of the Ministry of External Affairs issues Official Passports.
Identity Certificate: Yellow. Known as the IC, it is available to Tibetan Refugees and Stateless Persons. The IC is a valid travel document, which enables the bearer to travel internationally, and is the document in which to place a U.S. visa. It is valid for 10 years. Older ICs were paper booklets with a pasted photograph; the latest version (produced since 2007) is yellow and bears a digital photo. Only the Regional Passport Office in New Delhi can authorize Identity Certificates for Tibetan Refugees. Stateless persons can apply at the passport office within the jurisdiction they reside.
Fees: Fees range according to document and service. Those applying for a passport or identity certificate can use the fee calculator to determine costs.
Other Records
Not applicable.
- Visa Issuing Posts
Post Title: Mumbai, India (Consulate General)
Address: C-49, G-Block, Bandra Kurla Complex, Bandra East, Mumbai 400051
Phone Number: (022) 2672-4000, Fax: (022) 2672-4755
Visa Services: Immigrant visas, Nonimmigrant visas
Comments / Additional Information: None
Post Title: New Delhi, India (Embassy)
Address: Shantipath, Chanakyapuri 110021
Phone Number: (91) (11) 2419-8000, Fax: (91) (11) 2419-0017
Visa Services: Nonimmigrant Visas, Adoptions, and Specialized Immigrant Visas
Post Title: Chennai, India (Consulate General)
Address: 220 Anna Salai Gemini Circle, 600006
Phone Number: (91) (44) 2811-2000, Fax: (91) (44) 2811-2027
Visa Services: Nonimmigrant Visas ONLY
Post Title: Hyderabad, India (Consulate General)
Address: 1-8-323 Chiran Fort Lane Begumpet, Secunderabad 500 003
Phone Number: (91) (040) 4033-8300, Fax: (91) (040) 4033-8301
Post Title: Kolkata, India (Consulate General)
Address: 5/1 Ho Chi Minh Sarani, 700071
Phone Number: (91) (33) 2282-3611 through 2282-3615, Fax: (91) (33) 2282-2335
Visa Services: Nonimmigrant Visas ONLY
Visa Services
All U.S. immigrant visas for India are processed in Mumbai, except for adoption cases and follow-to-join asylees and refugees, which are processed in New Delhi. Although the embassy and consulates divide the country into separate consular districts, non-immigrant visa applicants are free to apply at any post. The one exception to this is Blanket L visa applicants, who can only apply in Chennai.
Additional Information for Reciprocity
- Reciprocity: What's New
- Temporary Reciprocity Schedule
- Country Acronyms
- Terrorist Designation Lists
- State Sponsors of Terrorism
- Treaty Countries
Afghanistan
Antigua and Barbuda
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Brunei Darussalam
Burkina Faso
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Congo the Democratic Republic of the
Curaçao
Czech Republic
Côte d'Ivoire
Dominican Republic
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Iran, Islamic Republic of
Israel, Jerusalem, the West Bank and Gaza
Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
Lao People's Democratic Republic
Liechtenstein
Marshall Islands
Micronesia, Federated States of
Moldova, Republic of
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
North Korea
North Macedonia
Palestinian Authority
Papua New Guinea
Philippines
Russian Federation
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Sierra Leone
Sint Maarten (Dutch part)
Solomon Islands
South Africa
South Korea
South Sudan
Switzerland
Timor-Leste
Trinidad and Tobago
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
Virgin Islands, British
Wallis and Futuna
External Link
You are about to leave travel.state.gov for an external website that is not maintained by the U.S. Department of State.
Links to external websites are provided as a convenience and should not be construed as an endorsement by the U.S. Department of State of the views or products contained therein. If you wish to remain on travel.state.gov, click the "cancel" message.
You are about to visit:
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
India Traveler View
Travel health notices, vaccines and medicines, non-vaccine-preventable diseases, stay healthy and safe.
- Packing List
After Your Trip
Be aware of current health issues in India. Learn how to protect yourself.
Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions
- Global Measles May 28, 2024 Many international destinations are reporting increased numbers of cases of measles. Destination List: Afghanistan, Angola, Armenia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Liberia, Libya, Malaysia, Mauritania, Nepal, Niger, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of South Sudan, Republic of the Congo, Romania, Russia, Senegal, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Togo, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Yemen, Zambia
⇧ Top
Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least a month before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need. If you or your doctor need help finding a location that provides certain vaccines or medicines, visit the Find a Clinic page.
Routine vaccines
Recommendations.
Make sure you are up-to-date on all routine vaccines before every trip. Some of these vaccines include
- Chickenpox (Varicella)
- Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis
- Flu (influenza)
- Measles-Mumps-Rubella (MMR)
Immunization schedules
All eligible travelers should be up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines. Please see Your COVID-19 Vaccination for more information.
COVID-19 vaccine
Chikungunya
There has been evidence of chikungunya virus transmission in India within the last 5 years. Chikungunya vaccination may be considered for the following travelers:
- People aged 65 years or older, especially those with underlying medical conditions, who may spend at least 2 weeks (cumulative time) in indoor or outdoor areas where mosquitoes are present in India, OR
- People planning to stay in India for a cumulative period of 6 months or more
Chikungunya - CDC Yellow Book
Cholera is presumed to be present in India. Cholera is rare in travelers. Certain factors may increase the risk of getting cholera or having severe disease ( more information ). Avoiding unsafe food and water and washing your hands can also help prevent cholera.
Vaccination may be considered for children and adults who are traveling to areas of active cholera transmission.
Cholera - CDC Yellow Book
Hepatitis A
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers one year old or older going to India.
Infants 6 to 11 months old should also be vaccinated against Hepatitis A. The dose does not count toward the routine 2-dose series.
Travelers allergic to a vaccine component or who are younger than 6 months should receive a single dose of immune globulin, which provides effective protection for up to 2 months depending on dosage given.
Unvaccinated travelers who are over 40 years old, immunocompromised, or have chronic medical conditions planning to depart to a risk area in less than 2 weeks should get the initial dose of vaccine and at the same appointment receive immune globulin.
Hepatitis A - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep A
Hepatitis B
Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to India. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to India.
Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Hep B
Japanese Encephalitis
Recommended for travelers who
- Are moving to an area with Japanese encephalitis to live
- Spend long periods of time, such as a month or more, in areas with Japanese encephalitis
- Frequently travel to areas with Japanese encephalitis
Consider vaccination for travelers
- Spending less than a month in areas with Japanese encephalitis but will be doing activities that increase risk of infection, such as visiting rural areas, hiking or camping, or staying in places without air conditioning, screens, or bed nets
- Going to areas with Japanese encephalitis who are uncertain of their activities or how long they will be there
Not recommended for travelers planning short-term travel to urban areas or travel to areas with no clear Japanese encephalitis season.
Japanese encephalitis - CDC Yellow Book
Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine for US Children
CDC recommends that travelers going to certain areas of India take prescription medicine to prevent malaria. Depending on the medicine you take, you will need to start taking this medicine multiple days before your trip, as well as during and after your trip. Talk to your doctor about which malaria medication you should take.
Find country-specific information about malaria.
Malaria - CDC Yellow Book
Considerations when choosing a drug for malaria prophylaxis (CDC Yellow Book)
Malaria information for India.
Cases of measles are on the rise worldwide. Travelers are at risk of measles if they have not been fully vaccinated at least two weeks prior to departure, or have not had measles in the past, and travel internationally to areas where measles is spreading.
All international travelers should be fully vaccinated against measles with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine, including an early dose for infants 6–11 months, according to CDC’s measles vaccination recommendations for international travel .
Measles (Rubeola) - CDC Yellow Book
Dogs infected with rabies are commonly found in India.
Rabies is also present in some terrestrial wildlife species.
If rabies exposures occur while in India, rabies vaccines are typically available throughout most of the country.
Rabies pre-exposure vaccination considerations include whether travelers 1) will be performing occupational or recreational activities that increase risk for exposure to potentially rabid animals and 2) might have difficulty getting prompt access to safe post-exposure prophylaxis.
Please consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether you should receive pre-exposure vaccination before travel.
For more information, see country rabies status assessments .
Rabies - CDC Yellow Book
Recommended for most travelers, especially those staying with friends or relatives or visiting smaller cities or rural areas.
Typhoid - CDC Yellow Book
Dosing info - Typhoid
Yellow Fever
- Arrive within 6 days of leaving an area with risk for YF virus transmission, or
- Have been in such an area in transit (exception: passengers and members of flight crews who, while in transit through an airport in an area with risk for YF virus transmission, remained in the airport during their entire stay and the health officer agrees to such an exemption), or
- Arrive on a ship that started from or touched at any port in an area with risk for YF virus transmission ≤30 days before its arrival in India, unless such a ship has been disinsected in accordance with the procedure recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), or
- Arrive on an aircraft that has been in an area with risk for YF virus transmission and has not been disinsected in accordance with the Indian Aircraft Public Health Rules, 1954, or as recommended by WHO.
- Africa: Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda
- Americas: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad & Tobago (Trinidad only), Venezuela
Yellow Fever - CDC Yellow Book
Avoid contaminated water
Leptospirosis
How most people get sick (most common modes of transmission)
- Touching urine or other body fluids from an animal infected with leptospirosis
- Swimming or wading in urine-contaminated fresh water, or contact with urine-contaminated mud
- Drinking water or eating food contaminated with animal urine
- Avoid contaminated water and soil
- Avoid floodwater
Clinical Guidance
Avoid bug bites.
Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic fever
- Tick bite
- Touching the body fluids of a person or animal infected with CCHF
- Avoid Bug Bites
- Mosquito bite
Leishmaniasis
- Sand fly bite
- An infected pregnant woman can spread it to her unborn baby
Airborne & droplet
Avian/bird flu.
- Being around, touching, or working with infected poultry, such as visiting poultry farms or live-animal markets
- Avoid domestic and wild poultry
- Breathing in air or accidentally eating food contaminated with the urine, droppings, or saliva of infected rodents
- Bite from an infected rodent
- Less commonly, being around someone sick with hantavirus (only occurs with Andes virus)
- Avoid rodents and areas where they live
- Avoid sick people
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Breathe in TB bacteria that is in the air from an infected and contagious person coughing, speaking, or singing.
Avoid skin contact
Antimicrobial-resistant (ar) ringworm.
- Close contact with infected person
- Shared objects (e.g., towels, bed sheets)
- Shared surfaces (e.g., locker room and shower floors)
- Keep skin clean and dry.
- Do not share bedding, towels, or clothes.
- Avoid touching the infected area so it does not spread to other parts of your body.
- Consult a healthcare provider for treatment and testing.
- Avoid steroid creams, as they can make the ringworm worse.
- Use prescribed or over-the-counter (OTC) antifungals exactly as directed and contact a healthcare provider if treatment is not working.
- Topical antifungals and oral terbinafine are frequently ineffective against AR ringworm.
Emerging Severe and Antimicrobial-Resistant Ringworm | Ringworm | CDC
Learn actions you can take to stay healthy and safe on your trip. Vaccines cannot protect you from many diseases in India, so your behaviors are important.
Eat and drink safely
Food and water standards around the world vary based on the destination. Standards may also differ within a country and risk may change depending on activity type (e.g., hiking versus business trip). You can learn more about safe food and drink choices when traveling by accessing the resources below.
- Choose Safe Food and Drinks When Traveling
- Water Treatment Options When Hiking, Camping or Traveling
- Global Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
- Avoid Contaminated Water During Travel
You can also visit the Department of State Country Information Pages for additional information about food and water safety.
Prevent bug bites
Bugs (like mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas) can spread a number of diseases in India. Many of these diseases cannot be prevented with a vaccine or medicine. You can reduce your risk by taking steps to prevent bug bites.
What can I do to prevent bug bites?
- Cover exposed skin by wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats.
- Use an appropriate insect repellent (see below).
- Use permethrin-treated clothing and gear (such as boots, pants, socks, and tents). Do not use permethrin directly on skin.
- Stay and sleep in air-conditioned or screened rooms.
- Use a bed net if the area where you are sleeping is exposed to the outdoors.
What type of insect repellent should I use?
- FOR PROTECTION AGAINST TICKS AND MOSQUITOES: Use a repellent that contains 20% or more DEET for protection that lasts up to several hours.
- Picaridin (also known as KBR 3023, Bayrepel, and icaridin)
- Oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE) or para-menthane-diol (PMD)
- 2-undecanone
- Always use insect repellent as directed.
What should I do if I am bitten by bugs?
- Avoid scratching bug bites, and apply hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion to reduce the itching.
- Check your entire body for ticks after outdoor activity. Be sure to remove ticks properly.
What can I do to avoid bed bugs?
Although bed bugs do not carry disease, they are an annoyance. See our information page about avoiding bug bites for some easy tips to avoid them. For more information on bed bugs, see Bed Bugs .
For more detailed information on avoiding bug bites, see Avoid Bug Bites .
Some diseases in India—such as dengue, Zika, filariasis, and leishmaniasis—are spread by bugs and cannot be prevented with a vaccine. Follow the insect avoidance measures described above to prevent these and other illnesses.
Stay safe outdoors
If your travel plans in India include outdoor activities, take these steps to stay safe and healthy during your trip.
- Stay alert to changing weather conditions and adjust your plans if conditions become unsafe.
- Prepare for activities by wearing the right clothes and packing protective items, such as bug spray, sunscreen, and a basic first aid kit.
- Consider learning basic first aid and CPR before travel. Bring a travel health kit with items appropriate for your activities.
- If you are outside for many hours in heat, eat salty snacks and drink water to stay hydrated and replace salt lost through sweating.
- Protect yourself from UV radiation : use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 15, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during the hottest time of day (10 a.m.–4 p.m.).
- Be especially careful during summer months and at high elevation. Because sunlight reflects off snow, sand, and water, sun exposure may be increased during activities like skiing, swimming, and sailing.
- Very cold temperatures can be dangerous. Dress in layers and cover heads, hands, and feet properly if you are visiting a cold location.
Stay safe around water
- Swim only in designated swimming areas. Obey lifeguards and warning flags on beaches.
- Practice safe boating—follow all boating safety laws, do not drink alcohol if driving a boat, and always wear a life jacket.
- Do not dive into shallow water.
- Do not swim in freshwater in developing areas or where sanitation is poor.
- Avoid swallowing water when swimming. Untreated water can carry germs that make you sick.
- To prevent infections, wear shoes on beaches where there may be animal waste.
Schistosomiasis and leptospirosis, infections that can be spread in fresh water, are found in India. Avoid swimming in fresh, unchlorinated water, such as lakes, ponds, or rivers.
Keep away from animals
Most animals avoid people, but they may attack if they feel threatened, are protecting their young or territory, or if they are injured or ill. Animal bites and scratches can lead to serious diseases such as rabies.
Follow these tips to protect yourself:
- Do not touch or feed any animals you do not know.
- Do not allow animals to lick open wounds, and do not get animal saliva in your eyes or mouth.
- Avoid rodents and their urine and feces.
- Traveling pets should be supervised closely and not allowed to come in contact with local animals.
- If you wake in a room with a bat, seek medical care immediately. Bat bites may be hard to see.
All animals can pose a threat, but be extra careful around dogs, bats, monkeys, sea animals such as jellyfish, and snakes. If you are bitten or scratched by an animal, immediately:
- Wash the wound with soap and clean water.
- Go to a doctor right away.
- Tell your doctor about your injury when you get back to the United States.
Consider buying medical evacuation insurance. Rabies is a deadly disease that must be treated quickly, and treatment may not be available in some countries.
Reduce your exposure to germs
Follow these tips to avoid getting sick or spreading illness to others while traveling:
- Wash your hands often, especially before eating.
- If soap and water aren’t available, clean hands with hand sanitizer (containing at least 60% alcohol).
- Don’t touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. If you need to touch your face, make sure your hands are clean.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing.
- Try to avoid contact with people who are sick.
- If you are sick, stay home or in your hotel room, unless you need medical care.
Avoid sharing body fluids
Diseases can be spread through body fluids, such as saliva, blood, vomit, and semen.
Protect yourself:
- Use latex condoms correctly.
- Do not inject drugs.
- Limit alcohol consumption. People take more risks when intoxicated.
- Do not share needles or any devices that can break the skin. That includes needles for tattoos, piercings, and acupuncture.
- If you receive medical or dental care, make sure the equipment is disinfected or sanitized.
Know how to get medical care while traveling
Plan for how you will get health care during your trip, should the need arise:
- Carry a list of local doctors and hospitals at your destination.
- Review your health insurance plan to determine what medical services it would cover during your trip. Consider purchasing travel health and medical evacuation insurance.
- Carry a card that identifies, in the local language, your blood type, chronic conditions or serious allergies, and the generic names of any medications you take.
- Some prescription drugs may be illegal in other countries. Call India’s embassy to verify that all of your prescription(s) are legal to bring with you.
- Bring all the medicines (including over-the-counter medicines) you think you might need during your trip, including extra in case of travel delays. Ask your doctor to help you get prescriptions filled early if you need to.
Many foreign hospitals and clinics are accredited by the Joint Commission International. A list of accredited facilities is available at their website ( www.jointcommissioninternational.org ).
In some countries, medicine (prescription and over-the-counter) may be substandard or counterfeit. Bring the medicines you will need from the United States to avoid having to buy them at your destination.
Malaria is a risk in India. Fill your malaria prescription before you leave and take enough with you for the entire length of your trip. Follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the pills; some need to be started before you leave.
Select safe transportation
Motor vehicle crashes are the #1 killer of healthy US citizens in foreign countries.
In many places cars, buses, large trucks, rickshaws, bikes, people on foot, and even animals share the same lanes of traffic, increasing the risk for crashes.
Be smart when you are traveling on foot.
- Use sidewalks and marked crosswalks.
- Pay attention to the traffic around you, especially in crowded areas.
- Remember, people on foot do not always have the right of way in other countries.
Riding/Driving
Choose a safe vehicle.
- Choose official taxis or public transportation, such as trains and buses.
- Ride only in cars that have seatbelts.
- Avoid overcrowded, overloaded, top-heavy buses and minivans.
- Avoid riding on motorcycles or motorbikes, especially motorbike taxis. (Many crashes are caused by inexperienced motorbike drivers.)
- Choose newer vehicles—they may have more safety features, such as airbags, and be more reliable.
- Choose larger vehicles, which may provide more protection in crashes.
Think about the driver.
- Do not drive after drinking alcohol or ride with someone who has been drinking.
- Consider hiring a licensed, trained driver familiar with the area.
- Arrange payment before departing.
Follow basic safety tips.
- Wear a seatbelt at all times.
- Sit in the back seat of cars and taxis.
- When on motorbikes or bicycles, always wear a helmet. (Bring a helmet from home, if needed.)
- Avoid driving at night; street lighting in certain parts of India may be poor.
- Do not use a cell phone or text while driving (illegal in many countries).
- Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas.
- If you choose to drive a vehicle in India, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork.
- Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
- Check with your auto insurance policy's international coverage, and get more coverage if needed. Make sure you have liability insurance.
- Avoid using local, unscheduled aircraft.
- If possible, fly on larger planes (more than 30 seats); larger airplanes are more likely to have regular safety inspections.
- Try to schedule flights during daylight hours and in good weather.
Medical Evacuation Insurance
If you are seriously injured, emergency care may not be available or may not meet US standards. Trauma care centers are uncommon outside urban areas. Having medical evacuation insurance can be helpful for these reasons.
Helpful Resources
Road Safety Overseas (Information from the US Department of State): Includes tips on driving in other countries, International Driving Permits, auto insurance, and other resources.
The Association for International Road Travel has country-specific Road Travel Reports available for most countries for a minimal fee.
Traffic flows on the left side of the road in India.
- Always pay close attention to the flow of traffic, especially when crossing the street.
- LOOK RIGHT for approaching traffic.
For information traffic safety and road conditions in India, see Travel and Transportation on US Department of State's country-specific information for India .
Maintain personal security
Use the same common sense traveling overseas that you would at home, and always stay alert and aware of your surroundings.
Before you leave
- Research your destination(s), including local laws, customs, and culture.
- Monitor travel advisories and alerts and read travel tips from the US Department of State.
- Enroll in the Smart Traveler Enrollment Program (STEP) .
- Leave a copy of your itinerary, contact information, credit cards, and passport with someone at home.
- Pack as light as possible, and leave at home any item you could not replace.
While at your destination(s)
- Carry contact information for the nearest US embassy or consulate .
- Carry a photocopy of your passport and entry stamp; leave the actual passport securely in your hotel.
- Follow all local laws and social customs.
- Do not wear expensive clothing or jewelry.
- Always keep hotel doors locked, and store valuables in secure areas.
- If possible, choose hotel rooms between the 2nd and 6th floors.
To call for emergency services while in India, dial 100 or, from a mobile phone, 112. Write these numbers down to carry with you during your trip.
Learn as much as you can about India before you travel there. A good place to start is the country-specific information on India from the US Department of State.
Healthy Travel Packing List
Use the Healthy Travel Packing List for India for a list of health-related items to consider packing for your trip. Talk to your doctor about which items are most important for you.
Why does CDC recommend packing these health-related items?
It’s best to be prepared to prevent and treat common illnesses and injuries. Some supplies and medicines may be difficult to find at your destination, may have different names, or may have different ingredients than what you normally use.
If you are not feeling well after your trip, you may need to see a doctor. If you need help finding a travel medicine specialist, see Find a Clinic . Be sure to tell your doctor about your travel, including where you went and what you did on your trip. Also tell your doctor if you were bitten or scratched by an animal while traveling.
If your doctor prescribed antimalarial medicine for your trip, keep taking the rest of your pills after you return home. If you stop taking your medicine too soon, you could still get sick.
Malaria is always a serious disease and may be a deadly illness. If you become ill with a fever either while traveling in a malaria-risk area or after you return home (for up to 1 year), you should seek immediate medical attention and should tell the doctor about your travel history.
For more information on what to do if you are sick after your trip, see Getting Sick after Travel .
Map Disclaimer - The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on maps do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement are generally marked.
Other Destinations
If you need help finding travel information:
Message & data rates may apply. CDC Privacy Policy
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Sorry, we couldn't find anything that matches your search.
Destination

Famous Places to Explore in Hyderabad
A vibrant city with the imposing...

Raipur Tourist Places | Best Place to Visit
The stronghold of several erstwhile...

Declared as India's first UNESCO World...

Ananthagiri
The verdant Ananthagiri Hills is...

Located on the banks of River Godavari,...

Situated around 40 km from Raipur,...

Boasting the famous Chand Baori...

Albert Hall Museum
A magnificent building built in...

2023. The year of India’s G20...
One of the oldest civilisations in the world, India is a mosaic of multicultural experiences. With a rich heritage and myriad attractions, the country is among the most popular tourist destinations in the world. It covers an area of 32, 87,263 sq. km, extending from the snow-covered Himalayan heights to the tropical rain forests of the south. As the 7th largest country in the world, India stands apart from the rest of Asia, marked off as it is by mountains and the sea, which give the country a distinct geographical entity.
Fringed by the Great Himalayas in the north, it stretches southwards and at the Tropic of Cancer, tapers off into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal on the east and the Arabian Sea on the west. As you travel the expanse of the country, you are greeted by diverse nuances of cuisines, faiths, arts, crafts, music, nature, lands, tribes, history and adventure sports. India has a mesmeric conflation of the old and the new. As the bustling old bazaars rub shoulders with swanky shopping malls, and majestic monuments accompany luxurious heritage hotels, the quintessential traveller can get the best of both worlds. Head to the mountains, enjoy a beach retreat or cruise through the golden Thar, India has options galore for all.

Popular in India
India is a home to the finest architectural heritage, serene ghats, spectacular landscapes and largest tiger reserve
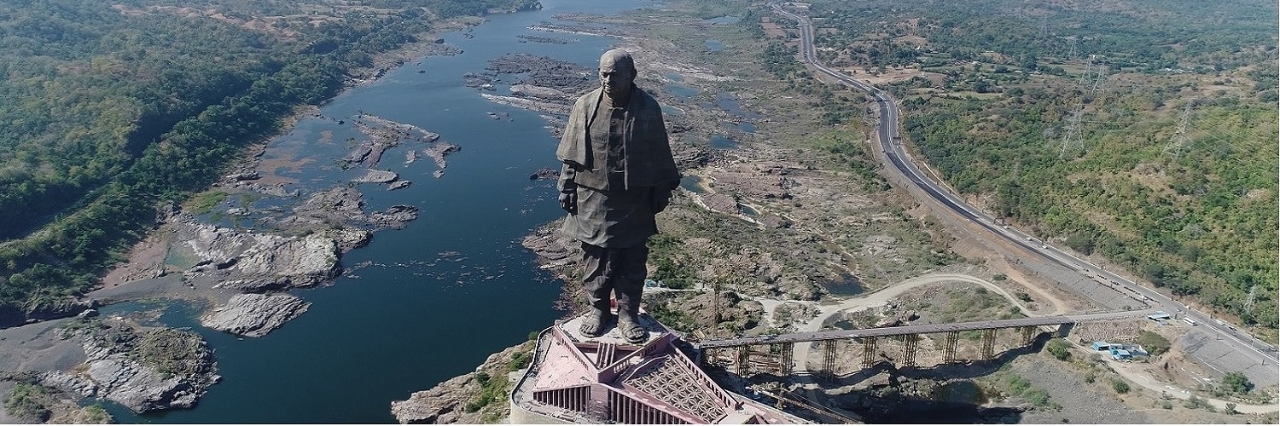

Statue of Unity
It’s huge, almost gigantic! That is the first reaction most people have as they speed down the winding road leading to the towering Statue of Unity (SoU). A long bridge connects the mainland to the...
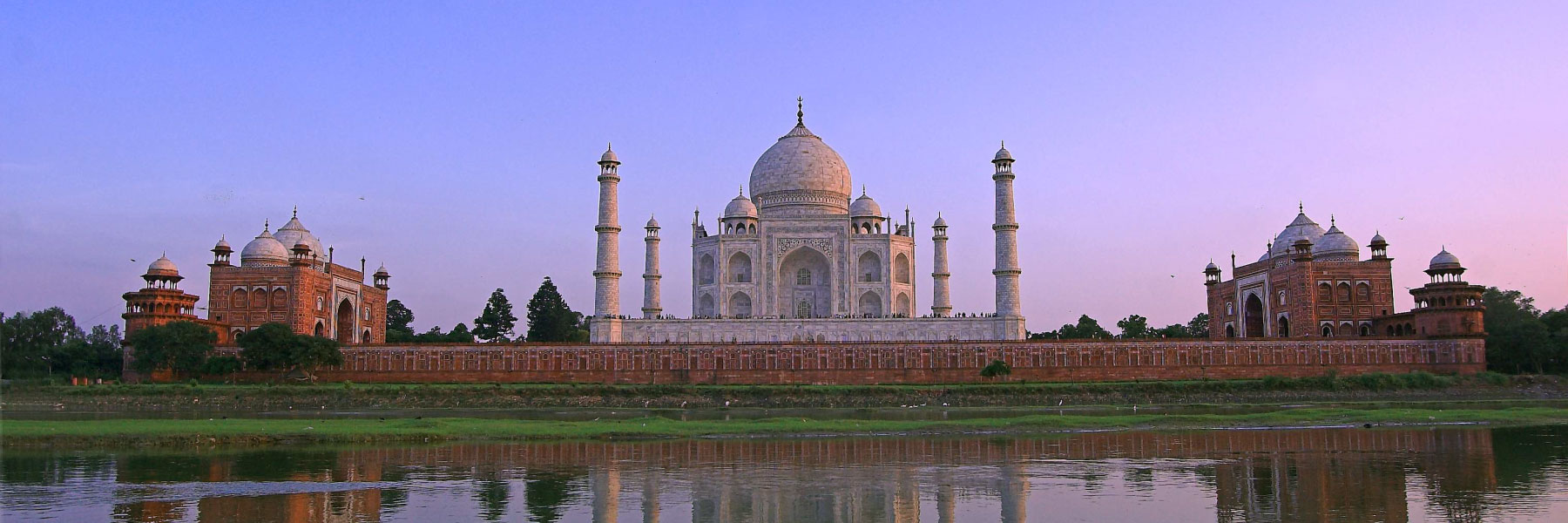

Most Famous
India is a remarkable tourist destination that offers a plethora of experiences to travellers. From the grandiose Taj Mahal, one of the wonders of the world, to opulent palaces and forts, India...

Museums In India
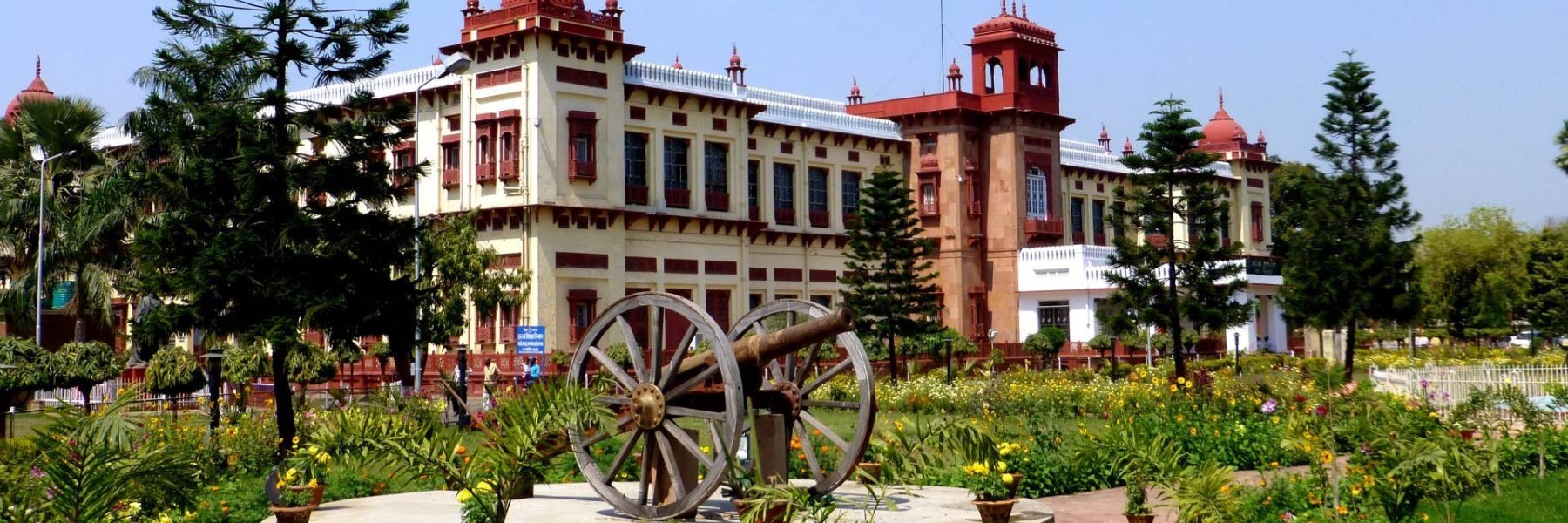
The glorious ancient history of India withits rich cultural heritage and a vibrant potpourri of traditions has beenimmortalised in various museums and galleries across the country. Frompre-historic...

Forts and Palaces
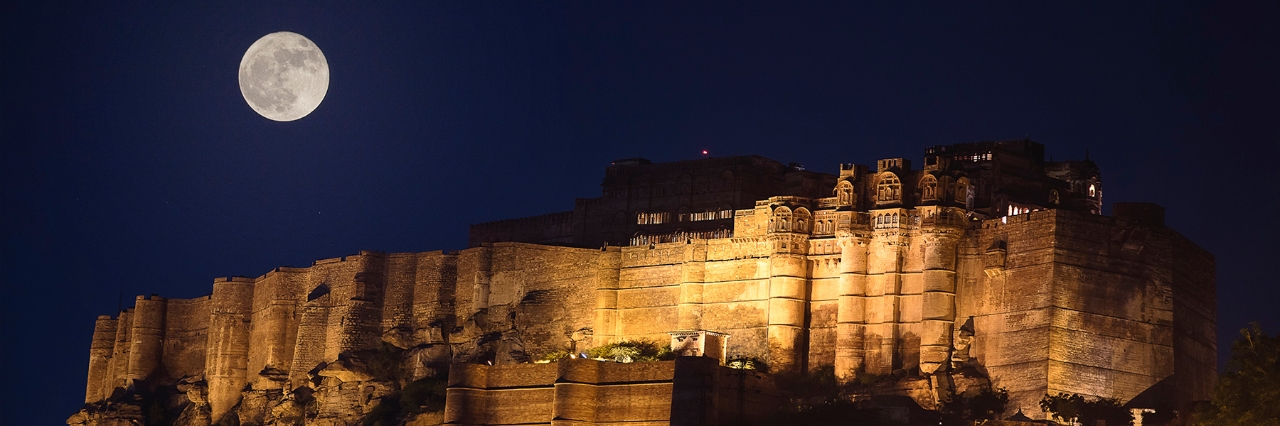
India is blessed with heritage riches and a regal lineage. Vestiges of Indian royalty can be felt in the various forts and palaces speckled across the country. From hill forts in Rajasthan to...

The Land of Gandhi
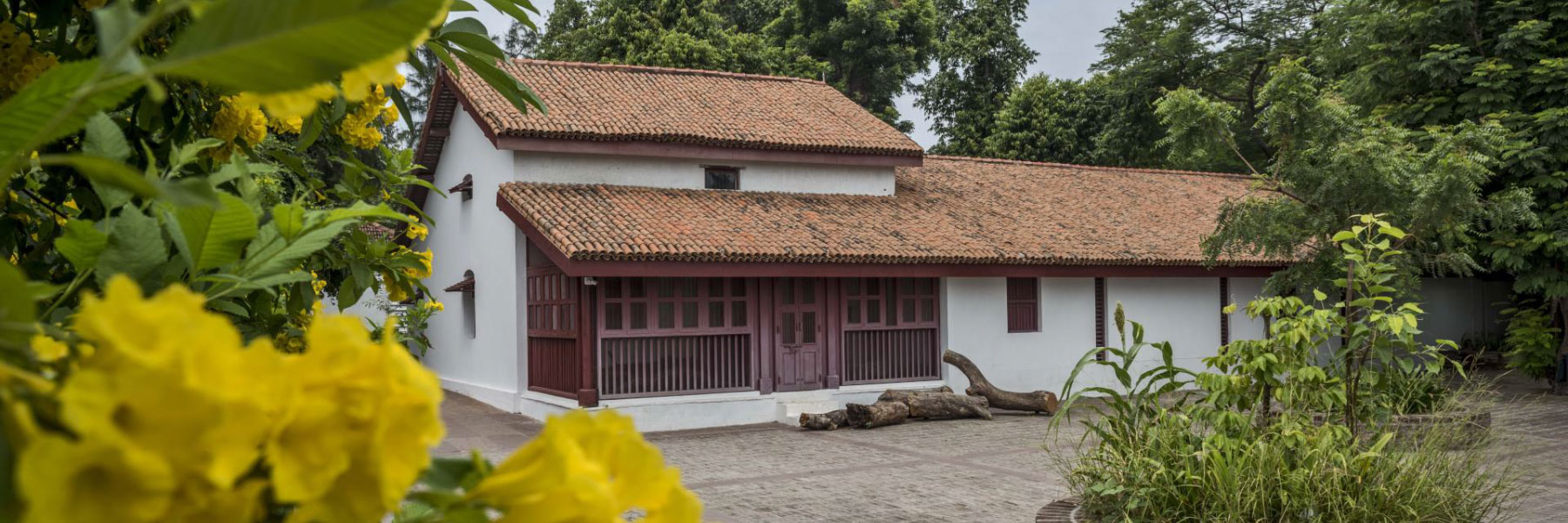
The legacy of Mahatma Gandhi, the Father of the Nation, is perfectly preserved in India. From various museums and memorials to Gandhiji's ashram, there are various stopovers in the country that...

It’s huge, almost gigantic! That is the first reaction most people...

India is a remarkable tourist destination that offers a plethora of...

The glorious ancient history of India withits rich cultural heritage...

India is blessed with heritage riches and a regal lineage. Vestiges...

The legacy of Mahatma Gandhi, the Father of the Nation, is perfectly...

Must Visit Destinations
From historical cities to natural splendours, come see the best of India

A lush carpet of rolling green, interrupted by low rises of mountains...

Shillong | Shillong Tourist Places
Colonial-era charm, a landscape of rolling green and pristine...

A coffer of coffee, cardamom and tea plantations, which envelope the...

Often referred to as the cultural capital of Kerala, Thrissur is a...

A quaint hill town, perched against the backdrop of Doddabetta (2,637...

Perched atop a rocky ridge, with snow-clad Dhauladhar mountains and...

A pristine green expanse ringed by the mist-shrouded Himalayas and a...

Places to Visit in Kavaratti
Exerting a magnetic pull over scuba divers, snorkellers and nature...

Explore before you visit
Dive deeper into India's rich culture and heritage

Khajuraho - Poetry in Unity

Ajanta Caves

Taj Mahal - Poetry of Love
Immersive experiences.
In the land of opulence, let loose and discover yourself

Popular Trips
Explore the best of India

48 hours in Bengaluru
%20%20Chandigarh.jpg/jcr:content/renditions/cq5dam.web.256.256.jpeg)
48 hours in Chandigarh

48 Hours in Chennai

48 hours in Delhi

A ride to the port

A slice of serenity in Ahmedabad

A trip along the coast

By the Tungabhadra

Eastern vignettes
The neighbouring states of West Bengal and Odisha in the eastern part...

Going South
Explore the southern fringes of India as you travel along the coast,...

Himalayan Odyssey
This 15-day trip across north India will not only take you to noted...

On Buddha’s Footsteps
This two-week-long trip takes you across four Indian states to sites...

Rhododendrons and Red Pandas
This trip takes you through the cultural heritage of a metropolis...

The best of Bengal and Sikkim
This one-of-a-kind trip will allow you to see, explore, immerse and...
Celebrate With Us
As you travel through the country, be a part of our festivals and feasts

Tue, June 20, 2023

International Day of Yoga
Wed, June 21, 2023

Sao Joao Feast of St John the Baptist
Sat, June 24, 2023

Hemis Festival
Wed, June 28- Thu, June 29, 2023

Eid-ul-Zuha
Thu, June 29- Fri, June 30, 2023

Champakulam Boat Race
Mon, July 3, 2023
An insight to the incredible experiences in India

Indian Monsoon Getaways
Incredible India

Rain-Rain please stay

Caravan Trip of MP: Your little home on wheels

4 quick weekend getaways from the 4 metros
We use cookies to ensure that you have the best experience on our website. Continued use of the website would be assumed to be an acceptance of these conditions.
Sign up to our newsletter to receive exciting content about the tourism destinations in India.
Thank you for subscribing! Explore India with us.

Authorized Portal for Visa Application to India Indianvisaonline.gov.in
All foreign nationals entering India are required to possess a valid international travel document in the form of a national passport with a valid visa from an Indian Mission/Post or eVisa (Limited Categories) from Bureau of Immigration, Ministry of Home Affairs.

Visa on Arrival for the nationals of Japan, South Korea and UAE (only for such UAE nationals who had earlier obtained e-Visa or regular/paper visa for India) Available at selected Airports

Advisory: Government of India has not authorized any agent or intermediary to charge any fee for facilitation of emergency / express Visa/eVisa. For travel to India a regular/eVisa along with passport is mandatory. Only categories exempted under bilateral arrangments may not need a visa. For persons of Indian origin (all categories), OCI card is mandatory.

e-Visa - Only Ordinary Passport holders may apply for eVisa application online. Select Visa Service as G20 eConference Visa and purpose as "To Attend G20 Conference/Meeting" .
Regular Visa - Diplomatic/Official/Ordinary Passport holders may fill online application and submit at concerned Indian Embassy/Mission in their country. Select Visa Service as Conference Visa and purpose as "To Attend G20 Conference/Meeting" .

Search Smartraveller

Latest update
Exercise a high degree of caution in India overall due to the threat of terrorism and crime and the risk of civil unrest.
Higher levels apply in some areas.

Asia (PDF 2.21 MB)
Local emergency contacts
All emergencies, fire and rescue services, medical emergencies, advice levels.
Exercise a high degree of caution in India overall.
Exercise a high degree of caution in India overall due to the threat of terrorism and crime and the risk of civil unrest. (see Safety ).
Do not travel to the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and the India-Pakistan border (except the Atari-Wagah border crossing). This doesn't apply to the Union Territory of Ladakh, which was established as its own union territory of India in October 2019, separate from the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
Do not travel to the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir; and the India-Pakistan border (except the Atari-Wagah border crossing) due to the danger of armed clashes, terrorist activities and violent demonstrations.
This doesn't apply to the Union Territory of Ladakh, which was established as its own union territory of India in October 2019, separate from the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir. (see ' Safety ')
Reconsider your need to travel to the Atari-Wagah border crossing, north-eastern states of Assam (except Guwahati), Nagaland and Manipur; and Chhattisgarh and the border areas of neighbouring states.
Reconsider your need to travel to:
- the Atari-Wagah border crossing
- North-eastern states of Assam (except Guwahati), Nagaland and Manipur;
- Chhattisgarh; and
- the border areas of neighbouring states
due to the high risk of violence (see ' Safety ').
- Terrorist activities, violent demonstrations and armed clashes sometimes occur in India. Avoid crowded places and possible targets. Large crowds at religious ceremonies and gatherings can also be dangerous. People have been killed in stampedes. Always have an exit plan.
- Women may face higher levels of verbal and physical harassment or sexual assault. Avoid travelling alone, even in major cities and tourist sites.
- Travellers have been robbed and assaulted after consuming spiked drinks or food. Don't leave your food or drinks unattended or accept food or drinks from strangers. Petty theft is common in crowded areas such as markets and public transport. Thieves on motorbikes snatch bags and jewellery. Carry only what you need. Pay close attention to your belongings.
- Scams are common. These can involve fake tour guides, ATM and credit card skimming, and fraudulent access to government services. If you're a scam victim, report it to the police to get an official report for your travel insurer.
- Severe weather is common. This includes heat waves and dust storms in summer and flooding during the monsoon season. Check with your tour operator for possible disruptions.
Curfews and restrictions have been imposed in parts of Manipur following violent demonstrations, resulting in casualties. Security agencies have increased their presence in the region. Mobile internet and transport services continue to be affected. Further restrictions may be imposed at short notice. If you are in Manipur, you should avoid demonstrations and large public gatherings, monitor local media for updates, follow the advice of local authorities, and take official warnings seriously.
Full travel advice: Safety
- Medical facilities in major cities have adequate treatment standards. The availability of treatment can be very limited or unavailable in remote and rural areas. You may need to be evacuated if you're seriously ill or injured. Medical evacuation can be very expensive.
- Various strains of influenza occur throughout India.
- Malaria is a risk in many parts of India, including major cities. Dengue is widespread, especially during the monsoon season. Zika virus outbreaks may occur. Other insect-borne diseases include Japanese encephalitis, chikungunya and filariasis. Ensure your accommodation is insect-proof. Use insect repellent. Get vaccinated. If you're pregnant, discuss this with your doctor.
- HIV/AIDS is widespread. Take precautions if you engage in high-risk activities.
- Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are very common. These include cholera, typhoid and hepatitis. Drink only treated or bottled water. Avoid raw or undercooked food.
- Air pollution can reach dangerous levels, especially in winter. It can disrupt transport and cause breathing problems. Discuss your travel plans with a doctor if you have an existing health condition.
Full travel advice: Health
- Always carry your passport and ensure you have a valid visa. It's illegal not to. Conducting missionary work without a proper visa is illegal.
- Carrying or using a satellite phone or device without official permission is illegal. You may be arrested for carrying a satellite phone or device.
- Don't use or carry illegal drugs. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe and include mandatory sentences and the death penalty.
- Check local alcohol laws before you visit. Laws on the legal drinking age and alcohol purchase vary between states.
- It's illegal to import, possess or use e-cigarettes, vaporisers or their components, such as refills. Penalties include imprisonment.
- It's illegal to fly drones and other unmanned aircraft without official permission. Contact local police for advice. It's illegal to carry or export antiquities without a permit. Contact your nearest Indian embassy or consulate for advice. It's illegal to photograph airports, military sites and dams. Some places of worship also prohibit photography.
- Cows roam freely in India. It's illegal to maim or kill them deliberately. In some states, the penalty is up to 5 years in jail.
- India has strict dress and behaviour codes, especially at religious sites. Physical contact between men and women in public might be considered inappropriate.
Full travel advice: Local laws
- You must apply for a visa before arrival. Check your eligibility and apply online for an e-visa by visiting the Government of India's Indian Visa Online website. For information on other visa types and immigration requirements, see the eFRRO and Bureau of Indian Immigration websites or contact the nearest high commission/embassy or consulate of India for the latest details.
- You may need permission from Indian authorities to visit 'restricted' or 'protected' areas, particularly in the north-east.
- Travelling by road in India can be dangerous, particularly at night. Accidents are common.
Full travel advice: Travel
Local contacts
- The Consular Services Charter details what we can and can't do to help you overseas.
- For consular help, contact the Australian High Commission in New Delhi , or the Australian Consulate-General in Mumbai, Chennai or Kolkata.
- To stay up to date with local information, follow the High Commission's social media accounts.
Full travel advice: Local contacts
Full advice
Terrorist attacks are possible in India anywhere and at any time.
The Australian Government continues to receive reports that terrorists are planning attacks in India.
The Indian Government regularly issues public alert warnings about possible terrorist attacks.
Terrorist attacks could target foreigners. Violence directed at others may affect you.
Terrorists have targeted popular tourist areas, including:
- hotels, markets and cinemas
- restaurants, bars and cafes
- tourist and religious sites
- transport hubs and public transport networks
- sporting events
- local courts and Indian security and political establishments
Targets could also include major tourist attractions and shopping centres.
Attacks could happen during significant times such as:
- Republic Day, 26 January
- Independence Day, 15 August
- periods of religious significance
- other major holidays - noting each state has different holidays
Many terrorist attacks in India have involved multiple explosions, one after the other. These attacks have caused a high number of deaths.
Militants have crossed the border into India to conduct attacks in the past. This will likely continue.
Attacks on the military and police in Jammu and Kashmir often lead to violent clashes.
Outside of major cities, security on public transport is limited, including on buses and railways.
Security at airports has improved due to the threat of terrorist attacks against Indian aviation interests.
To protect yourself from terrorist attacks:
- check the media for threats
- take official warnings seriously
- consider the level of security at your destination
- avoid areas that are possible terrorist targets
- have a clear exit plan for crowded places and potential targets
- report suspicious activity or items to the police
If there's an attack, leave the area as soon as it's safe to. Avoid the affected area in case of secondary attacks.
- Terrorism is a threat worldwide.
More information:
Jammu and Kashmir
On 5 August 2019, the Government of India announced constitutional changes that affected the internal political status of Jammu and Kashmir.
A heightened Indian security presence is now in place, with additional restrictive measures applying to public gatherings and internet and telecommunications services. Monitor local media and follow the advice of local authorities.
In the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir there is a high risk of:
- armed clashes
- terrorist attacks
- violent demonstrations
There is a higher risk in rural areas and areas close to the border with Pakistan.
Terrorists have kidnapped foreigners in Jammu and Kashmir. Terrorists have also targeted tourist buses.
People have been killed and seriously injured in widespread violent protests. More police have been sent to the region.
Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana
Maoist insurgents, known as Naxalites, have attacked rural and forested areas of the state of Chhattisgarh.
There is a risk of Naxalite violence in border regions of:
- Maharashtra
- Andhra Pradesh
Borders with Pakistan
Parts of the India-Pakistan border have a high risk of:
- cross-border attacks
Always be alert to possible threats near the Atari-Wagah border crossing.
North-eastern states of Assam (except Guwahati), Nagaland and Manipur
The north-eastern states of Nagaland, Manipur and Assam, except Guwahati city, have a high risk of:
- armed robbery
- separatist and insurgent violence
This includes rural areas.
Insurgent groups in these states have:
- attacked civilians
- bombed buildings
Kidnapping occurs across the world with political, ideological and criminal motives. Foreigners, including Australians, have been kidnapped overseas while travelling. Kidnaps can happen anywhere, anytime, including in destinations that are typically at lower risk.
There have been incidents of kidnappings in Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Rajasthan and the Northeastern Region.
If, despite our advice, you travel to an area with a high risk of kidnapping, our ability to provide consular assistance in these destinations will be limited.
To reduce the risk of kidnapping:
- always be alert to your personal security and surroundings
- get professional security advice for travel in locations with a heightened kidnap risk
- check your accommodation has appropriate security measures
- avoid isolated locations, particularly when travelling alone
- vary your movements, and don't set patterns
- notify family or friends of planned travel, and share your location
- avoid talking about your money or business affairs
- use ATMs in public places and during daylight hours
- avoid giving personal details to strangers online or over the phone
The Australian Government's longstanding policy is that it doesn't make payments or concessions to kidnappers. Ransom payments to kidnappers have funded further terrorist attacks and criminal activity. Paying a ransom to terrorist groups will likely break Australian counter-terrorism financing laws.
More information:
Civil unrest and political tension
Public protests and events that draw large groups of people can turn violent.
Violent protests and demonstrations occur from time to time. They can happen with little or no warning.
Many people have died due to civil unrest and communal violence in India.
Triggers for demonstrations include:
- international events
- political developments in the region
- election periods
- local events
Demonstrations may affect public transport.
Large crowds at religious ceremonies and gatherings can be dangerous. They have led to life-threatening situations such as stampedes.
Indian authorities may:
- set curfews
- limit mobile network availability
- restrict activity
To protect yourself from civil unrest and violence:
- avoid demonstrations, political events, rallies, processions and large public gatherings
- check the news and other sources for information
- avoid areas affected by civil unrest
- follow the advice of local authorities
- plan your activities to avoid days of national and commemorative significance
Be prepared to change your travel plans if there's an incident.
If you're affected by transport disruptions, contact your airline, travel agent or insurer for help.
Demonstrations and civil unrest
Sexual assault
Women in India may experience:
- unwanted attention
- sexual assault
It is rare for people who commit these crimes to be successfully prosecuted by the law.
There are consistent, ongoing allegations and reports of sexual misconduct. These reports have involved religious groups and their leaders. If you're visiting India for religious reasons, find out about your hosts before travelling.
Avoid travelling alone if you're female, even in major cities and tourist sites.
- Advice for women
- Sexual assault overseas
Drink and food spiking
Many travellers have been robbed and assaulted after consuming spiked drinks or food.
Home-made or unlabelled alcohol can be poisonous.
Drink spiking incidents have occurred:
- on public transport
- in hotels, restaurants and bars
Drink and food spiking is rare at:
- business-class hotels
- upscale bars and restaurants
The risk of drink and food spiking is higher in smaller establishments.
To protect yourself from food and drink spiking:
- don't accept food or drinks from strangers
- don't leave drinks unattended
- if you're not certain your drink is safe, don't drink it
Petty crime
Petty theft is common in crowded areas such as:
- trade fairs
- airports and train stations
- public transport, including overnight and long-distance trains
Thieves on motorcycles snatch bags and jewellery.
To protect yourself from petty crime:
- pay close attention to your personal belongings, especially in crowded areas
- keep car doors locked, windows up, and valuables out of sight, when parked and when moving
- carry only what you need, including your passport
- leave valuables in a secure location
- avoid wearing expensive watches, jewellery and cameras
- avoid carrying bags that are easy to snatch
If you're walking, stay on footpaths, if possible, and:
- away from the curb
- with your bag held away from traffic
Avoid travelling alone, especially at night:
- in cars, taxis and rickshaws
Avoid less populous and unlit areas. This includes city streets, village lanes and beaches.
Scams in India can involve:
- ATM and credit cards
- train tickets
- temple donations
- tour guides
Tour guide scams
Tour guides attempt to sell fraudulent tour packages. Some guides may try to 'prove' that your existing tour package is invalid to sell you their package. Strangers posing as 'guides' may attempt to take travellers to tourist areas. The fake guide transports the victim to an isolated area, where they then attempt to rob and assault them. Check that any person holding a placard with your name knows where you are going.
Card skimming scams
Card skimming devices copy details from the magnetic strip on your ATM and credit cards. These details are transferred onto a blank card for the criminal to use. There is a high risk of card skimming at ATMs.
To avoid credit and debit card scams:
- keep your credit card in sight at all times
- don't show your PIN to others, especially when using ATMs
- check your transaction statements
Government services scams
Touts or agents near government offices tell foreigners they can provide faster services for a fee. They may be present around places such as the Foreigner Regional Registration Office.
Reporting scams
If you're the victim of a scam report it immediately to the nearest police station. You may not be able to get your money or goods back. However, the police can give you an official report so you can make a claim with your insurer. See Local contacts.
Cyber security
You may be at risk of cyber-based threats during overseas travel to any country. Digital identity theft is a growing concern. Your devices and personal data can be compromised, especially if you're connecting to Wi-Fi, using or connecting to shared or public computers, or Bluetooth.
Social media can also be risky in destinations with social or political tensions or laws that may seem unreasonable by Australian standards. Travellers have been arrested for things they have said on social media. Don't comment on local or political events on your social media.
- Cyber security when travelling overseas
Tours and adventure activities
Touts may use aggressive tactics to persuade you to buy tickets for tours. You'll often see them at:
- railway stations
- bus stations
They may not have any connection to tour services. You may be overcharged.
Businesses don't always follow safety and maintenance standards. This includes:
- tour operators
- adventure activities
If you plan to do an adventure activity :
- check if your travel insurance policy covers it
- check the credentials of the operator
- ask about and insist on minimum safety requirements
- always use available safety gear, such as life jackets or seatbelts
If proper safety equipment isn't available, use another provider.
Wildlife safety
Tigers attack and kill people in India.
Monkeys may attempt to steal items from people at temples and busy tourist attractions.
If you plan to observe or photograph wildlife:
- always respect wildlife laws and park regulations
- only use reputable and professional guides
- keep a safe distance
Climate and natural disasters
Severe weather.
India experiences natural disasters and severe weather , including:
- heatwaves and drought
- floods and landslides
- cyclones and storms
- dust storms
- earthquakes and tsunamis
If there's a natural disaster:
- always carry your passport in a waterproof bag
- keep in touch with family and friends
- check the media, the India Meteorological Department website and other local sources for information
Heatwaves and drought
The climate in India is varied.
Heatwaves can cause droughts and water shortages in summer.
Floods and landslides
Monsoon rains occur. The highest risk is from June to October.
Monsoon rains can cause:
- extensive flooding and landslides
- disruptions to transportation
- areas to be cut off from roads for many days
- disruption to services, including phone, internet and electricity
High-risk areas include:
- Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in the north and east
- Andhra Pradesh, Kerala and Karnataka and Tamil Nadu in the south
Floods have affected millions of people and caused many deaths.
If you're travelling during monsoon season, ask your tour operator if services have been affected.
Cyclones and storms
Cyclones are common in Indian waters from April to December. They are particularly common around the Bay of Bengal in eastern India.
Coastal and some inland areas are vulnerable to storm surges, particularly:
- Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry
- Lakshadweep
- the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Western India (Goa, Maharashtra and Gujarat)
Cyclones and storms can disrupt critical services, including:
- emergency and medical care
- telecommunications
- food and water supplies
If there's a cyclone or storm:
- you may get stuck in the area
- flights could be delayed or suspended
- available flights may fill quickly
- adequate shelter may not be available
If you arrive during the wet season, contact your tour operator to check if services are affected.
Dust storms
Dust storms occur during summer and have caused deaths.
Earthquakes and tsunamis
Earth tremors are common in India, particularly in the north-eastern states.
Earth tremors can cause landslides in hilly and mountainous areas.
If there is an earthquake, expect severe disruptions to services.
To stay safe during an earthquake:
- know the emergency plans at your accommodation
- follow the instructions and advice of local authorities
- follow evacuation orders
All oceanic regions of the world can experience tsunamis. However, the Indian and Pacific Oceans experience large, destructive tsunamis more often. Be alert to warnings. A tsunami could quickly follow a tremor or earthquake.
Move to high ground straight away if:
- local authorities advise you to
- you feel a strong earthquake that makes it hard to stand up
- you feel a weak, rolling earthquake that lasts a minute or more
- you see a sudden rise or fall in sea level
- you hear loud and unusual noises from the sea
Don't wait for official warnings. Once on high ground, monitor local media and weather services.
Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System
Travel insurance
Get comprehensive travel insurance before you travel.
Your policy needs to cover all overseas medical costs, including medical evacuation. The Australian Government won't pay for these costs.
If you can't afford travel insurance, you can't afford to travel. This applies to everyone, no matter how healthy and fit you are.
If you're not insured, you may have to pay many thousands of dollars up-front for medical care.
- what activities and care your policy covers
- that your insurance covers you for the whole time you'll be away
Physical and mental health
Consider your physical and mental health before you travel, especially if you have an existing medical condition.
See your doctor or travel clinic to:
- have a basic health check-up
- ask if your travel plans may affect your health
- plan any vaccinations you need
Do this at least 8 weeks before you leave.
If you have immediate concerns for your welfare or the welfare of another Australian, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on +61 2 6261 3305 or contact your nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate to discuss counselling hotlines and services available in your location.
Mental health treatment and services can differ to those in Australia.
- General health advice
- Healthy holiday tips (Healthdirect Australia)
Medications
Not all medication available over the counter or by prescription in Australia is available in other countries. Some may even be considered illegal or a controlled substance, even if prescribed by an Australian doctor.
If you plan to bring medication, check if it's legal in India. Take enough legal medicine for your trip.
Carry a copy of your prescription or a letter from your doctor stating:
- what the medication is
- your required dosage
- that it's for personal use
Health risks
Various strains of influenza, including Swine flu or influenza A (H1N1) , occur throughout India.
Talk to your GP or travel doctor about vaccinations before you leave Australia.
Insect-borne diseases
Malaria is a risk in most parts of India, including major cities.
Dengue is widespread, especially after the monsoon season.
Other insect-borne diseases are common, including:
- Japanese encephalitis
- chikungunya
Zika virus outbreaks can occur in India. There's no vaccination available for the Zika virus.
If you're pregnant:
- talk to your doctor about your travel plans
- defer non-essential travel to affected areas
To protect yourself from disease:
- make sure your accommodation is insect-proof
- use insect repellent
- wear long, loose, light-coloured clothing
- consider taking medicine to prevent malaria
Zika virus fact sheet (WHO)
Nipah Virus
Nipah virus outbreaks can occur in India. There’s no vaccination available for the Nipah virus. Nipah virus is usually transmitted through contact with an infected person or through infected animals, such as bats, as well as food and materials contaminated with their saliva or urine.
HIV/AIDS is widespread in India. Take precautions if you engage in activities that expose you to the risk of infection.
Other health risks
Waterborne, foodborne, parasitic and other infectious diseases are very common, including:
- tuberculosis
Tap water is not safe to drink.
To protect yourself from illness:
- drink treated water or drink bottled water with intact seals
- avoid ice cubes
- avoid raw and undercooked food
- don't swim in freshwater
- avoid contact with dogs, monkeys and other mammals
If you're bitten or scratched by an animal, seek medical help straight away.
Get medical attention if you suspect food poisoning or have a fever or diarrhoea.
Infectious diseases
Air quality
Air pollution levels in parts of India can spike to hazardous levels during the winter months, October to February.
Severe pollution can cause:
- flight delays
- traffic delays
It can also increase the risk of breathing problems.
People who have pre-existing medical conditions, particularly heart and lung conditions, may be especially affected.
If you're concerned about the levels of air pollution:
- seek medical advice
- follow advice from local authorities about methods to reduce exposure
- monitor an air quality index
- reduce your exposure
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting Research (SAFAR)
- Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC)
Medical care
Medical facilities.
Medical facilities in major cities have adequate treatment standards. Facilities in remote and rural areas can be very limited or unavailable.
If you're seriously ill or injured, you may be evacuated to a place with better facilities. Medical evacuation can be very expensive with long lead times.
Restrictions on airspace in some locations (including, but not limited to, Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir) may prevent commercial medical evacuation. Should you be involved in a serious accident, air evacuation by the Indian Air Force may be the only option. Costs can be in the tens of thousands of dollars.
Medical tourism
Medical tourism has become more common in India, including for:
- cosmetic procedures
- experimental stem cell treatments
- dental treatments
Standards at a discount and uncertified medical establishments can be poor.
Serious and possibly life-threatening complications can and do occur.
If you plan to visit India for medical tourism:
- research and choose your medical service providers carefully
- don't use discounts or uncertified medical service providers
Decompression chambers
Decompression chambers are available at:
- the Indian Navy base in Port Blair, Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- the Goa Medical College, Goa
You're subject to all local laws and penalties, including those that may appear harsh by Australian standards. Research local laws before travelling.
If you're arrested or jailed, the Australian Government will do what it can to help you under our Consular Services Charter . But we can't get you out of trouble or out of jail.
If you're arrested for a major offence, you could go to prison for several years before you receive a verdict.
If you're imprisoned, there could be delays in getting help from the Australian Government. This is due to India's consular access approval requirements.
Satellite phones and satellite enabled navigation devices
It is illegal to carry or operate satellite phones or enabled devices in India without a licence. Australian citizens have been detained for carrying satellite phones and satellite-enabled navigational devices into the country without prior permission. This may occur even in the case of transits.
Drugs and alcohol
Penalties for drug offences are severe and can include mandatory sentences and the death penalty. There is a minimum sentence of 6 months imprisonment for possession of small amounts deemed for personal consumption only. A 10-year prison sentence applies for possession of other amounts. The judicial process is slow, and it is normal for you to be detained for months or years while your case is processed.
The legal drinking age varies, depending on the state. The legal drinking age can vary for different types of alcohol.
Some states permit alcohol use for medicinal purposes only. Others require you to hold a permit to buy, transport or drink alcohol.
Some states prohibit alcohol from being brought in from outside the state, and police may check vehicles to enforce this law.
Check the alcohol laws of each place you plan to visit.
E-cigarettes and vaporisers
It is illegal to import, possess or use e-cigarettes, vaporisers or their components, such as refills. Penalties include imprisonment.
Surrogacy laws
Commercial surrogacy is illegal in India.
- Going overseas for international surrogacy
- Going overseas to adopt a child
It's illegal to give or receive a dowry.
Courts can issue arrest alert notices for dowry claims a wronged party's request.
If you've been involved in giving or receiving a dowry or a case has been filed against you for dowry and harassment, you could be arrested on arrival into India.
It's illegal to fly unmanned aircraft systems, such as drones, without official permission, particularly:
- within a 30km radius of India Gate in New Delhi
- near military, transport and power facilities
Contact local police for advice and to get permission.
Antiquities
Possessing or exporting antiquities without official permission is illegal. For information contact the Indian Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs or an embassy or consulate of India .
Photography
It's illegal to photograph or trespass on:
- military establishments
It's also illegal to take pictures or videos of some places of worship. Always check with the building's administrative office before taking photos or videos.
In India, it's illegal to:
- not carry your passport and a valid visa
- possess firearms or ammunition
- do religious missionary work without an appropriate visa
In some states, attempting to convert a person to another religion is illegal by force or other enticement.
It's also illegal to maim or kill a cow deliberately. The penalty is up to 5 years imprisonment in some states.
Serious crimes
Some crimes may result in the death penalty, including:
- kidnapping for ransom
- armed robbery with murder
- rape, in certain circumstances
- Staying within the law and respecting customs
- Advice for LGBTQIA+ travellers
- Doing business
Australian laws
Some Australian criminal laws still apply when you're overseas. If you break these laws, you may face prosecution in Australia.
Staying within the law
Local customs
Codes of dress and behaviour are strict in India. These are particularly important at religious sites.
Physical contact between men and women in public might be considered inappropriate. Take care not to offend.
If in doubt, seek local advice.
In some areas of India, the Islamic holy month of Ramadan is observed. Respect religious and cultural customs and laws at this time.
During Ramadan, eating, drinking and smoking may be illegal in public during the day. If you're not fasting, avoid these activities around people who are. Seek local advice to avoid offence.
Explore our Ramadan page to learn more, including dates for Ramadan.
Dual citizenship
The Indian constitution doesn't recognise dual nationality.
Indian law allows people of Indian origin in some countries to apply for Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI). This includes people in Australia.
Check the Overseas Citizenship of India section of the Indian Government's Ministry of Home Affairs website for details.
Dual nationals
Visas and border measures
Every country or territory decides who can enter or leave through its borders. For specific information about the evidence you'll need to enter a foreign destination, check with the nearest embassy, consulate or immigration department of the destination you're entering.
Visa requirements
You must apply for a visa before arrival. Check if you're eligible for an e-visa on the Indian Visa Online website. For information regarding other visa categories or entry and exit requirements, see the Indian High Commission in Australia website. For information and advice regarding Indian visas and immigration regulations while in India, see the FRRO/FRO and the Bureau of Immigration websites.
If your visa has expired or you have overstayed your visa, make sure you regularise your immigration status with the FRRO/FRO before you seek to travel. Immigration authorities may prevent you from leaving India on an expired visa.
If you have had a baby in India, you need to register the baby with the FRRO and secure an exit permit before you travel.
Electronic visas
You may be eligible for an Electronic Visa (e-Visa) for:
- medical reasons
Get your e-Visa at least 4 days before you arrive.
Check that you're eligible before you apply. See the Government of India's Indian Visa Online website for details.
Tourist e-Visa
Indian Tourist e-Visas can be granted for 30 days, one year or five years. Additional conditions regarding the maximum length of stay may apply depending on the nationality shown on your passport. Detailed information regarding your visa validity and the maximum length of stay for each visa category can be found on the Indian Visa Online and Ministry of Home Affairs websites.
Beware of fake websites offering e-Visa services.
Carry a printed copy of your e-Visa, known as an electronic travel authorisation (ETA).
You'll get a formal visa in your passport when you arrive in India.
Long queues are common at immigration counters in India, regardless of visa type.
Not all international airports in India allow passengers to enter with an e-Visa. Check with your nearest Indian consulate, embassy or agent and organise a visa before you arrive.
If you present an e-Visa at an entry point where the e-Visa is not recognised, you:
- won't be able to apply for any other visa
- won't be allowed to enter India
- will be deported
If you have an e-Visa, you can leave India from any authorised immigration checkpoint.

Other visas
All other visa applicants should contact the nearest Indian embassy or consulate.
Other conditions
If you don't have a valid passport or visa, you could be deported by Indian authorities.
Some visas require you to register yourself within 14 days of your arrival. Failing to do so may prevent you from departing India. Visit the Ministry of Home Affairs website for details.
The Australian High Commission and Australian Consulate-Generals in India can't help you to stay if you don't have the correct documents.
Entry and exit conditions can change at short notice. Contact the Indian High Commission in Canberra for details about visas, currency, customs and quarantine rules.
Ministry of Home Affairs
Volunteering
If you're considering volunteer work, talk to the nearest embassy or consulate about visa requirements before travelling. This includes students visiting India under the New Colombo Plan.
Volunteer responsibly.
Make sure you are contributing in an ethical and meaningful way.
Overstays and exit visas
You could incur heavy penalties for overstaying your visa, including being jailed.
Check your visa conditions and make sure you comply.
Leave India before your visa expires.
If your passport is lost or stolen while you're in India, contact the nearest Australian mission to get a replacement travel document. You'll then need to get an exit visa through the online portal Foreigner's Regional Registration Office (FRRO) before you leave.
If your passport is lost or stolen:
- report it to the police
- arrange a replacement travel document from the nearest Australian Embassy, High Commission or Consulate
- apply for an exit visa from the Indian Ministry of Home Affairs
Other formalities
Currency laws.
Laws controlling the import and export of Indian rupees, foreign currency and other goods can change with little notice.
Contact your nearest Indian embassy or consulate for up-to-date information.
Yellow fever vaccination
You'll need a valid yellow fever vaccination certificate to enter India if you travel from an area where yellow fever occurs.
See the Indian Government's Bureau of Immigration for advice.
Countries with a risk of yellow fever (PDF 152KB)
Long-stay registration
If you plan to stay in India for more than 180 days and do not hold an OCI card, register within 14 days of arrival with the Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) in major cities.
In other areas, you can register with the Superintendent of Police.
All visitors on long-term visas must register. This includes the following visas:
- project visas
You must register even if you're a foreigner of Indian origin.
If you don't register, you could face fines or imprisonment.
You may not be able to leave India until the Bureau of Immigration grants permission.
If you or someone you're travelling with has a short-term Tourist Visa and is hospitalised, you may be able to extend or 'convert' to a Medical Visa .
Some countries require you to have at least 6 months of validity remaining on your passport after the date you plan to leave. This can apply even if you're transiting or stopping over.
Some foreign governments and airlines apply the rule inconsistently. Travellers can receive conflicting advice from different sources.
The Australian Government does not set these rules. Check your passport's expiry date before you travel. If you're not sure it'll be valid for long enough, consider getting a new passport .
Lost or stolen passport
Your passport is a valuable document. It's attractive to people who may try to use your identity to commit crimes.
Some people may try to trick you into giving them your passport. Always keep it in a safe place.
If your passport is lost or stolen, tell the Australian Government as soon as possible:
- In Australia, contact the Australian Passport Information Service .
- If you're overseas, contact the nearest Australian embassy or consulate .
Passport with 'X' gender identifier
Although Australian passports comply with international standards for sex and gender, we can't guarantee that a passport showing 'X' in the sex field will be accepted for entry or transit by another country. Contact the nearest embassy, high commission or consulate of your destination before you arrive at the border to confirm if authorities will accept passports with 'X' gender markers.
- LGBTQIA+ travellers
ATMs that accept international debit and credit cards are widely available in larger cities and towns. However, they're harder to find in rural areas.
Cash shortages at ATMs can be a problem in rural areas.
Traveller's cheques are not widely accepted.
Counterfeit currency is in circulation. Take care when dealing with cash.
Reserve Bank of India
Local travel
Travel delays.
Travel delays are common.
Expect delays around days of national significance, including:
Fog often affects northern India, particularly during December and January. Fog may cause:
- delays to air and rail travel
- dangerous road travel conditions
Travel restrictions
You may need permission from Indian authorities to visit areas designated as 'restricted' or 'protected', particularly in the north-east.
Some state and union territory governments restrict foreigners from travelling around these areas. Additional permission may be required for foreigners born in certain countries. This also applies to Australians born in those countries, even if travelling on an Australian passport.
There are heavy penalties for entering a protected or restricted area without permission.
The Ministry of Home Affairs has temporarily excluded the following areas from the Protected Area regime. Visit the Bureau of Indian Immigration webpage for details.
If you plan to visit a protected or restricted area or to confirm if additional requirements apply to your circumstances:
- seek advice from an embassy or consulate of India or the Ministry of Home Affairs
- apply at least 4 weeks in advance
Driving permit
You can drive without an Indian driver's licence for 3 months if you have both:
- an International Driving Permit
- your current Australian driver's licence
Your licence must be valid for the type of vehicle you are driving.
You need an Indian driver's licence if you plan to drive in India for over 3 months.
Your insurance may be void if you have an accident without the correct licence. You could be liable for the accident as an unlicensed driver.
Road travel
Travelling by road in India can be dangerous. Accidents are common.
Hazards include:
- poorly maintained vehicles
- poor quality and congested roads
- roads shared with pedestrians, carts, cattle and other livestock
- vehicles travelling in the wrong direction, often without warning
Travelling by road at night is particularly dangerous due to:
- insufficient or non-existent lighting
- other vehicles driving with headlights off or on high beam
If you hit a pedestrian or cow, you're at risk of being attacked or becoming a victim of extortion, even if you weren't driving the vehicle.
If it's unsafe to remain at the scene of an accident, go to the nearest police station.
To stay safe when driving:
- avoid driving at night
- avoid driving in fog
- if you hit a pedestrian or cow, go straight to the nearest police station
Driving or riding
Motorcycles
If you plan on riding a motorbike:
- check that your travel insurance policy covers you
- exercise caution
- always wear a helmet
Use a pre-paid taxi service when you arrive at the airport.
It's difficult to verify if street taxis are legitimate.
Use taxi services booked from hotels or taxi stands. Don't hail taxis on the street.
Don't use unmarked private cars as taxis.
Rideshare apps are widely used in major cities. You can use these apps with a SIM card.
Public transport
Bus and train services can be dangerous due to the following:
- overcrowding
- poor maintenance
- drivers who don't have adequate training
If you travel by train, find out where the emergency exits are located.
Transport and getting around safely
There may not be safety equipment, such as life jackets, on:
- tourist boats
- other small commercial craft
Before you book, check the operators' credentials and safety equipment.
Travelling by boat
DFAT doesn't provide information on the safety of individual commercial airlines or flight paths.
Check India's air safety profile with the Aviation Safety Network.
Call 1800 11 1363 for 24/7 tourist helpline (in 12 languages), run by the Ministry of Tourism.
Contact your provider with any complaints about tourist services or products.
Ministry of Tourism
Emergencies
Depending on what you need, contact your:
- family and friends
- travel agent
- insurance provider
Always get a police report when you report a crime.
Your insurer should have a 24-hour emergency number.
Consular contacts
Read the Consular Services Charter for what the Australian Government can and can't do to help you overseas.
For consular assistance, contact:
Australian High Commission, New Delhi
No. 1/50 G Shantipath (Gate 1) Chanakyapuri New Delhi 110 021
Phone: (+91 11) 4139 9900 Fax: (+91 11) 2687 2228
Website: india.highcommission.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
Facebook: Australia in India
X: @AusHCIndia
Instagram: AusHCIndia
Check the High Commission website for details about opening hours and any temporary closures.
Australian Consulate-General, Mumbai
Level 10, A Wing Crescenzo Building, Opp MCA Cricket Club G Block, Plot C 38-39 Bandra Kurla Complex Mumbai 400 051
Phone: (+91 22) 6757 4900 Fax: (+91 22) 6757 4955
Website: mumbai.consulate.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
Australian Consulate-General, Chennai
9th Floor, Express Chambers Express Avenue Estate Whites Road Royapettah Chennai 600 014 Tamil Nadu
Phone: (+91 44) 4592 1300 Fax: (+91 44) 4592 1320
Website: chennai.consulate.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
Australian Consulate-General, Kolkata
1A, Ho Chi Minh Sarani Kolkata 700 071 West Bengal
Phone: (+91 11 4910 5980)
Website: kolkata.consulate.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
Australian Consulate-General, Bengaluru
The Ritz-Carlton 99 Residency Road Bengaluru, Karnataka 560025
Phone: (+91 11) 4910 5960
Website: bengaluru.consulate.gov.au
Email: [email protected]
24-hour Consular Emergency Centre
In a consular emergency, if you can't contact an embassy, call the 24-hour Consular Emergency Centre on:
+61 2 6261 3305 from overseas
1300 555 135 in Australia
Travelling to India?
Sign up to get the latest travel advice updates..
Be the first to know official government advice when travelling.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
COVID-19: travel health notice for all travellers
India travel advice
Latest updates: Editorial change
Last updated: June 5, 2024 06:24 ET
On this page
Safety and security, entry and exit requirements, laws and culture, natural disasters and climate, india - exercise a high degree of caution.
Exercise a high degree of caution in India due to the threat of terrorist attacks throughout the country.
In and around Bengaluru, Chandigarh and Mumbai - Exercise a high degree of caution
Exercise a high degree of caution in and around Bengaluru, Chandigarh and Mumbai. Consular services in-person are temporarily unavailable in those cities or surrounding areas. If you need consular services, contact the High Commission of Canada in India, located in New Delhi. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
Parts of Northeastern India - Avoid non-essential travel
Union territory of jammu and kashmir - avoid all travel.
This advisory excludes travelling to or within the Union Territory of Ladakh.
Border areas with Pakistan - Avoid all travel
This advisory excludes the Wagah border crossing.
Back to top
General elections are scheduled to take place between April 19 and June 1, 2024. Demonstrations could occur before, during and after the elections.
Disruptions to traffic and public transportation may also occur. Curfews may be imposed without notice.
- Avoid areas where demonstrations and large gatherings are taking place
- Follow the instructions of local authorities
- Monitor local media for information on ongoing demonstrations
Mass gatherings (large-scale events)
Security situation
In the context of recent developments in Canada and in India, there are calls for protests and some negative sentiment towards Canada in traditional media and on social media. Demonstrations, including anti-Canada protests, could occur and Canadians may be subjected to intimidation or harassment. In Delhi and the National Capital Region, you should keep a low profile with strangers, and not share your personal information with them. Avoid crowded areas, including public transportation. You should always travel with someone and inform a friend or a family member of your travel plans.
Consular services in person are temporarily unavailable in and around Bengaluru, Chandigarh and Mumbai. Consular services in person at the High Commission of Canada in New Delhi will remain available.
Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir
The security situation in the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir is tense. There are high risks of violent protests, civil unrest and acts of terrorism and militancy.
Violent clashes between militants and security forces occur regularly. Terrorist attacks against security forces have led to civilian casualties. Further attacks could take place at any time. You could find yourself in the wrong place at the wrong time.
The Indian army has enhanced powers in this territory. Authorities may impose curfews and security restrictions on short notice.
- Avoid gatherings and demonstrations
- Always carry ID
- Expect a heightened security presence and security checks
Border areas with Pakistan
The level of tension between India and Pakistan may change suddenly. You could experience difficulties when travelling between the two countries. You may be subject to scrutiny if officials from either country become aware that you have recently travelled to the other.
The security situation along the border with Pakistan, especially along the Line of Control (LoC), which separates the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh from Pakistan-administered Kashmir, remains volatile. Cross-border gunfire and shelling are occurring sporadically along the LoC. The presence of landmines and unexploded ordnance also constitute a risk.
Although international travellers regularly use the Wagah border crossing linking Amritsar, India, to Lahore, Pakistan, it remains vulnerable to attack. Security measures are in place. You may experience long delays.
Parts of Northeastern India
Several extremist and insurgent groups are active in the northeastern states of Assam and Manipur. They regularly target local government and security forces and may use various criminal activities to finance their activities.
Ethnic tensions in the State can also lead to conflict and civil unrest.
There is a threat of terrorism in India, particularly in:
- the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir
- the State of Manipur
- the State of Assam
- areas of East India where Naxalites groups are active
Maoist extremist insurgents, known as Naxalites, are responsible for the majority of terrorist attacks in India. These groups are usually based in rural and forested areas within zones of concerns, as defined by the Government of India, which include:
- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Uttar Pradesh
- West Bengal
Extremist and insurgent groups usually target government and security forces, and sometimes, trains and railway tracks. While tourists are not usually specifically targeted, bystanders could be affected. Be particularly vigilant during election periods and in the lead-up to, and during, religious holidays and times of national significance, such as:
- Republic Day (January 26)
- Independence Day (August 15)
Targets of terrorist attacks could include:
- government buildings, including schools
- places of worship
- airports and other transportation hubs and networks
- public areas such as tourist attractions, restaurants, bars, coffee shops, shopping centres, markets, hotels and other sites frequented by foreigners
While in India:
- always be aware of your surroundings when in public places
- if you see a suspicious package, immediately leave the area and report it to authorities
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse snatching, is common. Criminals may target foreigners, especially in major cities and tourist areas.
- Be vigilant in all crowded locations
- Don’t carry large sums of money
- Ensure that your personal belongings, including your passport and other travel documents, are secure at all times
Petty crime frequently occurs on public transportation and overnight trains.
- Ensure that the train compartment contains packages belonging only to you and other occupants
- Store personal belongings in a safe place, and don’t leave the compartment unattended
- Securely lock the doors
Serious crime against foreigners is less frequent, but incidents do occur.
Credit card and ATM fraud occurs. Be cautious when using debit or credit cards:
- pay careful attention when your cards are being handled by others
- use ATMs located in well-lit public areas or inside a bank or business
- avoid using card readers with an irregular or unusual feature
- cover the keypad with one hand when entering your PIN
- check for any unauthorized transactions on your account statements
Exercise caution in tourist areas and airports where scammers particularly target foreigners.
Scams involving the exportation of jewels, gemstones, carpets, and other items have occurred. Taxi drivers may approach you, offering money to export such items.
- Don’t accept any offer, no matter how convincing
- Beware of offers for cheap transportation or accommodation, extended taxi rides and unsolicited guided tours
Romance scams
If you’re travelling to India to meet someone you’ve otherwise only met online, you may be the victim of a scam.
Be alert to attempts at fraud by persons who profess friendship or romantic interest over the internet.
Investment scams
Unsolicited emails offering attractive business or financial opportunities are most likely fraudulent.
Don’t travel to India to obtain restitution after losing money to a scam.
Overseas fraud
Spiked food and drinks
Never leave food or drinks unattended or in the care of strangers. Be wary of accepting snacks, beverages, gum or cigarettes from new acquaintances. These items may contain drugs that could put you at risk of sexual assault and robbery.
Women’s safety
Crimes committed against women frequently occur in India. Foreign women are often the target of unwanted attention.
Staring, verbal abuse, groping, and other forms of sexual harassment can occur anywhere, including in tourist sites and areas. Attackers sometimes act as a group.
Reports of rape and assault against foreign women have increased. You should be particularly vigilant:
- on all forms of public transportation
- at Yoga centres, ashrams and other places of spiritual retreats
Local authorities may not always respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment.
- Avoid travelling alone, particularly at night
- Be extremely vigilant on public transportation, taxis and auto-rickshaws
- Be careful when dealing with strangers or new acquaintances
- Be wary of accepting snacks or beverages from new acquaintances
- Avoid less populous and unlit areas
- Respect local customs and dress codes
- Reach police immediately if you feel threatened
If you are the victim of a sexual assault, you should report it immediately to local authorities and the nearest office of the Government of Canada.
Advice for women travellers
Forced marriages
Forced marriage affecting foreigners occurs, sometimes without the affected person’s prior knowledge or consent.
Some Canadians have been forced into marital arrangements and have been detained against their will. They have been subjected to threats, intimidation and violence by family members.
If you’re in Canada
If you’re in Canada and you believe that you’re being forced to travel overseas to marry, you should call your local police for assistance.
If you’re in India
If you’re in India and you believe that you’re being forced to marry, contact the nearest office of the Government of Canada. You may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre .
Family members may retain passports to prevent victims from returning to Canada. Keep digital or physical copies of your travel documents in a safe place.
General information and advice about forced marriage
Demonstrations and mass gatherings
Protests in manipur.
Violent demonstrations have been taking place in Manipur State since May 3, 2023, resulting in casualties. Protests have led to disruptions to traffic and public transportation. Curfews have been imposed in several districts and mobile and internet services may be limited.
If you are in Manipur:
- monitor local media for the most recent information
- follow the instructions of local authorities
- be prepared to modify your plans in case of disturbances
- expect enhanced security measures and an increased police presence
Demonstrations, mass gatherings, general strikes, “bandh” or “hartal,” take place frequently. Even peaceful demonstrations can turn violent at any time. They can also lead to disruptions to traffic and public transportation.
Stampedes have occurred during mass gatherings, including religious ceremonies, and resulted in deaths and injuries.
Local authorities may impose curfews and other restrictions on short notice.
- Follow the instructions of local authorities, including curfews
Road safety
Road conditions and road safety are poor throughout the country. Most roads, including major highways, are poorly maintained. There is severe traffic congestion. Driving conditions may be hazardous during the rainy season, and some roads can become impassable.
Drivers don’t respect traffic laws. They are often aggressive or reckless. Driving can be hazardous due to the presence of livestock or wandering cows, including in urban areas.
Fatal road accidents are frequent. They can lead to mob anger and assault.
- Avoid travelling outside urban centres after dark
- Avoid driving or riding motorcycles in India, even if you are an experienced motorcyclist
- Be very careful when crossing the street, even at pedestrian crossings
- If involved in an accident, contact local authorities immediately
Public transportation
India has an extensive passenger train system. Rail accidents are common, mostly due to poor maintenance. Thefts are frequent on certain train lines.
If you use a taxi, get it from a reputable hotel, an official taxi stand, or a trusted ride-sharing app. At the airport, use officially marked taxis or pre-paid transport services.
- Negotiate fares in advance, or insist that the driver use the meter, as you may be overcharged
- Avoid travelling alone, especially at night
- Don’t share taxis with strangers
Maritime transportation
Maritime accidents occur regularly due to the overloading and poor maintenance of some vessels.
- Don’t board vessels that appear overloaded or unseaworthy
- Always wear a life jacket
Pirate attacks and armed robbery against ships occur in coastal waters. Mariners should take appropriate precautions.
Live piracy report - International Maritime Bureau
Water activities
Coastal waters can be dangerous. Riptides are common. Several drownings occur each year.
Beaches are not usually supervised by lifeguards. Many beaches don’t display warnings of dangerous conditions.
- Seek local advice before swimming
- Avoid swimming if red flags are flown
- Avoid swimming during Monsoon season
- Always wear a life jacket if you use a boat or a small embarkation
Water safety abroad
No commercial mountain rescue services are operating above 3,000 metres.
If you intend on trekking:
- never do so alone and always hire an experienced guide from a reputable company
- buy travel insurance that includes helicopter rescue and medical evacuation
- ensure that your physical condition is good enough to meet the challenges of your activity
- ensure that you’re adequately equipped and well informed about weather and other conditions that may pose a hazard
- inform a family member or friend of your itinerary, including when you expect to be back to camp
- know the symptoms of acute altitude sickness, which can be fatal
- obtain detailed information on trekking routes or ski slopes before setting out and do not venture off marked trails or slopes
Wildlife viewing
Wildlife viewing may pose risks, particularly on foot or at close range. If you plan on visiting a wildlife area such as a tiger reserve:
- always maintain a safe distance when observing wildlife
- only exit a vehicle when a professional guide or warden says it’s safe to do so
- only use reputable and professional guides or tour operators
- closely follow park regulations and wardens’ advice
Large groups of monkeys are present in several parts of India, including some urban regions. Monkeys can get aggressive and rapidly overwhelm travellers in their search for food. They can also steal your belongings.
Be vigilant when in the presence of monkeys.
We do not make assessments on the compliance of foreign domestic airlines with international safety standards.
Information about foreign domestic airlines
Every country or territory decides who can enter or exit through its borders. The Government of Canada cannot intervene on your behalf if you do not meet your destination’s entry or exit requirements.
We have obtained the information on this page from the Indian authorities. It can, however, change at any time.
Verify this information with the Foreign Representatives in Canada .
Entry requirements vary depending on the type of passport you use for travel.
Before you travel, check with your transportation company about passport requirements. Its rules on passport validity may be more stringent than the country’s entry rules.
Regular Canadian passport
Your passport must be valid for 6 months from your date of entry into India and must contain at least two blank pages for use by immigration officials.
Passport for official travel
Different entry rules may apply.
Official travel
Passport with “X” gender identifier
While the Government of Canada issues passports with an “X” gender identifier, it cannot guarantee your entry or transit through other countries. You might face entry restrictions in countries that do not recognize the “X” gender identifier. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Other travel documents
Different entry rules may apply when travelling with a temporary passport or an emergency travel document. Before you leave, check with the closest foreign representative for your destination.
Useful links
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Canadian passports
Certain types of Indian visa services for Canadians have resumed. For additional information, please contact the visa service provider directly.
Latest information – Indian Visa Application Center in Canada
Ensure you apply for the proper type of visa for the specific purpose of your trip. If you are denied entry by immigration officials, you will be returned to your point of departure.
Canadian-Pakistani citizens are subject to different visa application and registration procedures.
You can only stay in India for up to 180 consecutive days on a tourist visa, even when its validity exceeds 180 days.
Residency registration
If you stay in India for more than 180 days, you must register within 14 days of arrival with the Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO).
- e-FRRO online portal (for Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Bengaluru) – India's Bureau of Immigration
- FRRO Contact List – India's Bureau of Immigration
Penalties for overstaying
Strict penalties are enforced for overstaying. If you overstay, you could be subject to fines, detention and a future travel ban.
If you have overstayed your visa, you must request an exit visa from the Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO). This process can be lengthy.
Other entry requirements
Customs officials may ask you to show them a return or onward ticket and proof of sufficient funds to cover your stay.
Dual citizenship
If you hold an Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) card, you must present it upon entry and exit.
You must present a boarding pass and a photo identification to access airport departure terminals and public areas.
Lost or stolen passport
If your passport is lost or stolen, an exit visa is required to leave India.
To obtain an exit visa, you must present the FRRO with:
- a police report
- two current passport-size photographs
- a letter providing details of the loss or theft from the High Commission of Canada to India in New Delhi or Consulate General of Canada in either Chandigarh or Mumbai
The FRRO will verify the entry details before issuing an exit visa. This process can take several days.
Restricted and Protected Areas
Special permits are required to visit certain parts of India designated as restricted or protected areas.
Restricted or protected areas – India's Bureau of Immigration
- Poliomyelitis
You may need to produce proof of polio vaccination if you are arriving in India from:
- Afghanistan
- the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Confirm this requirement with the nearest Indian diplomatic office before travelling.
- Foreign Representatives in Canada
- Children and travel
Learn more about travelling with children .
Yellow fever
Learn about potential entry requirements related to yellow fever (vaccines section).
Relevant Travel Health Notices
- Global Measles Notice - 13 March, 2024
- Zika virus: Advice for travellers - 31 August, 2023
- COVID-19 and International Travel - 13 March, 2024
This section contains information on possible health risks and restrictions regularly found or ongoing in the destination. Follow this advice to lower your risk of becoming ill while travelling. Not all risks are listed below.
Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic preferably 6 weeks before you travel to get personalized health advice and recommendations.
Routine vaccines
Be sure that your routine vaccinations , as per your province or territory , are up-to-date before travelling, regardless of your destination.
Some of these vaccinations include measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, varicella (chickenpox), influenza and others.
Pre-travel vaccines and medications
You may be at risk for preventable diseases while travelling in this destination. Talk to a travel health professional about which medications or vaccines may be right for you, based on your destination and itinerary.
Yellow fever is a disease caused by a flavivirus from the bite of an infected mosquito.
Travellers get vaccinated either because it is required to enter a country or because it is recommended for their protection.
- There is no risk of yellow fever in this country.
Country Entry Requirement*
- Proof of vaccination is required if you are coming from or have transited through an airport of a country where yellow fever occurs.
Recommendation
- Vaccination is not recommended.
- Discuss travel plans, activities, and destinations with a health care professional.
- Contact a designated Yellow Fever Vaccination Centre well in advance of your trip to arrange for vaccination.
About Yellow Fever
Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada * It is important to note that country entry requirements may not reflect your risk of yellow fever at your destination. It is recommended that you contact the nearest diplomatic or consular office of the destination(s) you will be visiting to verify any additional entry requirements.
There is a risk of hepatitis A in this destination. It is a disease of the liver. People can get hepatitis A if they ingest contaminated food or water, eat foods prepared by an infectious person, or if they have close physical contact (such as oral-anal sex) with an infectious person, although casual contact among people does not spread the virus.
Practise safe food and water precautions and wash your hands often. Vaccination is recommended for all travellers to areas where hepatitis A is present.
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease. It can spread quickly from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
Anyone who is not protected against measles is at risk of being infected with it when travelling internationally.
Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are fully protected against measles.
Japanese encephalitis is a viral infection that can cause swelling of the brain. It is spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Risk is very low for most travellers. Travellers at relatively higher risk may want to consider vaccination for JE prior to travelling.
Travellers are at higher risk if they will be:
- travelling long term (e.g. more than 30 days)
- making multiple trips to endemic areas
- staying for extended periods in rural areas
- visiting an area suffering a JE outbreak
- engaging in activities involving high contact with mosquitos (e.g., entomologists)
Hepatitis B is a risk in every destination. It is a viral liver disease that is easily transmitted from one person to another through exposure to blood and body fluids containing the hepatitis B virus. Travellers who may be exposed to blood or other bodily fluids (e.g., through sexual contact, medical treatment, sharing needles, tattooing, acupuncture or occupational exposure) are at higher risk of getting hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all travellers. Prevent hepatitis B infection by practicing safe sex, only using new and sterile drug equipment, and only getting tattoos and piercings in settings that follow public health regulations and standards.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious viral disease. It can spread from person to person by direct contact and through droplets in the air.
It is recommended that all eligible travellers complete a COVID-19 vaccine series along with any additional recommended doses in Canada before travelling. Evidence shows that vaccines are very effective at preventing severe illness, hospitalization and death from COVID-19. While vaccination provides better protection against serious illness, you may still be at risk of infection from the virus that causes COVID-19. Anyone who has not completed a vaccine series is at increased risk of being infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 and is at greater risk for severe disease when travelling internationally.
Before travelling, verify your destination’s COVID-19 vaccination entry/exit requirements. Regardless of where you are going, talk to a health care professional before travelling to make sure you are adequately protected against COVID-19.
The best way to protect yourself from seasonal influenza (flu) is to get vaccinated every year. Get the flu shot at least 2 weeks before travelling.
The flu occurs worldwide.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs from November to April.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, the flu season usually runs between April and October.
- In the tropics, there is flu activity year round.
The flu vaccine available in one hemisphere may only offer partial protection against the flu in the other hemisphere.
The flu virus spreads from person to person when they cough or sneeze or by touching objects and surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus. Clean your hands often and wear a mask if you have a fever or respiratory symptoms.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Travellers going to countries in South Asia should speak to a health care professional about getting vaccinated.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease that is caused by parasites spread through the bites of mosquitoes. There is a risk of malaria in certain areas and/or during a certain time of year in this destination.
Antimalarial medication may be recommended depending on your itinerary and the time of year you are travelling. Consult a health care professional or visit a travel health clinic before travelling to discuss your options. It is recommended to do this 6 weeks before travel, however, it is still a good idea any time before leaving. Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times: • Cover your skin and use an approved insect repellent on uncovered skin. • Exclude mosquitoes from your living area with screening and/or closed, well-sealed doors and windows. • Use insecticide-treated bed nets if mosquitoes cannot be excluded from your living area. • Wear permethrin-treated clothing. If you develop symptoms similar to malaria when you are travelling or up to a year after you return home, see a health care professional immediately. Tell them where you have been travelling or living.
In this destination, rabies is carried by dogs and some wildlife, including bats. Rabies is a deadly disease that spreads to humans primarily through bites or scratches from an infected animal. While travelling, take precautions , including keeping your distance from animals (including free-roaming dogs), and closely supervising children.
If you are bitten or scratched by an animal while travelling, immediately wash the wound with soap and clean water and see a health care professional. Rabies treatment is often available in this destination.
Before travel, discuss rabies vaccination with a health care professional. It may be recommended for travellers who are at high risk of exposure (e.g., occupational risk such as veterinarians and wildlife workers, children, adventure travellers and spelunkers, and others in close contact with animals).
Safe food and water precautions
Many illnesses can be caused by eating food or drinking beverages contaminated by bacteria, parasites, toxins, or viruses, or by swimming or bathing in contaminated water.
- Learn more about food and water precautions to take to avoid getting sick by visiting our eat and drink safely abroad page. Remember: Boil it, cook it, peel it, or leave it!
- Avoid getting water into your eyes, mouth or nose when swimming or participating in activities in freshwater (streams, canals, lakes), particularly after flooding or heavy rain. Water may look clean but could still be polluted or contaminated.
- Avoid inhaling or swallowing water while bathing, showering, or swimming in pools or hot tubs.
Cholera is a risk in parts of this country. Most travellers are at very low risk.
To protect against cholera, all travellers should practise safe food and water precautions .
Travellers at higher risk of getting cholera include those:
- visiting, working or living in areas with limited access to safe food, water and proper sanitation
- visiting areas where outbreaks are occurring
Vaccination may be recommended for high-risk travellers, and should be discussed with a health care professional.
Travellers' diarrhea is the most common illness affecting travellers. It is spread from eating or drinking contaminated food or water.
Risk of developing travellers' diarrhea increases when travelling in regions with poor standards of hygiene and sanitation. Practise safe food and water precautions.
The most important treatment for travellers' diarrhea is rehydration (drinking lots of fluids). Carry oral rehydration salts when travelling.
Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread by contaminated food or water. Risk is higher among children, travellers going to rural areas, travellers visiting friends and relatives or those travelling for a long period of time.
Travellers visiting regions with a risk of typhoid, especially those exposed to places with poor sanitation, should speak to a health care professional about vaccination.
Insect bite prevention
Many diseases are spread by the bites of infected insects such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas or flies. When travelling to areas where infected insects may be present:
- Use insect repellent (bug spray) on exposed skin
- Cover up with light-coloured, loose clothes made of tightly woven materials such as nylon or polyester
- Minimize exposure to insects
- Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in buildings that are not fully enclosed
To learn more about how you can reduce your risk of infection and disease caused by bites, both at home and abroad, visit our insect bite prevention page.
Find out what types of insects are present where you’re travelling, when they’re most active, and the symptoms of the diseases they spread.
There is a risk of chikungunya in this country. The risk may vary between regions of a country. Chikungunya is a virus spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. Chikungunya can cause a viral disease that typically causes fever and pain in the joints. In some cases, the joint pain can be severe and last for months or years.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites at all times. There is no vaccine available for chikungunya.
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever is a viral disease that can cause fever, pain and bleeding under the skin. In some cases, it can be fatal. It spreads to humans through contact with infected animal blood or tissues, or from the bite of an infected tick. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from tick bites and avoid animals, particularly livestock. There is no vaccine available for Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever.
Visceral leishmaniasis (or kala azar) affects the bone marrow and internal organs. It is caused by a parasite spread through the bite of a female sandfly. It can also be transmitted by blood transfusion or sharing contaminated needles. If left untreated it can cause death. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from sandfly bites, which typically occur after sunset in rural and forested areas and in some urban centres. There is no vaccine or medication to protect against leishmaniasis.
Lymphatic filariasis , also known as elephantiasis, is caused by filariae (tiny worms) spread to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can cause a range of illnesses. Risk is generally low for most travellers. Protect yourself from mosquito bites. There is no vaccine available for lymphatic filariasis although drug treatments exist.
- In this country, dengue is a risk to travellers. It is a viral disease spread to humans by mosquito bites.
- Dengue can cause flu-like symptoms. In some cases, it can lead to severe dengue, which can be fatal.
- The level of risk of dengue changes seasonally, and varies from year to year. The level of risk also varies between regions in a country and can depend on the elevation in the region.
- Mosquitoes carrying dengue typically bite during the daytime, particularly around sunrise and sunset.
- Protect yourself from mosquito bites . There is no vaccine or medication that protects against dengue.
Zika virus is a risk in this country.
Zika virus is primarily spread through the bite of an infected mosquito. It can also be sexually transmitted. Zika virus can cause serious birth defects.
During your trip:
- Prevent mosquito bites at all times.
- Use condoms correctly or avoid sexual contact, particularly if you are pregnant.
If you are pregnant or planning a pregnancy, you should discuss the potential risks of travelling to this destination with your health care provider. You may choose to avoid or postpone travel.
For more information, see Zika virus: Pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Animal precautions
Some infections, such as rabies and influenza, can be shared between humans and animals. Certain types of activities may increase your chance of contact with animals, such as travelling in rural or forested areas, camping, hiking, and visiting wet markets (places where live animals are slaughtered and sold) or caves.
Travellers are cautioned to avoid contact with animals, including dogs, livestock (pigs, cows), monkeys, snakes, rodents, birds, and bats, and to avoid eating undercooked wild game.
Closely supervise children, as they are more likely to come in contact with animals.
There is a risk of Nipah virus infection in this country. Nipah virus infections can range from asymptomatic (no symptoms) to severe illness and death.
Nipah virus is spread to people from animals (such as fruit bats) but it can also be spread through contaminated food or close contact with someone who is ill.
Travellers to areas where Nipah virus is found should:
- avoid consuming date palm sap products, including raw date palm juice
- thoroughly wash and peel fruit before consumption
- wash hands regularly with soap and water
- discard fruit with signs of bites or fruit that has been found on the ground
- avoid contact with fruit bats and areas where they are known to roost
For more information on preventing Nipah virus infection, visit Nipah virus: Prevention and risks .
There is no vaccine or medication that protects against Nipah virus infection.
Human cases of avian influenza have been reported in this destination. Avian influenza is a viral infection that can spread quickly and easily among birds and in rare cases it can infect mammals, including people. The risk is low for most travellers.
Avoid contact with birds, including wild, farm, and backyard birds (alive or dead) and surfaces that may have bird droppings on them. Ensure all poultry dishes, including eggs and wild game, are properly cooked.
Travellers with a higher risk of exposure include those:
- visiting live bird/animal markets or poultry farms
- working with poultry (such as chickens, turkeys, domestic ducks)
- hunting, de-feathering, field dressing and butchering wild birds and wild mammals
- working with wild birds for activities such as research, conservation, or rehabilitation
- working with wild mammals, especially those that eat wild birds (e.g., foxes)
All eligible people are encouraged to get the seasonal influenza shot, which will protect them against human influenza viruses. While the seasonal influenza shot does not prevent infection with avian influenza, it can reduce the chance of getting sick with human and avian influenza viruses at the same time.
Person-to-person infections
Stay home if you’re sick and practise proper cough and sneeze etiquette , which includes coughing or sneezing into a tissue or the bend of your arm, not your hand. Reduce your risk of colds, the flu and other illnesses by:
- washing your hands often
- avoiding or limiting the amount of time spent in closed spaces, crowded places, or at large-scale events (concerts, sporting events, rallies)
- avoiding close physical contact with people who may be showing symptoms of illness
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) , HIV , and mpox are spread through blood and bodily fluids; use condoms, practise safe sex, and limit your number of sexual partners. Check with your local public health authority pre-travel to determine your eligibility for mpox vaccine.
Tuberculosis is an infection caused by bacteria and usually affects the lungs.
For most travellers the risk of tuberculosis is low.
Travellers who may be at high risk while travelling in regions with risk of tuberculosis should discuss pre- and post-travel options with a health care professional.
High-risk travellers include those visiting or working in prisons, refugee camps, homeless shelters, or hospitals, or travellers visiting friends and relatives.
Medical services and facilities
The quality of health care varies significantly throughout the country.
Medical care in major cities may be good, but it’s usually very limited or unavailable in rural areas.
Government hospitals provide free services or at a minimal cost. Private facilities often offer a higher level of care but can be expensive. Most hospitals require up-front payment or confirmation of insurance coverage before commencing treatment.
Specialised treatment for psychiatric illness may not be available outside major cities.
Make sure you get travel insurance that includes coverage for medical evacuation and hospital stays.
Travel health and safety
Ambulances are often equipped with basic and old medical equipment.
Response times can be very slow. Traffic doesn’t yield to emergency vehicles.
In case of serious illness or injury, you may consider taking a taxi or private vehicle to go to the hospital rather than wait for an ambulance.
Medical tourism
Some Canadian citizens have had severe health complications following cosmetic or other elective surgeries abroad.
Before leaving for medical travel:
- make sure you have done your research
- use competent health-care providers only
Receiving Medical Care in Other Countries
Keep in Mind...
The decision to travel is the sole responsibility of the traveller. The traveller is also responsible for his or her own personal safety.
Be prepared. Do not expect medical services to be the same as in Canada. Pack a travel health kit , especially if you will be travelling away from major city centres.
You must abide by local laws.
Learn about what you should do and how we can help if you are arrested or detained abroad .
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect heavy fines and jail sentences. Detention during the investigation is common and can be lengthy.
Laws regarding the purchase and consumption of alcohol, including the legal drinking age, differ from state to state. Authorities often call for dry periods during:
- religious festivals
- national holidays
Drugs, alcohol and travel
It is prohibited to import, possess or use e-cigarettes, vaporisers and their refills.
Beef consumption
Cows are protected and venerated by several groups of faith in India.
Several states impose prohibitions on beef slaughter and consumption. In some rural areas, cow protection vigilantes have attacked people suspected of selling, consuming, or possessing beef or items made with cowhide.
Avoid consuming beef or its derived products while in India.
Religious proselytism
In certain states, it’s illegal to engage in religious proselytism, such as preaching, possessing, or distributing religious literature or material with the intent of converting. Indian authorities require foreign missionaries to obtain a missionary visa.
If you plan to conduct religious activities in India, ensure that:
- the activities are legal
- you possess the proper visa for the activities you plan to perform
Satellite devices
It’s illegal to carry or use a satellite device in India.
Photography
It is prohibited to take pictures of military installations, airports and dams.
Ask permission before photographing places of worship such as temples or mosques.
Imports and exports
There are strict regulations on the importation or exportation of items such as:
- antiquities
- electronic equipment
- local currency
- ivory and gold objects
- protected animals
- pornographic material
Among others, you must register antique items for export with local police, with a photograph of each item.
Customs Guide for Travellers - India’s Central Board of Excise and Customs
Dress and behaviour
India is a traditional, conservative and multi-faith society. To avoid offending local sensitivities:
- Dress conservatively
- Behave discreetly
- Respect religious and social traditions
- Avoid displays of affection in public
- Avoid using footwear in places of worship
Indian family law is very different from Canadian law.
In case of dispute, consult a local lawyer to be fully aware of local laws regarding marital fraud, dowry abuse or extortion, custody, guardianship and visitation rights. Individuals facing charges may be forced to remain in India until their cases have been settled or charges dismissed.
Commercial surrogacy
If you’re planning to visit India to commission surrogacy arrangements, you should consider the potential challenges involved in pursuing international surrogacy. Seek specialist legal advice on Indian and Canadian laws before making any arrangements.
A proposed Indian government ban on foreign commercial surrogacy could affect Canadians travelling to India to enter into a surrogacy agreement.
You should also consult with Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) on current policies regarding citizenship through descent and the issuance of Canadian travel documents.
Land and property disputes
If you plan on buying property or are involved in a land dispute in India, you should seek legal advice. Do so before making commitments. Related disputes could take time and be costly to resolve.
The offices of the Government of Canada in India can’t provide assistance or legal advice related to private legal matters.
2SLGBTQI+ travellers
Indian law doesn’t criminalize sexual acts or relationships between persons of the same sex.
However, 2SLGBTQI+ travellers could be discriminated against based on their sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, or sex characteristics.
Travel and your sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics
Dual citizenship is not legally recognized in India.
If local authorities consider you a citizen of India, they may refuse to grant you access to Canadian consular services. This will prevent us from providing you with those services.
Travellers with dual citizenship
International Child Abduction
The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction is an international treaty. It can help parents with the return of children who have been removed to or retained in certain countries in violation of custody rights. It does not apply between Canada and India.
If your child was wrongfully taken to, or is being held in India by an abducting parent:
- act as quickly as you can
- consult a lawyer in Canada and in India to explore all the legal options for the return of your child
- report the situation to the nearest Canadian government office abroad or to the Vulnerable Children's Consular Unit at Global Affairs Canada by calling the Emergency Watch and Response Centre
If your child was removed from a country other than Canada, consult a lawyer to determine if The Hague Convention applies.
Be aware that Canadian consular officials cannot interfere in private legal matters or in another country's judicial affairs.
- International Child Abductions: A guide for affected parents
- Canadian embassies and consulates by destination
- Request emergency assistance
Identification
You must carry your passport and Indian visa at all times.
Traffic drives on the left.
You must carry an international driving permit.
International Driving Permit
The currency in India is the Indian Rupee (INR).
Non-residents are prohibited from importing or exporting the Indian rupee. A limit of 25,000 rupees is imposed on residents.
Upon entering or leaving India, you must make a declaration to customs if you have USD 5,000 or more, or the equivalent in other currencies.
India is prone to extreme weather events such as:
- dust storms
- earthquakes
Extreme temperatures can occur in both spring and summer.
The rainy (or monsoon) season extends from June to September.
Heavy rain can cause flooding throughout the country, resulting in significant loss of life and extensive damage to infrastructure. Seasonal flooding and landslides can hamper overland travel and reduce the provision of essential services. Roads may become impassable and bridges damaged.
India’s coastline is subject to cyclones, particularly between April and December. These severe storms can put you at risk and hamper the provision of essential services.
If you decide to travel to a coastal area:
- know that you may expose yourself to serious safety risks
- be prepared to change your travel plans on short notice, including cutting short or cancelling your trip
- stay informed of the latest regional weather forecasts
- carry emergency contact information for your airline or tour operator
- follow the advice and instructions of local authorities
- Tornadoes, cyclones, hurricanes, typhoons and monsoons
- Large-scale emergencies abroad
- Weather forecasts and warnings - Indian Meteorological Department
- Current cyclone activity - Tropical storm risk
Seismic activity
Parts of India are located in active seismic zones. Earthquakes occur.
In the event of an earthquake, follow the instructions of local authorities.
What to do during an earthquake
Air pollution
Smoke haze and other types of air pollution can be extremely hazardous in urban areas and cities such as Delhi. It’s typically at its worst in winter. In rural areas, air quality can be affected by agricultural burning.
Dust storms also occur across northern India.
Monitor air pollution levels, which change quickly, especially if you suffer from respiratory ailments or have pre-existing medical conditions.
During periods of high pollution:
- limit your activities outdoors
- monitor local media
- System of Air Quality Weather Forecasting and Research - Ministry of Earth Science of India
- Real time ambient air quality data - Delhi Pollution Control Committee
- Air pollution in India - World Air Quality Index
In mountainous regions, avalanches present a risk and have resulted in fatalities.
- Monitor local media and weather forecasts
- Follow the advice of local authorities
Local services
In case of emergency, dial:
- police: 100/112 from cellular telephones
- firefighters: 101
- medical assistance: 102
- victims of sexual harassment: 1091
General services
The Indian Ministry of Tourism offers 24-hour general advice for tourists.
Dial: 1-800 111-363.
Consular assistance
The Consulates General of Canada in Bengaluru, Chandigarh and Mumbai are temporarily suspending in-person operations. You can obtain consular assistance and further consular information from the High Commission of Canada in New Delhi.
Consular services in person remain available at the High Commission of Canada in New Delhi.
Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chandigarh, Chhattisgarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Delhi, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Pondicherry, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
For emergency consular assistance, call the High Commission of Canada in India, in New Delhi and follow the instructions. At any time, you may also contact the Emergency Watch and Response Centre in Ottawa.
The decision to travel is your choice and you are responsible for your personal safety abroad. We take the safety and security of Canadians abroad very seriously and provide credible and timely information in our Travel Advice to enable you to make well-informed decisions regarding your travel abroad.
The content on this page is provided for information only. While we make every effort to give you correct information, it is provided on an "as is" basis without warranty of any kind, expressed or implied. The Government of Canada does not assume responsibility and will not be liable for any damages in connection to the information provided.
If you need consular assistance while abroad, we will make every effort to help you. However, there may be constraints that will limit the ability of the Government of Canada to provide services.
Learn more about consular services .
Risk Levels
take normal security precautions.
Take similar precautions to those you would take in Canada.
Exercise a high degree of caution
There are certain safety and security concerns or the situation could change quickly. Be very cautious at all times, monitor local media and follow the instructions of local authorities.
IMPORTANT: The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk.
Avoid non-essential travel
Your safety and security could be at risk. You should think about your need to travel to this country, territory or region based on family or business requirements, knowledge of or familiarity with the region, and other factors. If you are already there, think about whether you really need to be there. If you do not need to be there, you should think about leaving.
Avoid all travel
You should not travel to this country, territory or region. Your personal safety and security are at great risk. If you are already there, you should think about leaving if it is safe to do so.
22 things you need to know before visiting India

Dec 15, 2023 • 14 min read

India is a feast for the senses and we've got everything you need to know before you visit © Andrii Lutsyk / Ascent Xmedia / Getty Images
India is a place that overwhelms your senses in the best possible way – nowhere else delivers quite the same barrage of sights, sounds and sensations as this continent-sized country at the heart of Asia.
It would take a lifetime to see all of India , let alone understand every nuance and facet of this nation of 1.4 billion inhabitants. But with a little preparation, you can learn to navigate the richness of this country, from its snow-capped peaks and velvety beaches to its historic temples and luxuriant palaces.
We've collated the top things you need to know about visiting India, but the journey begins before you leave home. Apply for your Indian visa online for a smooth arrival on the subcontinent. Read on for 22 more insider tips that will help make your vacation unforgettable.
1. Plan your trip around the seasons
India has a reputation for being hot and humid, but with beaches, mountains, hills, coastlines and plains all jammed into a relatively small geographical area, the climate is quite diverse. The southwest monsoon brings rainy weather to most of the country from June to September, but this is the best time of year to visit the high-altitude deserts of Ladakh , although depending on the route you take, you risk encountering landslides and floods.
In the far south, there’s also a milder rainy season from October to December. The ideal weather window for travel is from October to May, though temperatures and humidity climb to agonizing levels from March onwards in the run-up to the monsoon. If you find yourself in India in the spring, head to the Himalayan foothills for milder temperatures and good trekking conditions.
2. Get your jabs before you travel
There is no official requirement for vaccinations to enter India (although yellow fever vaccination is needed if you are traveling from a country where the disease is endemic).
That said, it is important that you contact a health professional at least eight weeks before you travel to ensure your jabs are up to date. Vaccinations for diphtheria and tetanus, hepatitis A and B, polio and typhoid are usually recommended, on top of childhood vaccinations for measles, mumps, rubella and varicella.
Vaccinations worth considering for longer trips include Japanese B encephalitis, meningitis and rabies. Monkeys, dogs and cats can all carry the rabies parasite, and infection is fatal if untreated.

3. Take malaria precautions
Depending on where in India you are traveling to, you may want to speak to your healthcare provider about taking a course of anti-malarial tablets. For instance, northeastern and eastern parts of India, as well as the city of Mangalore, have a higher malaria risk.
Always take precautions to avoid mosquito bites – this will also help you avoid dengue fever, a viral infection that is transmitted by mosquitoes to humans. Sleeping under a mosquito net, wearing long sleeves and trousers in light colors, and using a repellent and/or a plug-in mosquito killer with a high concentration of DEET (diethyltoluamide) is advisable.
4. Get insured
Travel insurance is essential for India. Depending on where you travel to, you may find public hospitals are poorly equipped. Additionally, most private clinics and hospitals require payment ahead of treatment. Make sure you are covered for emergency evacuation and also for any adventure activities you plan to get involved in.
If you’re unlucky enough to be a victim of crime, contact the local police station or dial 100 or 112, the national emergency number. You’ll need to get the police to file a report (a “FIR" – First Information Report) to make a claim on your travel insurance.
5. Book ahead for busy times and festivals
India can get very busy from November to February, so affordable accommodation is usually swamped in peak season. It’s a good idea to book ahead, either directly with the venues or via booking aggregator sites such as Agoda and MakeMyTrip .
Also, book train tickets in advance where possible , particularly for popular routes. Tickets can be booked (with a fair amount of hassle) via the government booking site IRCTC or more easily through local booking sites such as 12Go or Cleartrip .
6. Plan your comms before you travel
Many things in India (including train bookings or ordering food online) get easier if you have a local SIM card. Bring an unlocked phone from home (or pick one up locally) and get a phone shop to sign you up for a local pay-as-you-go SIM package on arrival. You’ll need to bring passport photos and photocopies of your passport ID pages to complete the application.

7. Check your lunar calendars
While India officially follows the Gregorian calendar, the major festivals for Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Islam and several other religions follow lunar calendars and fall on different dates from year to year. Always check festival dates before you book your trip (bearing in mind these dates are subject to change); the Indian government maintains a useful online list of public holidays .
8. Learn local etiquette
English is the lingua franca in most metropolitan areas in India, and you’ll get away with polite hellos, goodbyes and thank yous in smaller towns too. However, if you’re traveling in northern India, you can say "namaste" (I bow to you) with your hands together in a prayer-like gesture in front of your chest. Similarly, when meeting Muslims in north India, you can say "salaam alaikum" (peace be with you) – the correct response is "alaikum salaam." Most of the time, it’s the effort that’s welcomed over pronunciation, so don’t be shy!
Shaking hands is a standard business greeting between men, but outside metropolitan regions, men and women rarely shake. Only ever use your right hand. The same rule applies when passing things to people – including money.
If you get invited to someone’s home, bring a small gift (flowers or sweets are always a safe bet) and remove your shoes before entering. It’s polite to eat and drink what you are offered, even if you don’t really fancy it.
9. Dress modestly
Depending on where in India you are, modesty is taken seriously – especially for women. Travelers of any gender will have an easier time if they wear loose-fitting clothing that covers their legs and arms. Swimwear is only appropriate for the beach – although it is not uncommon to see locals swim fully clothed. To fit in, consider investing in a kurta pyjama (a traditional garment resembling a long shirt and loose trousers for men) or a salwar kameez (a long shirt, loose trousers and scarf for women).
10. What to eat and how to eat it
Many religions in India have their own dietary rules. Muslims avoid pork, many Hindus avoid beef, and some Hindus and Buddhists are vegetarian or vegan. Many Jains are vegetarians who avoid some vegetables (most notably onions, garlic and potatoes) and who try to avoid causing harm to all living creatures. These rules mean vegan and vegetarian food is often easy to find in India.
Eating with your hands is the norm in many restaurants, particularly in parts of southern India. Take your cue from other patrons in the restaurant, and remember to eat with your right hand. Mix rice and curry into balls with your fingers and push it into your mouth with your thumb. Some thalis (plate meals consisting of multiple dishes served in tandem) are served not on a plate but on a washed and flash-heated banana leaf.
11. Haggling is not a game of life and death
Haggling for a fair price when buying things – in street stalls and open-air markets – is a way of life in India. Although it can sometimes be a frustrating experience, losing your temper is extremely bad form – if you can’t agree on a price with the vendor that you are both happy with, politely decline and shop somewhere else.
The rules of the game are as follows. The vendor will quote you a price that is more than the item is worth, then you’ll come back with a counter-offer, working up from there until you reach a mutually agreeable figure.
The “walking away” trick may bring a few last-minute adjustments, but before long, you’ll reach a threshold that the vendor won’t go below. Throwing in extra items may bring a discount on the overall cost. Many travelers prefer not to haggle in places where the money goes directly to artisans.

12. Respect etiquette at religious sites
Religion is taken very seriously in India, so it pays to know the rules and expectations for visits to temples, mosques, monasteries, gurdwaras (Sikh shrines), synagogues and churches. Always check if you are allowed to enter – some temples and mosques are closed to people who don’t follow the faith. Mosques may also be closed to visitors during prayers or on Fridays.
If asked to do so, remove your shoes before entering any religious building, and be prepared to cover your head with a scarf or shawl. Generally, always cover your legs and arms (a sarong can be handy as an emergency cover-all). Some temples also ban leather goods, and many religious sites do not allow photography.
Avoid pointing the soles of your feet towards a person or deity – this is considered disrespectful. The same goes for touching any person or effigy on the head. It is conventional to walk around Buddhist and Hindu shrines in a clockwise direction, in a ceremonial circuit known as a parikrama .
Making an offering or leaving a donation is often expected – locals always offer something, but be wary of people waving receipts showing huge donations. Giving something is appropriate, but don’t feel pressured into leaving large sums.
13. Giving alms is common but up to you
The giving of alms has a long history in India, and foreigners can expect to be approached regularly with requests for money. Whether you give or not is a personal choice, but many Indians give on a daily basis, particularly when visiting temples and mosques. Be aware that some requests for money will be scams, and you may be able to do more good by giving your time or cash to charity or aid organizations you’ve taken time to research, rather than handing out cash.
14. Respect local social attitudes
India has complex social rules about respect for elders. Depending on where you are traveling to, older people are often greeted with the honorific “auntie” or “uncle,” and the ending ji may also be added to someone’s name as a sign of respect.
Outside bigger cities, India can be quite conservative when it comes to interactions between unmarried men and women. Also, most parts of India are conservative when it comes to same-sex relationships. Whatever your sexuality, it’s best to avoid public displays of affection.
15. Street harassment is unfortunately common
Although harassment can happen anywhere, parts of India are constantly in the news owing to a lack of women’s safety. Beyond long, unwelcome stares and persistent attempts to start a conversation, more serious assaults are also a risk. Groping is common in crowds (particularly during festivals).
Exercise caution like you would anywhere else, and remain alert. Never get into a taxi or auto rickshaw containing anyone other than the driver, and avoid walking alone in quiet areas, particularly at night. Decline offers of food or drinks from strangers.
If traveling by public transport as a woman, it's best to seek out train carriages and designated seating reserved for women. Wearing a wedding ring (even if not married) and using dark sunglasses and headphones can buy you some privacy on public transport. If you are being hassled, drawing loud attention to the intrusion may encourage others to come to your aid.
16. Keep track of security situations in India
India has seen deadly attacks by separatist and Marxist groups and Kashmiri insurgents. Monitor the local news and be alert for suspicious behavior, particularly around major tourist sites. Always check the security situation before traveling to Srinagar and the Kashmir Valley in case of flare-ups of unrest. Strikes, demonstrations and protests are also best avoided, as violence is a risk. It goes without saying but in the event of trouble, obey local curfews and stay inside – your hotel is probably the safest place to be.

17. Take the altitude seriously when hiking
Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) is a risk when traveling above 2500m (8202ft), which covers most of the Indian Himalayas . AMS can be fatal, so always ascend slowly and take rest days to allow your body to acclimate to significant elevation changes. If you begin to feel ill while hiking in the mountains, stop, and if your symptoms don’t improve, descend immediately.
18. Familiarize yourself with local rules and regulations
India has a few laws and regulations that visitors might be unfamiliar with. For instance, taking photographs of bridges, the periphery of military camps and border crossings – or flying drones over them – is considered a serious security issue.
When traveling by plane internally in India, you may be asked to surrender batteries from devices in your cabin bags. Smoking is banned in most public places, and a few states also have bans on the consumption of beef – killing or injuring a cow in a road accident, even accidentally, can lead to violent reprisals.
To avoid sticky situations, take the time to research where you’re going, and talk to staff at your hotel or hostel or your B&B host for advice on things to be aware of.
19. Steer clear of drugs
India may have a reputation amongst travelers as a place to push boundaries, but its drug laws are strict. Possessing even small amounts of drugs for personal use can lead to a prison sentence.
Some religious groups are permitted to consume marijuana for ceremonial purposes, but that often doesn’t extend to tourists. You can, however, find bhaang – a marijuana mixture made with the leaves (rather than the bud) of the cannabis plant – at government-approved bhaang shops.
20. Avoid the tap water
The tap water in India is not potable. Drinking or brushing your teeth with it can be a fast track to stomach troubles – the most common illness tourists experience in India. Stick to purified or bottled water (or even better, purify your own to avoid contributing to India’s plastic waste mountain).
The water rule extends to ice (be wary of ice in drinks and ice cream) and to uncooked foods, particularly salads and dishes such as coriander chutneys, which may have been washed with contaminated water. When eating fruit, stick to things you can peel or wash thoroughly yourself, and be cautious of freshly prepared juices. Hot drinks are generally fine, so drink your fill of chai (milky tea, often spiced and sweet).

21. Watch local news to keep track of natural disasters
Some geographical areas in India are prone to natural disasters, and the risk is higher in certain seasons. Hilly areas of Himachal Pradesh, for instance, often see flash flooding and landslides during the monsoon. Be alert to signs of natural disasters and keep an eye on the local news so you know which areas to avoid. Follow the Indian Meteorological Department’s website as well as their social media handle for timely updates.
If you are caught up in a natural disaster, follow the advice of emergency workers and try to leave the area quickly.
22. Spot the scams
India has a reputation for scams designed to separate tourists from their money, and touts and confidence tricksters can often be found where tourists gather. Get tourist information and make bookings at official offices, rather than “tourist offices” you have been led to by people offering unsolicited help.
If anyone steers you to a hotel, shop or other establishment without you asking, they may be angling for a commission, which will be added to the price you pay. Be dubious of claims that the place you want to go is “closed” – always check yourself to be sure.
Exercise common sense and be wary of deals that sound too good to be true – for example, the gem scam, where travelers are tricked into buying worthless gems to “sell at a profit back home.”
This article was first published Mar 19, 2022 and updated Dec 15, 2023.
Explore related stories

Destination Practicalities
Jun 26, 2024 • 9 min read
Discover Nepal's Terai, a lush paradise of vibrant culture, fertile lands, and breathtaking biodiversity. Here's what you need to know before you go.

May 31, 2024 • 6 min read

May 29, 2024 • 8 min read

May 28, 2024 • 9 min read

Jan 11, 2024 • 4 min read

Jan 5, 2024 • 20 min read

Jan 2, 2024 • 8 min read

Dec 27, 2023 • 8 min read

Dec 20, 2023 • 11 min read

Dec 13, 2023 • 7 min read
India’s Next Budget: What Travel Executives Want
Bulbul Dhawan , Skift
July 5th, 2024 at 11:00 PM EDT
Earlier this year, the Indian government gave a boost to the tourism budget for development, but cut down the global promotion allocation by 97%. Now, as the final Budget is around the corner, the industry is hoping for a more significant resolution to its challenges.
Bulbul Dhawan
In February, the Indian government had allocated INR 24.5 billion ($293 million) to the tourism sector as part of the interim budget, a slight increase from the prior year’s initial allocation of INR 24 billion ($290 million). But the Union Budget also reduced the global promotion allocation by a staggering 97% to just INR 30 million ($361,000).
The reduction came even as there have been significant efforts to upgrade and develop destinations across the country and travel makes up a bigger part of the Indian economy: A total contribution of about $200 billion, or just over 6% to the country’s GDP, according to the India Brand Equity Foundation (IBEF). The government wants to increase this contribution to 10% .
The recent elections saw the return of Modi as Prime Minister, but the government in power is a coalition one with a budget to be presented later this month.
Skift spoke to travel executives to better understand what they want out of the budget and government policy:
They Want ‘Industry Status’
Travel companies have long wanted “industry status” for tourism, a recognition at the state-level that gives the opportunity for better property tax calculations, benefits in land allocations, energy costs, and other government benefits.
Some states have already granted the industry status, including Assam, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Gujarat, but the hope is for it to be broader.
“Recognizing tourism as a sustainable engine for economic growth and development, it is imperative to accord industry status to the travel and tourism sector, which will help in the regularization of policies and processes,” said Amit Jain, founder of travel company MagicFares.
GST: One Rate for Hotel Taxes
At present, the hotel rooms are taxed on a tiered basis under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
“The tiered GST based on hotel room tariffs can lead to price disparities as hotels adjust room rates based on demand and peak season rates. For example, a room night costing INR 10,000 ($120) falls under the 18% GST rate, while an off-season rate of INR 7,000 ($84) falls under the 12% GST rate. We urge the government to consider a uniform GST rate of 12% on hotels,” said Rajesh Magow, Co-founder and Group CEO, MakeMyTrip.
The Hotel Association of India (HAI) has also sought the lowering of GST rate from the current 18%.
Streamlined Registrations for OTAs
According to Magow, online travel companies in the country are facing challenges in obtaining required registrations under the GST regime.
“The current regulation compels OTAs to establish a physical presence in each state even when it is not required, leading to high administrative costs. Allowing OTAs to register in states through their central head office would significantly alleviate these burdens, streamline operations, and enhance efficiency. Furthermore, this requirement puts domestic OTAs at a disadvantage compared to international competitors who are not subjected to similar regulations,” he said.
Magow has also called for removal of disparities between ecommerce operators and ecommerce suppliers within the domestic market. “Currently, a customer pays a 5% GST charge when booking a non-AC bus through an ecommerce platform. This charge is zero for a direct booking from bus operator irrespective whether it is done in online or offline mode.”
Infrastructure Status for Hotels
The hospitality sector has often complained about high taxes, and expensive and cumbersome rules for licenses. Infrastructure status for hotels will allow them access to softer finances at better interest rates with longer periods for re-payment thereby attracting investment.
“The hospitality sector is capital intensive and requires substantial investments. Our long-standing demand for infrastructure status and industry benefits at the state level will provide advantages such as lower utility tariffs, reduced property taxes, easier access to finance, and softer loans. These are crucial for reducing the cost of doing business, ensuring the long-term viability of the sector,” said Sanjay Sethi, MD and CEO, Chalet Hotels Limited.
Boosting Sustainability
There has been overcrowding of popular tourist destinations across the country, prompting Tamil Nadu , Madhya Pradesh , and Uttarakhand, to look at measures curbing this issue.
Magow has urged the government to encourage corporations to invest in developing and improving tourist destinations as part of a corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiative.
“A weighted deduction under income tax and under GST on CSR funds deployed to improve tourist destinations will garner larger participation from the private sector. Such a symbiotic relationship not only helps preserve tourist sites but also ensures all-around sustainable development,” he said.
He further called for tax incentives to hotels and homestays adopting sustainable practices aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, particularly SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and SDG 13 (Climate Action).
Skift India Report
India is booming. Discover the subcontinent’s most important travel news here every Tuesday-Thursday.
Have a confidential tip for Skift? Get in touch
Tags: chalet hotels , easemytrip , hotel rates , hotels , india , india budget , india travel , makemytrip , online travel companies , otas , tourism , tourism tax
Photo credit: Travel and tourism are two of the largest industries in India, with a total contribution of about $199.6 billion to the country's GDP. Banita Tour / Pixabay

Countries, economies and regions
Select a country, economy or region to find embassies, country briefs, economic fact sheets, trade agreements, aid programs, information on sanctions and more.
International relations
Global security.
- Australia and sanctions
- Australian Safeguards and Non-proliferation Office (ASNO)
- Counter-terrorism
- Non-proliferation, disarmament and arms control
- Peacekeeping and peacebuilding
Regional architecture
- Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- East Asia Summit (EAS)
- Australia and the Indian Ocean region
- Pacific Islands regional organisations
Global themes
- Child protection
- Climate change
- Cyber affairs and critical technology
- Disability Equity and Rights
- Gender equality
- Human rights
- Indigenous peoples
- People Smuggling, Human Trafficking and Modern Slavery
- Preventing Sexual Exploitation, Abuse and Harassment
- Australia’s treaty-making process
International organisations
- The Commonwealth of Nations
- United Nations (UN)
- World Trade Organization
Foreign Arrangements Scheme
Trade and investment, about free trade agreements (ftas).
- The benefits of FTAs
- How to get free trade agreement tariff cuts
- Look up FTA tariffs and services market access - DFAT FTA Portal
- Discussion paper on potential modernisation – DFAT FTA Portal
About foreign investment
- The benefits of foreign investment
- Investor-state dispute settlement (ISDS)
- Australia's bilateral investment treaties
- Australia's foreign investment policy
For Australian business
- Addressing non-tariff trade barriers
Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai
Stakeholder engagement.
- Ministerial Council on Trade and Investment
- Trade 2040 Taskforce
- First Nations trade
Australia's free trade agreements (FTAs)
- ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand (AANZFTA)
- Chile (ACLFTA)
- China (ChAFTA)
- Hong Kong ( A-HKFTA & IA)
- India (AI-ECTA)
- Indonesia (IA-CEPA)
- Japan (JAEPA)
- Korea (KAFTA)
- Malaysia (MAFTA)
- New Zealand (ANZCERTA)
- Peru (PAFTA)
- Singapore (SAFTA)
- Thailand (TAFTA)
- United Kingdom (A-UKFTA)
- USA (AUSFTA)
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)
- European Union (A-EUFTA)
- India (AI-CECA)
- Australia-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement
- Australia-Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Trade and investment data, information and publications
- Fact sheets for countries and regions
- Australia's trade balance
- Trade statistics
- Foreign investment statistics
- Trade and investment publications
- Australia's Trade through Time
WTO, G20, OECD, APEC and IPEF and ITAG
Services and digital trade.
- Service trade policy
- Australia-Singapore Digital Economy Agreement
- Digital trade & the digital economy
Development
Australia’s development program, performance assessment.
- Development evaluation
- Budget and statistical information
Who we work with
- Multilateral organisations
- Non-government organisations (NGOs)
- List of Australian accredited non-government organisations (NGOs)
Development topics
- Development issues
- Development sectors
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Sustainable Development Goals
Where we deliver our Development Program
Humanitarian action.
Where and how Australia provides emergency assistance.
People-to-people
Australia awards.
- Australia Awards Scholarships
- Australia Awards Fellowships
New Colombo Plan
- Scholarship program
- Mobility program
Public diplomacy
- Australian Cultural Diplomacy Grants Program
- Australia now
- UK/Australia Season 2021-22
Foundations, councils and institutes
- Australia-ASEAN Council
- Australia-India Council
- Australia-Indonesia Institute
- Australia-Japan Foundation
- Australia-Korea Foundation
- Council for Australian-Arab Relations (CAAR)
- Council on Australia Latin America Relations (COALAR)
International Labour Mobility
- Pacific Labour Mobility Scheme
- Agriculture Visa
Australian Volunteers Program
Supporting organisations in developing countries by matching them with skilled Australians.
Sports diplomacy
Australia is a successful global leader and innovator in sport.
A global platform for achievement, innovation, collaboration, and cooperation
About Australia
Australia is a stable, democratic and culturally diverse nation with a highly skilled workforce and one of the strongest performing economies in the world.
Australia in Brief publication
This is the 52nd edition of Australia in Brief, revised and updated in February 2021
Travel advice
To help Australians avoid difficulties overseas, we maintain travel advisories for more than 170 destinations.
- Smartraveller – travel advice
International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate
Prove your COVID-19 vaccinations when you travel overseas.
- Services Australia
The Australian Passport Office and its agents are committed to providing a secure, efficient and responsive passport service for Australia.
- Australian Passport Office
24-hour consular emergency helpline
- Within Australia: 1300 555 135
- Outside Australia: +61 2 6261 3305
- Getting help overseas
- Visas for Australians travelling overseas
- Visas to visit Australia
News, speeches and media
Quad senior officials’ meeting, 3 july 2024.
On 3 July, senior officials from Australia's Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, India’s Ministry of External Affairs, Japan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the US Department of State met by videoconference to review progress on initiatives agreed by Quad leaders at the 2023 Summit in Hiroshima.
At the meeting, officials discussed the significant, tangible contributions the Quad is delivering in the Indo-Pacific in 2024. The Quad is training the region’s infrastructure experts, enhancing health security, providing vital maritime domain awareness training and data, responding to climate change, countering terrorism and building resilience through undersea cable and telecommunications connectivity.
Officials exchanged views on regional and international challenges and reaffirmed the Quad’s support for ASEAN centrality, the Pacific Islands Forum and the Indian Ocean Rim Association.
Officials will continue regular consultation at all levels to further deepen the engagement and habits of cooperation that have been established between Quad foreign ministries and across our respective diplomatic networks.

Supreme Court reopens on July 8 after summer vacations; big cases to watch out for
A fter a seven-week break for summer vacations, the Supreme Court of India reopens on July 8, and the list of important cases before it where hearings and verdicts are pending is a long one.
From the NEET-UG paper leak , to the Hathras stampede , the bridge collapses in Bihar, Arvind Kejriwal's plea seeking quashing of arrest in the ED case, to the Constitution Bench judgment on the minority status of Aligarh Muslim University, and the hearing on misleading advertisements, to name a few, will be heard and decided by the top court.
Here's a brief round-up of the big cases before the Supreme Court:
NEET-UG PAPER LEAK
As soon as India's top court reopens, all eyes will be on the crucial hearing in the batch of petitions by students who have appeared in the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET-UG) and have sought re-test and proper investigation into the alleged paper leak. A top court bench headed by Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud is slated to hear the batch of petitions concerning NEET-UG 2024 on July 8. The NEET-UG 2024 was held on May 5 across 4,750 centres and around 24 lakh candidates appeared for the medical entrance exam.
HATHRAS STAMPEDE
The Supreme Court will hear the PIL filed by advocate Vishal Tiwari regarding the stampede in Hathras, Uttar Pradesh. The plea has requested an investigation by a 5-member expert committee under the supervision of a retired judge of the Supreme Court. The petition has also requested legal action against the people and officials responsible for the incident. In the petition, an appeal has been made to lay down the guidelines for organising such large religious gatherings.
BIHAR BRIDGE COLLAPSE
The top court will also hear a public interest Litigation (PIL) seeking a direction to the Bihar government to conduct proper structural audit of all existing bridges and under-construction bridges and to demolish or retrofit weak structures. Nine bridges have collapsed in the last 15 days in the rain-affected state. The plea filed by Brajesh Singh sought the setting up of a high-level expert committee to examine all bridges.
BIHAR GOVERNMENT PLEA ON 65 PC QUOTA
The Supreme Court will hear the plea filed by the Bihar government that has challenged the Patna High Court judgment that set aside the increase in reservations for Backward Classes from 50 per cent to 65 per cent in government jobs and educational institutions.
The Patna High Court had scrapped the Nitish Kumar government's decision to hike reservations for backward classes, scheduled castes and scheduled tribes from 50 to 65 per cent. After the caste-based survey report, the Bihar government had in November last year raised the quota for the deprived classes in government jobs and educational institutions. The high court had struck down the amendments passed by the Bihar Assembly in 2023, saying that they are beyond the powers of the Constitution and violate the equality clause under Articles 14, 15, and 16 of the Constitution.
KEJRIWAL PLEA IN ED CASE
The Supreme Court is likely to deliver its verdict on the plea filed by Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal, challenging his arrest by the Enforcement Directorate (ED) in the Delhi excise policy case in the coming days. A bench of Justices Sanjiv Khanna and Dipankar Datta had reserved the judgment on May 17.
MINORITY STATUS FOR AMU
A seven-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court had reserved its judgment in February on the minority status of Aligarh Muslim University. The court will pronounce its order in the coming days to decide if AMU enjoys a minority status under Article 30 of the Constitution of India. Article 30 of the Constitution provides that all minorities, whether based on religion or language, shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
SAME-SEX MARRIAGE REVIEW PLEAS
On July 10, the Supreme Court will reconsider in chambers the batch of review petitions challenging the Constitution Bench verdict in the same-sex marriage case.
EXCLUSION OF MARITAL RAPE IN NEW LAWS
The top court will also hear a petition challenging the exclusion of marital rape in the New Criminal Laws. The petition has been filed by the All India Democratic Women's Association (AIDWA).
SPECIAL LOK ADALAT IN SUPREME COURT
A special Lok Adalat will be organised by the Supreme Court of India from July 29 to August 3 for litigants to get their disputes resolved amicably and speedily.
WHAT'S NEW FOR LAWYERS / LITIGANTS?
During the seven-week break, the Supreme Court undertook several structural changes, including air-conditioned corridors for lawyers and litigants, portacabin waiting rooms on either side of the CJI court and a huge underground water tank being built in the lawn area.
Watch Live TV in English
Watch Live TV in Hindi

India, China foreign ministers agree to work on border issues
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Tanvi Mehta Additional reporting by Ryan Woo in Beijing Editing by Sudipto Ganguly, Raju Gopalakrishnan and Frances Kerry
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab
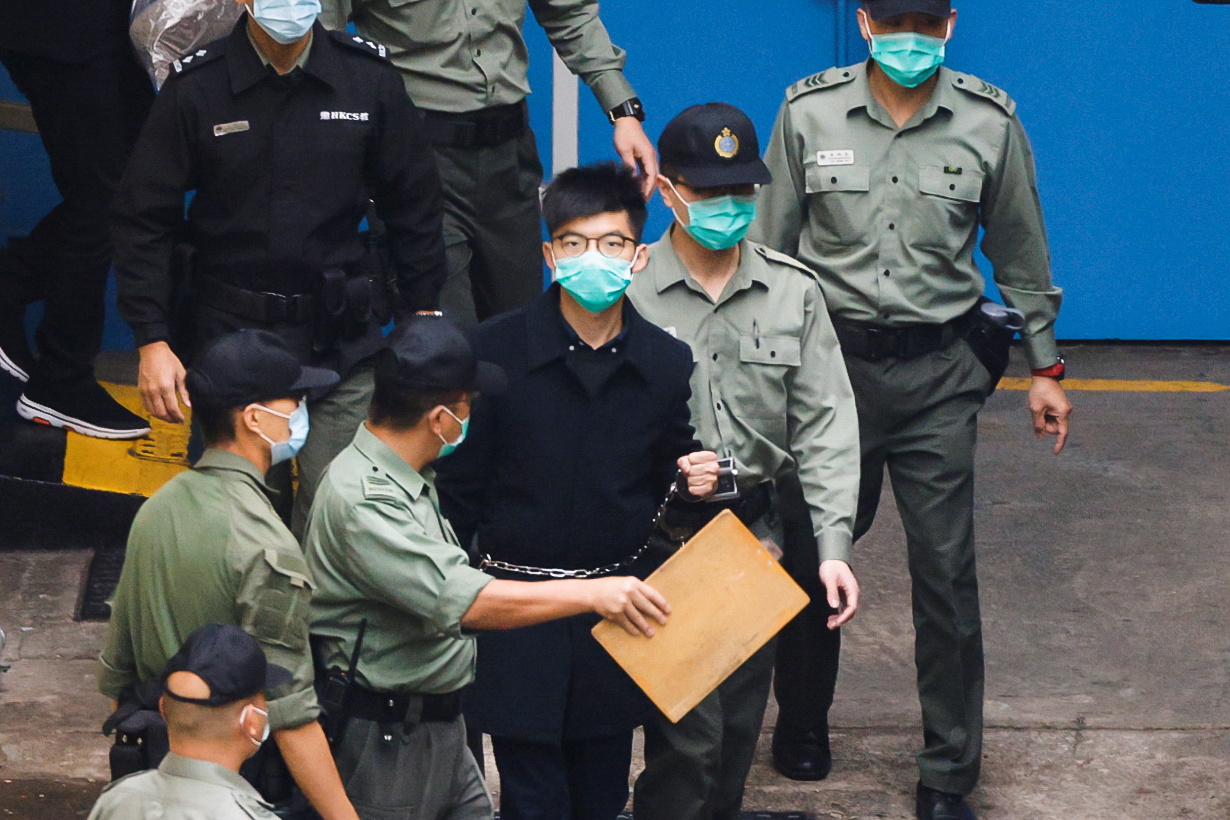

World Chevron
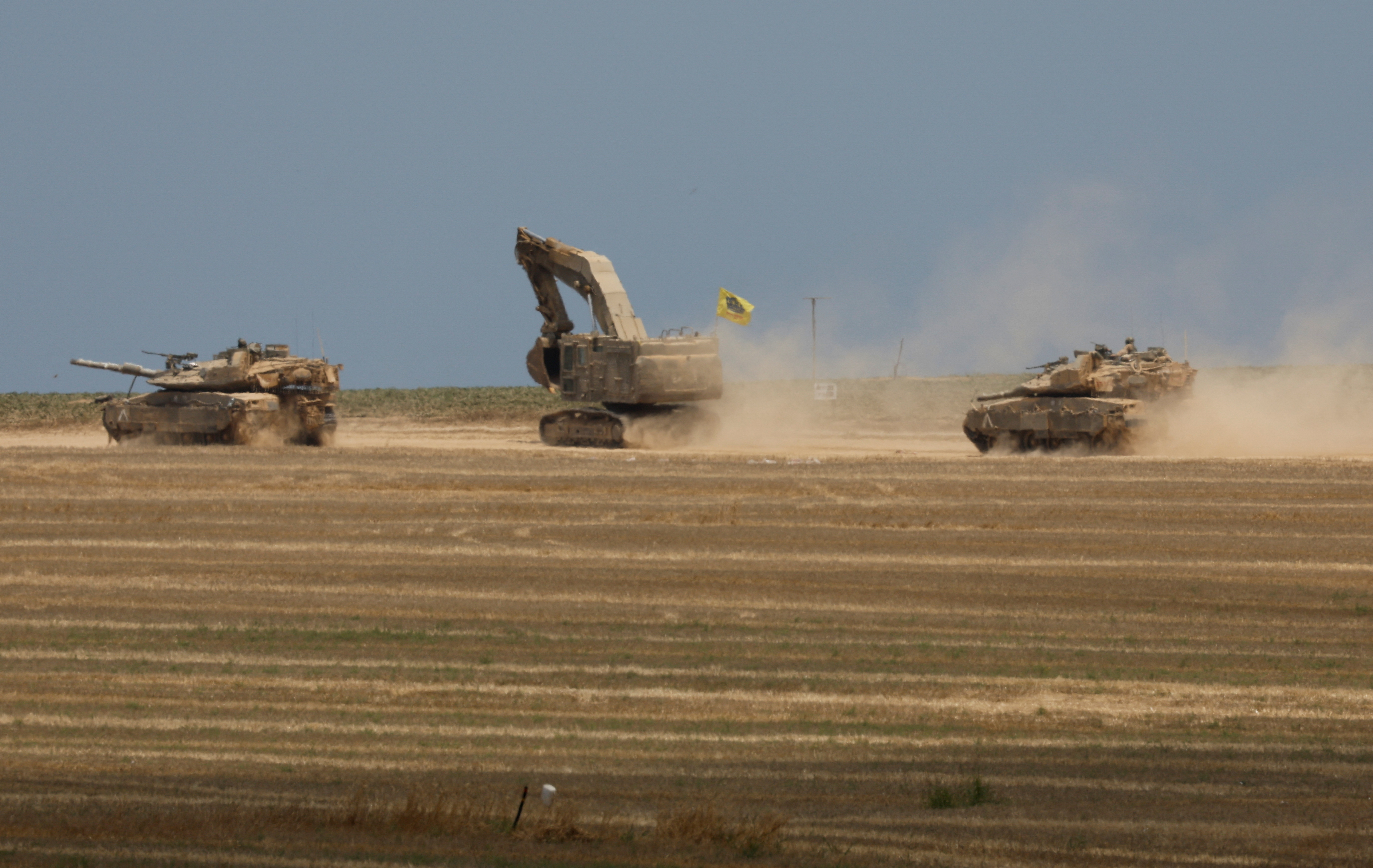

Hamas agrees to proposal on talks to free Israeli hostages 16 days after first phase, Hamas source says
Hamas has accepted a U.S. proposal to begin talks on releasing Israeli hostages, including soldiers and men, 16 days after the first phase of an agreement aimed at ending the Gaza war, a senior Hamas source said on Saturday.
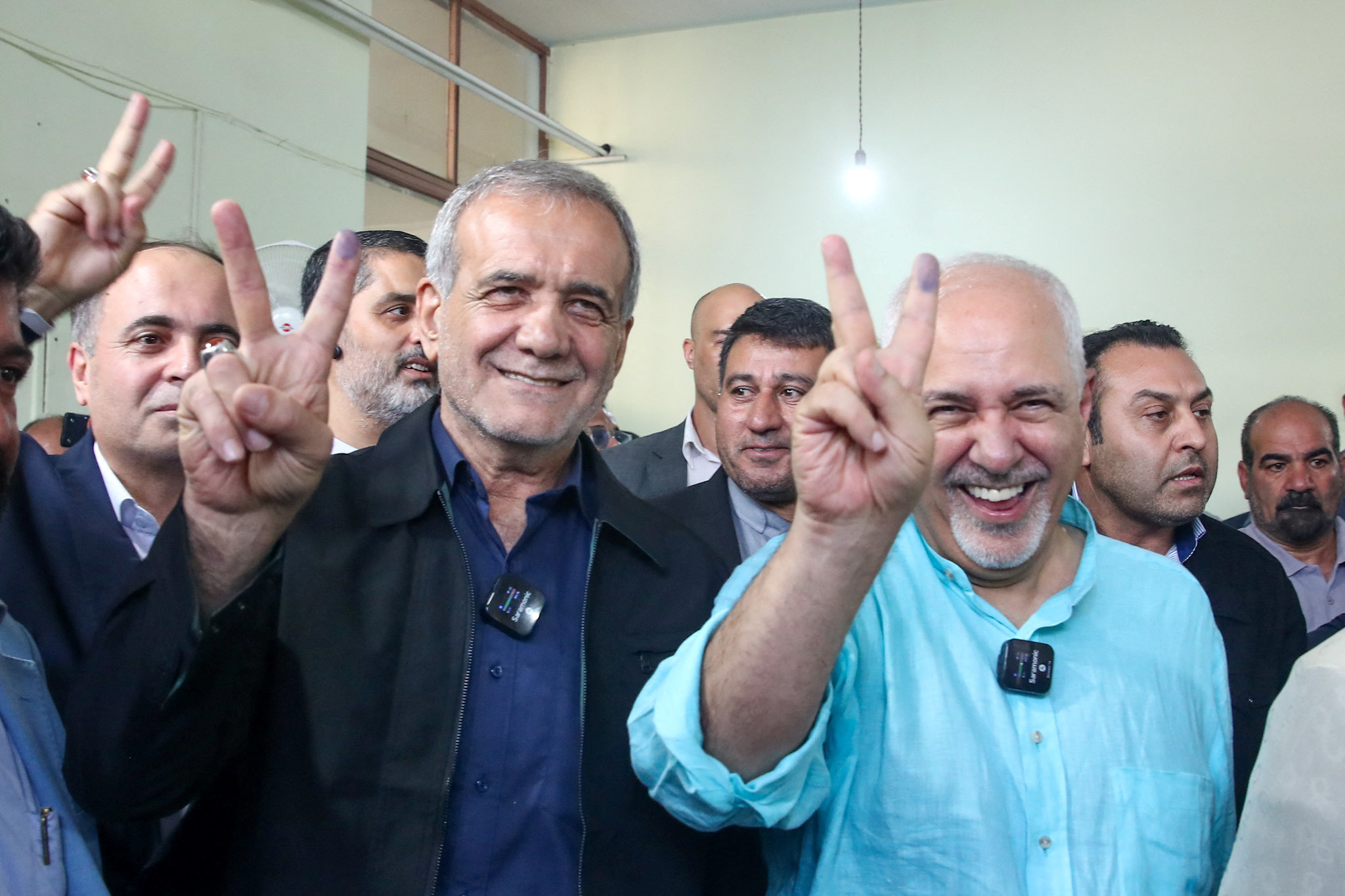

Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
beta This is a test version of the layout of this page. Take the survey to help us improve it
- Help and services around the world
- UK help and services in India
Travelling to India
Includes travel advice and how to get married abroad.
Subscriptions
- Get emails for this topic Travelling to India
Getting married or registering a civil partnership abroad
Requirements, paperwork and processes for weddings and civil partnerships overseas - registration, restrictions, fees
India travel advice
Latest FCDO travel advice for India including on entry requirements, safety and security and local laws and customs.
Reduce your risk from terrorism while abroad
How to minimise your risk, and what to do if there's a terrorist attack.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

COMMENTS
Travel Advisory. June 23, 2023. India - Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution. O U T C. Reissued with updates to health information. Exercise increased caution in India due to crime and terrorism. Do not travel to: The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (except the eastern Ladakh region and its capital, Leh) due to terrorism and civil unrest ...
Call us in Washington, D.C. at 1-888-407-4747 (toll-free in the United States and Canada) or 1-202-501-4444 (from all other countries) from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Standard Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays). See the State Department's travel website for the Worldwide Caution and Travel Advisories.
FCDO advises against all but essential travel to the state of Manipur. In April-May 2023 violent ethnic clashes broke out across Manipur, including in the state capital Imphal. Curfews and other ...
Website of Indian Institute of Tourism and Travel Management. National Portal of India provides a single-window access to information and services that are electronically delivered from all Government Departments, Institutions and Organizations. It has been a popular source of information to a wide range of stakeholders - from citizens, to ...
COVID-19, Guidelines for International Arrivals, For latest guidelines for international arrivals, Ministry of External Affair, Government of India
Passport validity requirements. Make sure your passport is valid for at least 6 months from your date of entry into India. Your passport must also: - have 2 blank pages for your visa. Check with ...
Website Content Managed by Ministry of Tourism, Government of India Designed, Developed and Hosted by National Informatics Centre ( NIC ) Last Update : 02-07-2024Ministry of Tourism, Government of India Designed, Developed and Hosted by National Informatics Centre ( NIC ) Last Update : 02-07-2024
Government of India, through concerned airlines before they are allowed to undertake the journey that they would abide by the decision of the appropriate government authority any post arrival requirement to undergo home/institutional quarantine/ self-health monitoring, as warranted. A.2. Before Boarding iii.
Travel Advisories . Guidelines for International Arrivals (updated on 19th July 2023) - Source : mohfw.gov.in . Facebook ... This website belongs to MyGov, Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India. Platform is designed, developed and hosted by National Informatics Centre.
National Portal of India provides a single-window access to information and services that are electronically delivered from all Government Departments, Institutions and Organizations. It has been a popular source of information to a wide range of stakeholders - from citizens, to government, business and Indian Diasporas. It is a gateway to access Indian Government websites at Centre, State and ...
Visa Classification: The type of nonimmigrant visa you are applying for. Fee: The reciprocity fee, also known as the visa issuance fee, you must pay. This fee is in addition to the nonimmigrant visa application fee (MRV fee). Number of Entries: The number of times you may seek entry into the United States with that visa. "M" means multiple times.
The Indian government issued the latest advisory guidance for international travel to India that mandates all travellers to undergo home quarantine for seven days and undertake an RT-PCR test on ...
Travel during daylight hours only, especially in rural areas. If you choose to drive a vehicle in India, learn the local traffic laws and have the proper paperwork. Get any driving permits and insurance you may need. Get an International Driving Permit (IDP). Carry the IDP and a US-issued driver's license at all times.
Travel advisory for Iran and Israel. April 12, 2024. Advisory for Indian nationals traveling abroad. July 08, 2020. Government of India Ministry of Health & FW Additional Travel Advisory for Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) (March 16, 2020) March 16, 2020. Travel Advisory for Indian nationals travelling to Iraq. February 18, 2020.
One of the oldest civilisations in the world, India is a mosaic of multicultural experiences. With a rich heritage and myriad attractions, the country is among the most popular tourist destinations in the world. It covers an area of 32, 87,263 sq. km, extending from the snow-covered Himalayan heights to the tropical rain forests of the south.
Serious sexual attacks involving both Indian and foreign nationals have been reported. British women have been victims of sexual assault, including rape, in Goa, Delhi, Rajasthan, Mumbai and ...
Authorized Portal for Visa Application to India Indianvisaonline.gov.in. All foreign nationals entering India are required to possess a valid international travel document in the form of a national passport with a valid visa from an Indian Mission/Post or eVisa (Limited Categories) from Bureau of Immigration, Ministry of Home Affairs.
See the Indian Government's Bureau of Immigration for advice. More information: Countries with a risk of yellow fever (PDF 152KB) Long-stay registration. If you plan to stay in India for more than 180 days and do not hold an OCI card, register within 14 days of arrival with the Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) in major cities.
Don't travel to India to obtain restitution after losing money to a scam. Overseas fraud. ... IMPORTANT:The two levels below are official Government of Canada Travel Advisories and are issued when the safety and security of Canadians travelling or living in the country or region may be at risk. Avoid non-essential travel
Tickets can be booked (with a fair amount of hassle) via the government booking site IRCTC or more easily through local booking sites such as 12Go or Cleartrip. 6. Plan your comms before you travel. Many things in India (including train bookings or ordering food online) get easier if you have a local SIM card.
Permits from the Government of India are needed for travel to Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and parts of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Apply at least 3 months in advance.
In February, the Indian government had allocated INR 24.5 billion ($293 million) to the tourism sector as part of the interim budget, a slight increase from the prior year's initial allocation ...
On 3 July, senior officials from Australia's Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, India's Ministry of External Affairs, Japan's Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the US Department of State met by videoconference to review progress on initiatives agreed by Quad leaders at the 2023 Summit in Hiroshima.
A fter a seven-week break for summer vacations, the Supreme Court of India reopens on July 8, and the list of important cases before it where hearings and verdicts are pending is a long one.
Latest FCDO travel advice for India including on entry requirements, safety and security and local laws and customs.
CNN has contacted India's Ministry of External Affairs for comment. The upcoming trip will be Modi's first to the country since 2019 and comes less than a month after he was narrowly re ...
India's Foreign Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar met his Chinese counterpart Wang Yi on Thursday in Kazakhstan where the two agreed to step up talks to resolve issues along their border, New Delhi ...
India travel advice. Latest FCDO travel advice for India including on entry requirements, safety and security and local laws and customs.