TRAPPIST-1: How Long Would It Take to Fly to 7-Planet System?
The discovery of seven Earth-size planets around a nearby star, TRAPPIST-1, is certainly exciting news. But what would it take to visit one of these potentially Earth-like alien worlds?
TRAPPIST-1 is 39 light-years away from Earth, or about 229 trillion miles (369 trillion kilometers). It would take 39 years to get to its current location traveling at the speed of light . But no spacecraft ever built can travel anywhere near that fast.
That said, people have sent some pretty fast vehicles into outer space. With today's technology, how long would it take to get to TRAPPIST-1 ?

Given a spacecraft's speed, calculating the amount of time it would take to travel to TRAPPIST-1's present location is simple. Because speed is equal to distance divided by time, the total travel time must equal the distance to TRAPPIST-1 (39 light-years) divided by the spacecraft's speed.

New Horizons
New Horizons, the fastest spacecraft ever launched, flew past Pluto in 2015 and is currently traveling out of the solar system at 14.31 kilometers per second, or about 32,000 mph, according to NASA's New Horizons tracking page . At this rate, it would take the Pluto probe about 817,000 years to travel the 39 light-years.
NASA's Juno spacecraft actually flew faster than New Horizons during its approach to the gas giant Jupiter in 2016. With the help of Jupiter's gravity, Juno hit a top speed of about 165,000 mph (265,000 km/h) relative to Earth, making it the fastest human-made object ever (though New Horizons' initial speed was faster than Juno's speed after launch).
Even if Juno were constantly traveling that fast — not just getting a speed boost en route — it would take the spacecraft 159,000 years to reach TRAPPIST-1's current location.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Voyager 1 , Earth's most distant spacecraft, left the solar system and entered interstellar space in 2012. According to NASA, it is currently speeding away at 38,200 mph. For Voyager 1 to travel 39 light-years, it would take the spacecraft 685,000 years.
But Voyager 1 isn't going there anytime soon, or ever. Instead, the spacecraft is heading for a different star , AC +79 3888: It will fly within 1.6 light-years of this star in about 40,000 years (NASA's calculation takes into account that the star is moving , also).
Space Shuttle
NASA's space shuttle traveled around the Earth at a maximum speed of about 17,500 mph (28,160 km/h). A spaceship traveling at this speed would take around 1.5 million years to get to TRAPPIST-1's current location.
So for a human mission to the TRAPPIST-1 solar system, the space shuttle would not be a practical mode of transportation.
Breakthrough Starshot
One ultrafast spacecraft that could reach TRAPPIST-1 in a much shorter time span is an interstellar mission advocated by Stephen Hawking, the Breakthrough Starshot initiative.
Hawking's tiny, laser-propelled probes could theoretically fly as fast as 20 percent of the speed of light, or 134 million mph (216 million km/h). That's about 4,000 times faster than NASA's record-breaking New Horizons spacecraft! A spacecraft that fast could travel 39 light-years in less than 200 years. But that concept has yet to leave the ground.

With today's technology, there's no way that anyone alive right now could make it to TRAPPIST-1 in a lifetime. While discussing the new discovery at a news conference today (Feb. 22), NASA officials suggested that it would likely take at least 800,000 years to reach the TRAPPIST-1 system.
So don't start making any interstellar vacation plans anytime soon.
Correction: A previous version of this article stated that Stephen hawking dreamed up the Breakthrough Starshot initiative. Hawking helped to launch it and serves on the board of directors, but the concept was first conceived by Russian entrepreneur Yuri Milner.
Editor's Note: This article has been updated to clarify NASA's calculation of when Voyager will pass near the star AC +79 3888, which factors in the star's movement. Our calculations describe the time to travel 39 light-years, to TRAPPIST-1's current location.
Email Hanneke Weitering at [email protected] or follow her @hannekescience . Follow us @Spacedotcom , Facebook and Google+ . Original article on Space.com .
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].

Hanneke Weitering is a multimedia journalist in the Pacific Northwest reporting on the future of aviation at FutureFlight.aero and Aviation International News and was previously the Editor for Spaceflight and Astronomy news here at Space.com. As an editor with over 10 years of experience in science journalism she has previously written for Scholastic Classroom Magazines, MedPage Today and The Joint Institute for Computational Sciences at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. After studying physics at the University of Tennessee in her hometown of Knoxville, she earned her graduate degree in Science, Health and Environmental Reporting (SHERP) from New York University. Hanneke joined the Space.com team in 2016 as a staff writer and producer, covering topics including spaceflight and astronomy. She currently lives in Seattle, home of the Space Needle, with her cat and two snakes. In her spare time, Hanneke enjoys exploring the Rocky Mountains, basking in nature and looking for dark skies to gaze at the cosmos.
Lego Star Wars Millennium Falcon (2024) review
Space-based solar power may be one step closer to reality, thanks to this key test (video)
Watch China launch 3 astronauts to Tiangong space station today
Most Popular
- 2 Buried in the Cat's Paw Nebula lies one of the largest space molecules ever seen
- 3 Netflix releases official trailer for Jennifer Lopez mech combat sci-fi film 'Atlas' (video)
- 4 Ancient rocks hold proof of Earth's magnetic field. Here's why that's puzzling
- 5 Hubble telescope celebrates 34th anniversary with an iridescent Dumbbell Nebula (image)

How Long Would It Take To Travel A Light Year

Using the fastest man-made vehicle, NASA’s Juno spacecraft, which travels at 165,000 mph (365,000 kmph), it would take 2,958 years to travel a light year. A light year is equivalent to about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).
Traveling at the speed of light would be the fastest way to cover vast distances in space, but current technology makes it impossible for humans or even our most advanced spacecraft to reach this speed.
Can people match the speed of a light year?
According to Einstein, it is impossible to match the speed of light. It is because light is the fastest thing in the universe, traveling at 186,000 miles per second (300,000 kilometers per second). There is not one thing that we could invent that could even match a fraction of how fast light travels.
Some scientists have theorized that a new type of engine, called a warp drive , could potentially allow humans to reach the speed of travel required to match the speed of light. However, even if future spacecrafts were able to achieve this level of propulsion, it would still take thousands of years to travel from one star system to another.
Despite the challenges, scientists continue to study space travel at faster-than-light speeds, as they are optimistic that one day we will be able to explore the vast reaches of our universe and even discover life on other planets.
For now, it would take many thousands of years to travel a light year using current technology. However, scientists remain hopeful that one day we will be able to explore the far reaches of space and perhaps even discover other life forms in distant star systems. Until then, we can continue marveling at the
Related Posts:
- How Long Would It Take To Get To Venus?
- How Long Would It Take To Get To Saturn?
- How Many Years Is A Light Year?
- What Is The 33-Year Cycle?
- How Far Can We Travel In Space With Current Technology?
- How Long Does A Solar Eclipse Last?
Advertisement
TRAPPIST-1 Is Only 40 Light Years Away! Wait. What?
- Joelle Renstrom
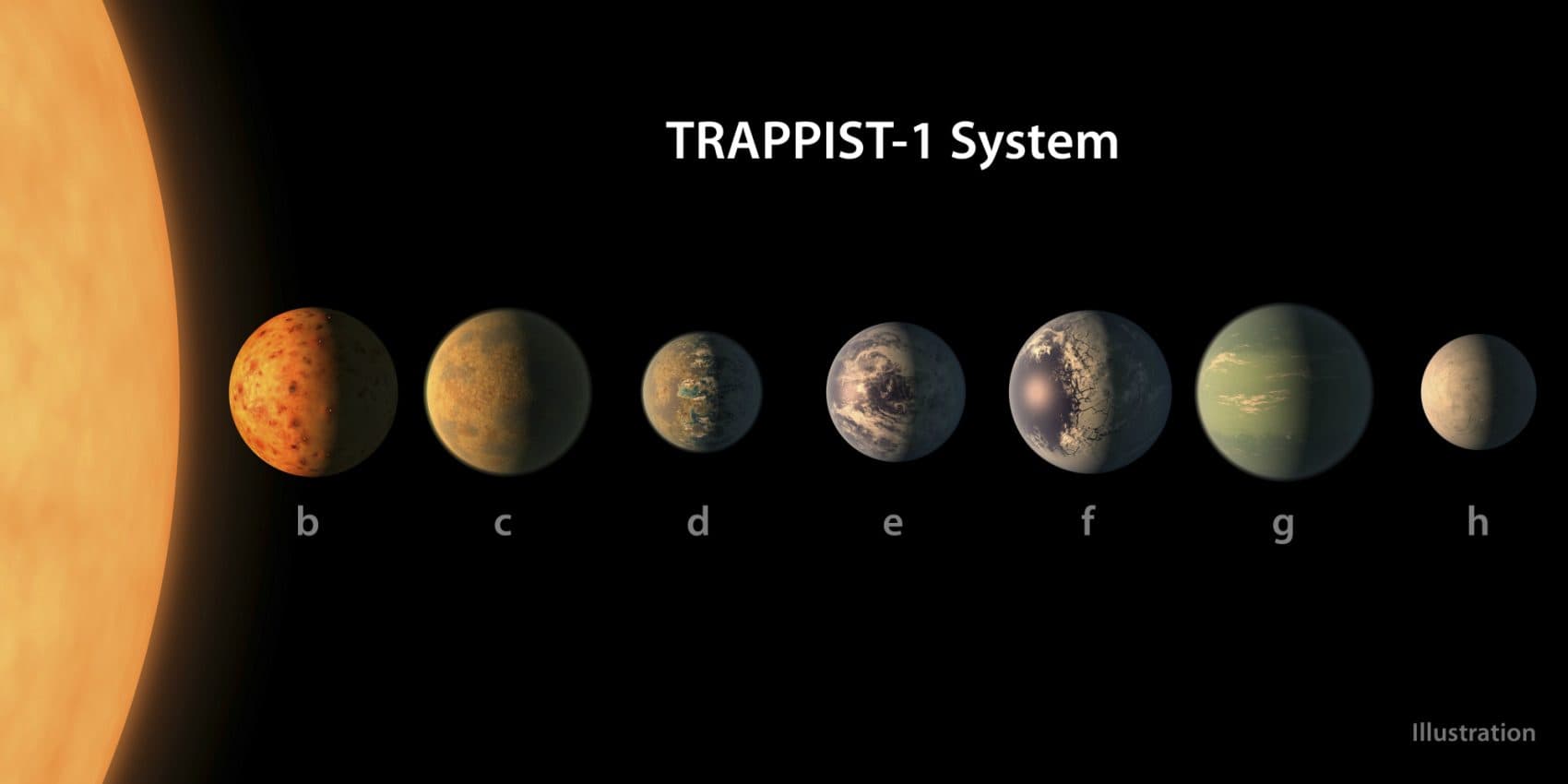
TRAPPIST recently found a solar system with seven planets , three of which are potentially habitable . We know the galaxy teems with exoplanets — we’ve discovered over 3,400 of them so far — but one reason for the excitement around this discovery is the proximity of this system: It’s only 40 light years away.
Only 40 light years.
Exactly how far away is this system? How long would it take to get there?
A light year is a measurement of distance based on the speed of light. Light travels at 186,282 miles per second . By my calculations, that’s 670,615,200 miles per hour, 16,094,764,800 miles per day, and 5,874,589,152,000 miles per year. Thus, the TRAPPIST-1 star system is roughly 235 trillion miles away.
Traveling at the speed of light, it would take approximately 40 years to reach TRAPPIST-1...which, in cosmic terms, is a neighborly jaunt.
To put that distance in perspective, the moon is 239,900 miles away; at their closest, Mars is 33.9 million miles away and Pluto is 2.66 billion miles away; the next closest star system, Alpha Centauri , is approximately 25 trillion miles (4.3 light years) away.
But the distance is only half of the equation. The other part is how quickly a spacecraft can travel. Traveling at the speed of light, it would take approximately 40 years to reach TRAPPIST-1 (not taking relativity into account for simplicity’s sake), which, in cosmic terms, is a neighborly jaunt.
The problem is that we can’t travel anywhere near the speed of light. Most scientists believe that one-tenth the speed of light is when relativity becomes a factor , and thus may represent the upper limit, but even that may be optimistic.
Most passenger planes top out at approximately 500 mph. The fastest aircraft, the X-15 plane designed by NASA and the U.S. Air Force, hit 4,520 miles per hour . NASA’s space shuttles reached 18,000 mph . At that speed, it would take approximately 165,000 years to arrive at Alpha Centauri and approximately 1,491,280 years to reach the TRAPPIST-1 system.

If this were Star Wars, Chewbacca would set the coordinates, and we’d initiate the hyperdrive . If this were Babylon 5, we’d identify the jump gate nearest to this system and get there via hyperspace. If this were Battlestar Galactica, we’d spool up the FTL (faster than light) drive and jump.
But we have no idea how to do any of those things.
The size and payload of a spacecraft also determine its maximum velocity. A small, uncrewed spacecraft such as New Horizons , which is currently near Pluto, can travel at over 36,000 miles per hour; it arrived at its destination in less than a decade. But if it wanted to head to Alpha Centauri, the trip would take another 80,000 years . Still, there are ways we can dramatically improve our propulsion systems to decrease travel time.
One possibility is a thruster that doesn’t require conventional fuel, such as magnetoplasmadynamic thrusters , quantum vacuum plasma thrusters (Q-thrusters), and/or ion thrusters . NASA recently tested out the first two; while promising in concept, there’s still much left unknown — namely, the role of quantum forces. While this approach remains theoretical for now, its successful implementation could get crews to Mars in weeks, rather than seven to eight months, or a spacecraft to Alpha Centauri in about 30 years.
One idea common in science fiction is placing place crew members in a state of suspended animation for the long trip and then reawakening them upon arrival. While trauma centers have begun to use this approach by lowering patients’ body temperatures to induce hypothermia, buying time for surgeons to repair injuries such as gunshot wounds, there are hurdles to employing this technique for long-duration missions, as sci-fi writer Kim Stanley Robinson points out . He raises the possibility of bringing frozen embryos on such a mission or using “generation ships” on which entire generations would live, reproduce and die onboard. But those bring challenges too.
...humanity has proven itself capable of meeting seemingly insurmountable challenges. In 1903, a New York Times editorial declared that making a “flying machine” would take at least one million years... Nine weeks later, the Wright Brothers made history.
While the TRAPPIST-1 discovery is deeply exciting, both because of its proximity and because it raises the possibility that life could exist in star systems we previously thought uninhabitable, getting ourselves or our spacecraft there is an immense challenge. But humanity has proven itself capable of meeting seemingly insurmountable challenges. In 1903, a New York Times editorial declared that making a “flying machine” would take at least one million years of mechanical and mathematical collaboration. Nine weeks later, the Wright Brothers made history at Kitty Hawk. Decades later, breaking the sound barrier in flight—at least, not without killing the pilot—seemed impossible. But in 1947, Chuck Yeager did just that . In 1962, John F. Kennedy told the American people that we’d put a man on the moon before the end of the decade, despite being woefully behind in the Space Race. Seven years later, Neil Armstrong took a giant leap for mankind.
Who knows where the next leap will lead?
- Astronomers Discover 7 Earth-Size Planets That May Be Habitable

Joelle Renstrom Cognoscenti contributor Joelle Renstrom is a science writer whose work has appeared in Slate, The Guardian, Aeon, Undark and other publications. She also wrote the essay collection "Closing the Book: Travels in Life, Loss, and Literature." She teaches at Boston University.
More from WBUR
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My watchlist
- Stock market
- Biden economy
- Personal finance
- Stocks: most active
- Stocks: gainers
- Stocks: losers
- Trending tickers
- World indices
- US Treasury bonds
- Top mutual funds
- Highest open interest
- Highest implied volatility
- Currency converter
- Basic materials
- Communication services
- Consumer cyclical
- Consumer defensive
- Financial services
- Industrials
- Real estate
- Mutual funds
- Credit cards
- Balance transfer cards
- Cash back cards
- Rewards cards
- Travel cards
- Online checking
- High-yield savings
- Money market
- Home equity loan
- Personal loans
- Student loans
- Options pit
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
TRAPPIST-1: How Long Would It Take to Fly to 7-Planet System?
The discovery of seven Earth-size planets around a nearby star, TRAPPIST-1, is certainly exciting news. TRAPPIST-1 is 39 light-years away from Earth, or about 229 trillion miles (369 trillion kilometers). It would take 39 years to get to its current location traveling at the speed of light.
Recommended Stories
Nfl draft: packers fan upset with team's 1st pick, and lions fans hilariously rubbed it in.
Not everyone was thrilled with their team's draft on Thursday night.
NFL Draft: Bears take Iowa punter, who immediately receives funny text from Caleb Williams
There haven't been many punters drafted in the fourth round or higher like Tory Taylor just was. Chicago's No. 1 overall pick welcomed him in unique fashion.
NFL to allow players to wear protective Guardian Caps in games beginning with 2024 season
The NFL will allow players to wear protective Guardian Caps during games beginning with the 2024 season. The caps were previously mandated for practices.
NFL Draft: Spencer Rattler's long wait ends, as Saints draft him in the 5th round
Spencer Rattler once looked like a good bet to be a first-round pick.
Michael Penix Jr. said Kirk Cousins called him after Falcons' surprising draft selection
Atlanta Falcons first-round draft pick Michael Penix Jr. said quarterback Kirk Cousins called him after he was picked No. 8 overall in one of the 2024 NFL Draft's more puzzling selections.
Cowboys owner Jerry Jones compared his 2024 NFL Draft strategy to robbing a bank
Dallas Cowboys owner Jerry Jones made an amusing analogy when asked why the team selected three offensive lineman in the 2024 NFL Draft.
Korey Cunningham, former NFL lineman, found dead in New Jersey home at age 28
Cunningham played 31 games in the NFL with the Cardinals, Patriots and Giants.
NFL Draft: Brenden Rice, son of Hall of Famer Jerry Rice, picked by Chargers
Brenden Rice played the same position as his legendary father.
NFL Draft fashion: Caleb Williams, Malik Nabers dressed to impress, but Marvin Harrison Jr.'s medallion stole the show
Every player was dressed to impress at the 2024 NFL Draft.
Based on the odds, here's what the top 10 picks of the NFL Draft will be
What would a mock draft look like using just betting odds?
NBA playoffs: Tyrese Hailburton game-winner and potential Damian Lillard Achilles injury leaves Bucks in nightmare
Tyrese Haliburton hit a floater with 1.1 seconds left in overtime to give the Indiana Pacers a 121–118 win over the Milwaukee Bucks. The Pacers lead their first-round playoff series two games to one.
Fantasy Baseball Waiver Wire: Widely available players ready to help your squad
Andy Behrens has a fresh batch of priority pickups for fantasy managers looking to close out the week in strong fashion.
Dave McCarty, player on 2004 Red Sox championship team, dies 1 week after team's reunion
The Red Sox were already mourning the loss of Tim Wakefield from that 2004 team.
Everyone's still talking about the 'SNL' Beavis and Butt-Head sketch. Cast members and experts explain why it's an instant classic.
Ryan Gosling, who starred in the skit, couldn't keep a straight face — and neither could some of the "Saturday Night Live" cast.
UPS and FedEx find it harder to replace gas guzzlers than expected
Shipping companies like UPS and FedEx are facing uncertainty in U.S. supplies of big, boxy electric step vans they need to replace their gas guzzlers.
Skelly, Home Depot's 12-foot skeleton, gets a dog — and he's a very good boy
Halloween may be six months away, but Home Depot unveiled some of its latest and greatest decorations, including a dog pal for Skelly, the brand’s gigantic and popular 12-foot skeleton.
NFL Draft: Sorry Jim Harbaugh, Michigan RB Blake Corum goes to cross-town Rams
The Rams seemed like an unlikely landing spot for Blake Corum.
NFL Draft: Joe Milton III selected by the Patriots, who double up at quarterback
The Patriots took a shot on strong-armed Joe Milton III in the sixth round.
Chiefs make Andy Reid NFL's highest-paid coach, sign president Mark Donovan, GM Brett Veach to extensions
Reid's deal reportedly runs through 2029 and makes him the highest-paid coach in the NFL.
NBA playoffs: Who's had the most impressive start to the postseason? Most surprising?
Our NBA writers weigh in on the first week of the playoffs and look ahead to what they're watching as the series shift to crucial Game 3s.
- Mathematics
- Paranormal Phenomena
- Other - Science
- Earth Sciences & Geology
- Engineering
- Astronomy & Space
- Parapsychology
- Other - Alternative
- Agriculture
- Earth Sciences & Geology
- Alternative
- Astronomy & Space
- Alternative & Paranormal Phenomena
How long would it take To travel 39 light years if we were to go to the new 7 habitual planets?
- What is the slope of a line parallel to y=5/4x?
- What do you call planets orbiting a star?
- not concerned with how it happened but can you exp..
- What would happen if the moon was going to crash i..
- How did it become like this? Factorization?
- Do you believe in density ?
- Related rates and applications: How to find dy/dt ..
- If time is the 4th dimension, then what is the 5th..
- If a huge asteroid were coming towards earth, and ..
- Is high blood pressure and serious condition? What..
- parallel worlds really exist or is it one on flash..
- The kinetic energy of a boat is calculated at 45,0..
- I live in Thailand. At night I think I see geostat..
- can you eat an atom?
- Have we ever sent bacteria to the space ? A source..
- When was the last leap year?
- People!! Its a yes or no question...is north Ameri..
- If a 8km rocky asteroid?
- What exactly does the term "horsepower&am..
- Do you think science will ever be able to explain ..
- What is the slope of a line parallel..
- How long would it take To travel 39 ..
- What do you call planets orbiting a ..
- not concerned with how it happened b..
- What would happen if the moon was go..
- How did it become like this? Factori..
- Related rates and applications: How ..
- If time is the 4th dimension, then w..
- If a huge asteroid were coming towar..
- Is high blood pressure and serious c..
- parallel worlds really exist or is i..
- The kinetic energy of a boat is calc..
- 3 times a number is 12 more than a n..
- Is Tibet a Country?
- I live in Thailand. At night I think..
- Simplify e^(2lnx) help
- If the partial pressure of the diato..
- Force question: Boxes A and B are in..
- Do chickens asexually reproduce
- 465mK/s = ______ μK/ms
- Balance the following equation in ba..
- What are four different chemical mea..
- What is difference between hydrolysi..
- What is the label for this orbital t..
- Angular velocity...need some help!
- Based on the first and fourth sketch..
- An electron in the n=7 level of the ..
- Which element is oxidized and which ..
- CHEM LAB HELP PLEASE! 10 pts
- 3 Geography questions, can someone c..
- Oxidation number of Sulfur in FeSO4
- Privacy Policy
How Long Would it Take Us to Reach the Most Earth-like Planet We Know of?
How long would it take to reach Trappist-1?
Just last week, NASA announced its most exciting discovery in years (and that's saying something given that this happened recently. And this . And this, too ). They discovered that Trappist-1, a solar system only about 39 light years away, has seven Earth-sized planets that are all capable of hosting life .
It is an amazing discovery that has everyone's imaginations going wild. Seven new worlds? Are there oceans there? Animals? Plant life? Do they look like life on Earth at all? Are there creatures like... us? With civilizations, technology, inventions?
It is inevitable after hearing such groundbreaking news that someone will step forward and ask the question on everyone else's mind: When can we go there?
Let's answer that one together now.
The trip of your life... if you could make it
On the scale of the universe, 40 light years away is actually very close. If the universe was the size of our solar system, we'd practically be next-door neighbours.
But in the physical world, 39 light years is 369 trillion kilometres (229 trillion miles) away. Even if you were piggybacking on a beam of light, it would take around 39 years to get there. That is a crazy long trip (about as long as some of your parents have been alive!), but it is a length of time that a human being could technically survive.
The only problem?
Going as fast as the speed of light is impossible. So we'll need to look at the next available options. (Spoiler alert: they are a lot slower than we'd need them to be...)
Take the shuttle... better bring a book
When we think of humans going into space, we naturally think of the space shuttle. It's maximum speed sits at around 28,160 km/h (17,500 mph). That might be a lot faster than a car on the highway, but it would take 1.5 million years to reach Trappist-1.
New Horizons needs new technology
If we forgot about getting human beings there for a moment and just focus on getting a probe to the solar system, the options get a little better. New Horizons is the fastest spacecraft ever launched by humans. Its top speed of 51,500 km/h (32,000 mph) is twice as fast as the space shuttle. Though it would still need 815,000 years to reach Trappist-1.
Breakthrough Starshot gives us our best shot (if we actually build it)
Given present technology, actually observing Trappist-1 up close looks like wishful thinking. But there is one curious possibility (which we wrote about already last year ). It is called the Breakthrough Starshot, a pretty fitting name really. This involves sending a nanocraft ("nano" means super tiny) for a laser-propelled "sail" across the cosmos. In theory, it could travel at about 20% the speed of light. That's 216 million km/h (134 million mph)! And it would reach Trappist-1 in under 200 years. Not bad, right?
Unfortunately, this is still just a theory. No one has built the Starshot yet.
Still, don't lose heart, you space dreamers. Because you know what also moves really fast? The progress of the space program! It was only 60 years ago in 1957 that the Soviet Union launched Sputnik-1, the first artificial satellite. Since then, scientists and astronauts have achieved so much in exploring the our own solar system and beyond. Will you grow up to see pictures beamed back home from one of these brand new worlds?
Honestly? We wouldn't bet against it!
Tell US what you think Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Your name *
Your email *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The varied information you have on Owlconnect is wonderful for me to hear about, in a brief and informative way, about news that otherwise I might not know about. Thank you!
This is so cool! I’m gonna write a sort story about it next time our teacher tells us to write one!!! 😉
I think there would be aliens. Maybe they are blue

It's National Science Reading Day!
September 20, 2023

The Moon (crash) landing!
September 13, 2023

Coffee grounds to concrete!
September 12, 2023


Meet the winners of the 2023 Science Odyssey Contest
September 8, 2023

India's lunar breakthrough!
September 1, 2023

Did Mars once have wet-dry cycles?
August 26, 2023

That is some shocking growth!
August 21, 2023

The AURA is like a bike helmet from the future
August 12, 2023

Dark matter telescope releases test image
August 9, 2023

Some fungi can eat plastic
August 4, 2023
- Privacy policy
By Darin Anthony - Last Updated: April 17, 2024
How Long Would It Take to Travel One Light Year?

Article Contents
We hear the term “light-years” almost anytime a new star or exo-planet is discovered. But how long would it take to travel one light year?
The fastest human-made vehicle, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, would take 1,698 years to travel one light-year , the sum of roughly 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers), the distance light travels in one year.
In September 2023, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe set a new record, clocking a blistering speed of 394,736 miles per hour (635,266 kilometers per hour)—the fastest ever recorded.
But 1,698 years is an incredibly long time. The Parker Solar Probe would have just completed a distance of one light year if it had left during the 4th century (326 A.D.) and maintained its top speed the entire journey.
Let’s look more closely at the speed of light and what it means to travel one light-year.

Understanding Light Years
Speed of light.
Over one hundred years ago, Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity deciphered the math of a cosmic limit. It says nothing can go faster than the speed of light , which is approximately 186,282 miles per second (299,792 km/s) within the vacuum of space.
To help understand how fast light speed is, we’ll compare it to the longest intercontinental flight in the world today.
A flight from New York to Singapore covers 9,526 miles (15.332km) and, on average, takes 18hrs 40 minutes. If a commercial airliner could travel the speed of light, symbolically, it could make that trip almost 20 times in one second!
Measuring Distances
Understanding the vastness of space begins with grasping the concept of a light-year . It’s a unit of measurement scientists use to note the length of astronomical distances.
Astronomers use two common measurements to help make an incredibly long distance, a huge number, more manageable.
Astronomical Unit (AU) : It’s the distance the Sun’s light takes to reach the Earth. This distance is approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) and takes eight light minutes.
Light-Year (LY): It represents the unit of distance that light travels in one Earth year , which is approximately 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).
So, the time it takes Light to travel one light year? One Earth year or roughly 365 days .
When speaking of distances in the universe, an astronomer refers to distances in an (AU) or (LY) depending on how great of a distance.
For example, when referring to the distance of the Andromeda Galaxy from Earth, it is stated as 2.5m (LY) light years( i ). However, the shorter distance to Neptune from the Sun is noted as approximately 30.7 (AU)( i ).
Since a light-year is a larger unit of distance than (AU) it is more likely to be used when expressing bigger numbers.
Travel Time

If we could travel the distance of one light-year from Earth, we would end up in the mid-region of the Oort cloud .
It is the outermost area of our solar system before reaching the realm of deep outer space. The time it would take to journey this one light-year would greatly depend on our mode of transportation.
I’ve put together several calculations using a light-year (ly) calculator. Using the average miles per hour (mph) for current technology we use today. It makes the complexity of traversing such an immense distance very obvious.
See the infographic I have provided below, which has a link to the calculator within the caption.

Let’s look at some of the examples the infographic highlights in relation to how long it takes to travel a light-year.
If you decide to put on some walking shoes and head off towards the mid-region of the Oort cloud , a light year away, be sure to pack lunch. At a normal pace of 3/mph, it would take nearly 224 million years to get there without stopping to eat, sleep, or bathroom breaks.
Walking (3/mph) >>> One Light Year >>> 224M Years
You could pull the car cover off the Corvette stored in the garage for a quicker ride. Even then, traveling at an average speed of 100 mph would take six million and seven hundred thousand years (6.7m years) to travel a light year . That’s without stopping or slowing down.
Drive (100/mph) >>> One Light Year >>> 6.7M Years
How about a ticket on the “Big ol’ Jet Airliner”? It would still take you over one million years (1.118m yrs) to span the distance of one light year on a commercial Jet .
Commercial Jet (600/mph) >>> One Light Year >>> 1.18M Years
The point is that the distances between objects in our solar system, galaxy, and universe are so vast it’s very challenging for our minds to grasp and comprehend it.
As of today, we do not have technology that can travel the distance of a light-year within the span of a human life, but there are future concepts. Let’s take a look.
Future Concepts to Travel Light-Years
Considering our Milky Way galaxy stretches across 100,000 light-years. Even at the speed of light, it takes 100,000 Earth years to journey from edge to edge. To bridge that distance, we’ll need to inspire some new ideas through quantum physics.
But some interesting concepts are in the works right now to dramatically shorten the length of time it takes to travel a light year.
Breakthrough Starshot
In 2016, Physicist Yuri Milner announced an engineering endeavor named “ Breakthrough Starshot ,” with backing support from such notable figures as Stephen Hawking (now deceased), and Mark Zuckerberg.
Their aim is to develop a fleet of light sail centimeter-sized probes called StarChips . These probes are designed to travel to the Alpha Centauri star system , located 4.37 light-years away, potentially within 20 to 30 years at speeds of 15-20% the speed of light.
Currently, using the Parker Solar Probe’s top speed, to travel 4 light-years would take over 7000 years, so that would be an amazing feat.
The project proposes a flyby mission to our next closest star beyond our Sun, Proxima Centauri. It is believed to be home to an Earth-sized exoplanet in the habitable zone.
The concept will leverage advanced laser technology to propel the spacecraft. Current estimates for launch are 2036.

Helical Engine
A space and aeronautics engineer has developed a concept that, in theory, would reach 99% of the speed of light without conflicting with Einstein’s theory of relativity .
Dr Burn, now a former engineer from NASA’s Space Flight Center in Alabama , believes that a system where instead of expelling propellant, it is retained, could generate an almost limitless specific impulse and open the door to interstellar space exploration.
This method involves accelerating ions near the light speed limit within a closed circuit, adjusting their speed to modify momentum. Thrust is generated by oscillating the ions back and forth in the direction of travel.
It’s Designed for long-term satellite operations without the need for refueling or powering voyages across vast distances; this engine operates without any mechanical components, relying solely on ions circulating in a vacuum loop contained by electric and magnetic fields.
If this concept is proven and successful it would mean we could travel a light-year in a little more than one year!

It’s impossible to talk about traveling at the speed of light without discussing the theory of warp drive , which was popularized by the 1960s Star Trek series.
NASA has explored this concept and will continue to do so as science and modern physics expand with future breakthroughs.
The idea behind warp drive is to manipulate the fabric of spacetime to create a bubble or a wave, often referred to as a “ warp bubble ,” that would contract space in front of the ship and expand it from behind , allowing the vessel to move from one point to another faster than light would in normal space.
It would theoretically enable interstellar travel within human lifetimes without violating the fundamental principles of Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which states that nothing can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum.
If this concept is ever proven, it will be a game changer for space travel in our cosmic neighborhood and beyond.

For now, the Parker Solar Probe’s top speed makes it the fastest vehicle to span the distance of a light year . The enormity of the universe will make reaching distant stars and exoplanets impossible until we can develop technologies like the Warp Drive, Starshot, or Helical engine.
It’s a humbling distance across our Milky Way. But scientists continue to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos, and one day, we may crack the code to bridge the vast galactic space within the universe.
Astronomy has peaked my curiosity and imagination from an early age. I am always thrilled to read about the latest galactic discovery or planning my next celestial observation. More about me [..]
You May Also Like
The article you just read is part of the City Astronomy “ Astronomy ” collection . If you enjoyed it we think you'll love these other recommendations:

Discover why this lesser known phase called the Gibbous Moon is a great time to observe the lunar surface.

In this article we explain what a Shooting star is and where they come from.

Find out what color the Moon REALLY is and why it can look different from night to night.
About CityAstronomy
CityAstronomy.com - As an astronomy enthusiast, I created this site with the objective to be a helpful resource to all readers who share a desire to learn about space and astronomy. More About me [..]
Astronomy Stargazing Astrotourism Outer Limits
Contac t | About | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | Disclaimer Policy 112 2nd Ave. N. Nashville, TN 37201 CityAstronomy.com © 2024
Light Year Conversion
What is light year, how to convert light years to miles, how to convert light years to kilometers, how to convert light years to astronomical units.
With this light year conversion tool, we aim to help you convert light year into different length units . To understand more on this topic, please check out our speed of light calculator and light year calculator .
We have written this article to help you understand the following:
- What light year is ;
- How to convert light years to miles ;
- How to convert light years to kilometers ; and
- How to convert light years to meters .
We will also demonstrate some examples to help you understand the light year conversion calculation.
A light year is the distance that light travels in one year, which is about 5.88 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers . Because the speed of light is constant, this distance provides a useful way to measure the vast distances in space.
For example, the closest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is about 4.24 light years away, meaning that the light we see from that star today left it over four years ago.
To convert light years into miles or kilometers, we need to multiply the distance in light years by the number of miles or kilometers in one light year, which is 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion km) .
For example, if we want to know how many miles are in 3 light years, we would multiply 3 by 5.88 trillion miles to get 17.64 trillion miles.
For the conversion of light years into kilometers, we need to multiply the distance in light years by the number of miles or kilometers in one light year . One light year is approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers , so we can use this conversion factor to convert between the two units.
For example, if we want to know how many kilometers are in 2 light years, we would multiply 2 by 9.46 trillion kilometers to get 18.92 trillion kilometers.
Another unit of measurement often used in astronomy is the astronomical unit (AU) , which is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun . This distance is approximately 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) and is often used to measure distances within our own solar system.
For the conversion of light years into astronomical units, we need to divide the distance in light years by the number of light years in one astronomical unit, which is 0.000015813 .
For example, if we want to know how many astronomical units are in 5 light years, we would divide 5 by 0.000015813 to get approximately 316,602 astronomical units.
With our calculator, we can also help you convert light years into Earth radii, Sun radii, and megaparsecs. You can also check out our length converter to understand more about this topic.
It's worth noting that these distances are so vast that they are difficult to comprehend. Even the distance to our closest star, Proxima Centauri, is so large that it would take over 30,000 years to travel there at the speed of our fastest spacecraft.
What is 1 light year converted to miles?
1 light year is approximately 5.88 trillion miles . 1 light year is converted to miles by multiplying 1 by 5.88 trillion.
Is a light year a unit of time or distance?
A light year is a unit of distance , specifically the distance that light travels in one year.
Can we travel faster than the speed of light?
According to our current understanding of physics, it is not possible for anything with mass to travel faster than the speed of light .
How to convert light years to meters?
You can convert light years into meters in 3 steps:
- Determine the number of light years to convert.
- Multiply the number of light years by 9,461 trillion.
- Analyse the results in meters.
Chilled drink
Circumference, pints to gallons converter, weight converter.
- Biology (100)
- Chemistry (100)
- Construction (144)
- Conversion (295)
- Ecology (30)
- Everyday life (262)
- Finance (570)
- Health (440)
- Physics (510)
- Sports (105)
- Statistics (182)
- Other (182)
- Discover Omni (40)
- Virtual Events
- BBC Astronomy
- How we review
- Telescope mounts
- Finderscopes
- Astronomy accessories
- Top astro kit
- Astronomy for beginners
- Astronomy DIY
- Buyers' guides
- Online Planetarium
- Astronomy news
- Astrophoto guides
- Send us your images
A guide to lightyears, the unit used by astronomers to measure vast distances in the cosmos
Using lightyears to measure distance in the Universe and how long it would take to travel one lightyear by foot, car, plane and rocket.
Jenny Winder
The numbers we use in astronomy are, literally, astronomical. It can be hard to get your head around so many zeros.
If we were to use kilometres and miles it would be like measuring your commute in millimetres.
To try to simplify things, when we discuss objects within our Solar System, we use the Astronomical Unit (AU) to measure distance.
One AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun or 150 million kilometres (93 million miles). Our Solar System has a diameter of just 1,921 AUs. So far so good.
To measure vast distances across space , scientists use the Parsec , the distance 1AU subtends an angle of 1 arc-second (1/3600 of a degree) which is 206,265 AUs, or 30.9 trillion km (19.2 trillion miles) and difficult for most of us to comprehend.
So the lightyear is the standard measure of distance for anything outside the Solar System.

A simple definition of lightyear
Put simply, a lightyear is the distance light travels in space in a year, 9.46 trillion km (5.88 trillion miles) or 63,241 AU, 0.30 parsecs.
Nothing travels faster than light. It travels nearly one million times faster than sound. A lightsecond equals 300,000 km (186,000 miles).
A lightminute is about 18 million km ( 11 million miles) and a lighthour is 1.1 billion km.
One AU equals 8.3 light minutes and a Parsec equals 3.26 lightyears.
Lightyears and looking back in time
The further we look into space, the farther back in time we see.
Proxima Centauri , the nearest star is 4.25 lightyears away, so the light we see from it today, started its journey four years and three months ago.
If Proxima Centauri exploded today it would take 4 years and 3 months before we saw it happen.
The radius of the observable Universe and so the farthest we can see into space is 46.6 billion lightyears.

Travelling a lightyear
Our crewed spaceships, like Apollo, reach speeds of around 39,400 km/h (24,500 mph). It would still take around 27 thousand years to travel one lightyear.
A plane travelling at 965 km/h (600 mp/h) would take 1 million years to travel one lightyear.
A car with an average speed of 90 km/h (56 mph) would take 12 million years, and if you fancied a walk, at 5 km/h (3 mph) it would take you a whopping 216 million years to travel one lightyear, with no comfort breaks!
Earth orbits the Sun at 107 thousand km/h or 67 thousand mph, so it would take 10 thousand years for Earth travel one lightyear.
But our Solar system is also travelling through the Galaxy at 720 thousand km/h (448 thousand mph) which takes just 1,500 years to travel one lightyear.

Travelling at the speed of light
Currently, faster-than-light travel seems an unreachable goal, despite movies showing us using wormholes , warp drives and spore drives in the future.
The closest proposition is to use the energy and momentum of light itself to propel a spacecraft.
A city-sized arrangement of synchronised lasers, firing photons to push a small hand-sized spacecraft to 25 per cent the speed of light.
That would get us 4.25 light years to Proxima Centauri in under 20 years.
Share this article

Science writer

- Terms and conditions
- Manage preferences
How Far is a Light Year?
How far is a light-year ? It might seem like a weird question because isn’t a ‘year’ a unit of time, and ‘far’ a unit of distance? While that is correct, a ‘light-year’ is actually a measure of distance. A light-year is the distance light can travel in one year.
Light is the fastest thing in our Universe traveling through interstellar space at 186,000 miles/second (300,000 km/sec). In one year, light can travel 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion km).
A light year is a basic unit astronomers use to measure the vast distances in space.
To give you a great example of how far a light year actually is, it will take Voyager 1 (NASA’s longest-lived spacecraft) over 17,000 years to reach 1 light year in distance traveling at a speed of 61,000 kph.
Related Post: 13 Amazing Facts About Space
Why Do We Use Light-Years?
Because space is so vast, the measurements we use here on Earth are not very helpful and would result in enormous numbers.
When talking about locations in our own galaxy we would have numbers with over 18 zeros. Instead, astronomers use light-time measurements to measure vast distances in space. A light-time measurement is how far light can travel in a given increment of time.
- Light-minute: 11,160,000 miles
- Light-hour: 671 million miles
- Light-year: 5.88 trillion miles
Understanding Light-Years
To help wrap our heads around how to use light-years, let’s look at how far things are away from the Earth starting with our closest neighbor, the Moon.
The Moon is 1.3 light-seconds from the Earth.
Earth is about 8 light-minutes (~92 million miles) away from the Sun. This means light from the Sun takes 8 minutes to reach us.
Jupiter is approximately 35 light minutes from the Earth. This means if you shone a light from Earth it would take about a half hour for it to hit Jupiter.
Pluto is not the edge of our solar system, in fact, past Pluto, there is the Kieper Belt , and past this is the Oort Cloud . The Oort cloud is a spherical layer of icy objects surrounding our entire solar system.
If you could travel at the speed of light, it would take you 1.87 years to reach the edge of the Oort cloud. This means that our solar system is about 4 light-years across from edge to edge of the Oort Cloud.

The distance between the Sun and Interstellar Space. NASA/JPL-Caltech .
The nearest known exoplanet orbits the star Proxima Centauri , which is four light years away (~24 trillion miles). If a modern-day jet were to fly to this exoplanet it would not arrive for 5 million years.
One of the most distant exoplanets is 3,000 light-years (17.6 quadrillion miles) away from us in the Milky Way. If you were to travel at 60 miles an hour, you would not reach this exoplanet for 28 billion years.
Our Milky Way galaxy is approximately 100,000 light-years across (~588 quadrillion miles). Moving further into our Universe, our nearest neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy is 2.537 million light-years (14.7 quintillion miles) away from us.

The Andromeda Galaxy is 2.537 million light-years away from us.
Light, a Window into the Past
While we cannot actually travel through time, we can see into the past. How? We see objects because they either emit light or light has bounced off their surface and is traveling back to us.
Even though light is the fastest thing in our Universe, it takes time to reach us. This means that for any object we are seeing it how it was in the past. How far in the past? However long it took the light to reach us.
For day-to-day objects like a book or your dog, it takes a mere fraction of a fraction of a second for the light bouncing off the object to reach your eye. The further away an object is, the further into its past you are looking.
For instance, light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes to reach Earth, this means we are always seeing the Sun how it looked 8 minutes ago if you were on its surface.

The differences between Lunar Distance, an Astronomical Unit, and a Light Year. Illustration by Star Walk .
Traveling back through our solar system, Jupiter is approximately 30 light-minutes from Earth, so we see Jupiter how it looked 30 minutes ago if you were on its surface. Extending out into the Universe to our neighbor the Andromeda galaxy, we see it how it was 2.537 million years ago.
If there is another civilization out in the Universe watching Earth, they would not see us here today, they would see Earth in the past. A civilization that lives 65 million light-years away would see dinosaurs roaming the Earth.
Helpful Resources:
- How big is the Solar System? (Universe Today)
- What is an Astronomical Unit? (EarthSky)
- How close is Proxima Centauri? (NASA Imagine The Universe)

Light Years to Normal Years Calculator
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one Earth year. To convert light-years to “normal” or Earth years, you simply use the value 1 light-year equals 1 year, as it represents the passage of time required for light to traverse that distance. So, 55 light-years would equal 55 Earth years.
Light-Years to Years Converter
How long is a Lightyear in normal years? A light-year is approximately 9.461 trillion kilometers (5.878 trillion miles) long. In terms of “normal” or Earth years, it represents the distance that light travels in one year.
How long is 40 light years in human years? 40 light years is approximately 377.8 trillion kilometers (234.3 trillion miles). In human years, it depends on the context you mean. If you’re asking about the time it would take to travel 40 light years at a significant fraction of the speed of light, it would still take many years, possibly decades or even centuries with current technology.
How do you calculate light years from years? To calculate light years from years, you multiply the number of years by the speed of light (approximately 299,792 kilometers per second or 186,282 miles per second).
How many regular years is a 100 light years? 100 light years is approximately 946.1 trillion kilometers (587.8 trillion miles). In terms of human years, it would take an enormous amount of time to travel this distance with current technology.
How long would it take to travel 1 lightyear? Assuming you could travel at the speed of light (which is currently impossible according to our understanding of physics), it would take one year to travel one light-year.
How much time passes in Lightyear? A light-year is a measure of distance, not time. It represents the distance that light travels in one year.
How much time is 500 light years? 500 light years is approximately 4.73 quadrillion kilometers (2.94 quadrillion miles). In terms of time, it would take an incredibly long time to travel this distance with current technology.
Can we travel light years away? With current technology, humans cannot travel light years away because our spacecraft are nowhere near fast enough to reach even a small fraction of the speed of light.
How much time is 3000 light years? 3000 light years is approximately 28.38 quadrillion kilometers (17.63 quadrillion miles). In terms of time, it would take an extremely long time to travel this distance with current technology, likely thousands or even millions of years.
Is a light-year 365 days? No, a light-year is not 365 days. It is the distance that light travels in one Earth year. It’s a measure of distance, not time.
Is light years actual years? No, light years are not actual years. They are a measure of distance, specifically the distance that light travels in one year.
How long would it take to travel 4.2 light years? Assuming you could travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light (which is currently beyond our technological capabilities), it would still take several years to reach a destination 4.2 light years away, potentially many decades or more.
How long is 1 lightyear in Earth years? 1 light-year is equivalent to 1 Earth year in terms of the time it takes for light to travel that distance.
How long is 50 light-years in time? 50 light-years is approximately 473.1 trillion kilometers (293.9 trillion miles). In terms of time, it would take an immense amount of time to travel this distance with current technology.
How many light-years is the Milky Way? The Milky Way galaxy is estimated to be about 100,000 to 120,000 light-years in diameter.
Would it take 1 light year to travel to the sun? No, it would not take 1 light year to travel to the Sun. The Sun is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth, which is much less than 1 light-year.
What is the speed of light in mph? The speed of light is approximately 671 million miles per hour (1.08 billion kilometers per hour).
How long would it take to get to Mars? The time it takes to travel to Mars depends on the relative positions of Earth and Mars in their orbits. On average, it takes about 6 to 9 months to travel from Earth to Mars using current spacecraft technology.
Is time dilation in Lightyear accurate? “Lightyear” appears to be a reference to a fictional universe or story, so any depiction of time dilation in that context would be based on the rules and fiction of that universe. Time dilation is a real phenomenon predicted by Einstein’s theory of relativity and has been observed in various experiments involving fast-moving objects.
How does the time travel work in Lightyear? Without specific details about the fictional universe or story you’re referring to, it’s difficult to explain how time travel works in “Lightyear.” Time travel concepts can vary widely in different works of fiction, and the rules governing time travel are determined by the creators of the story.
How did Buzz travel back in time? The context of Buzz traveling back in time is not provided, so it’s unclear which story or universe you’re referring to. Time travel methods in fiction can vary greatly, ranging from technological devices to supernatural or science-fictional phenomena.
How long would 10 light-years take? Assuming you could travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light (which is currently impossible with our technology), it would still take 10 years to travel a distance of 10 light-years.
How far is 1000 light-years away from Earth? 1000 light-years is approximately 9.461 quadrillion kilometers (5.878 quadrillion miles) away from Earth.
How long would it take to go 16 light-years? Assuming you could travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light, it would take 16 years to travel a distance of 16 light-years.
Can a human time travel? As of our current understanding of physics, humans cannot time travel in the sense often depicted in science fiction, where one can travel backward or forward in time at will. Time travel is a concept that remains theoretical and has not been achieved.
Will humans ever reach another galaxy? Reaching another galaxy is currently beyond our technological capabilities and may remain so for a very long time, if not indefinitely. The distances between galaxies are immense, and the energy and time required to travel to another galaxy would be astronomical.
Why can’t we travel in light-years? We can’t currently travel significant distances in light-years because our current spacecraft technology is nowhere near fast enough to reach even a small fraction of the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (about 186,282 miles per second). Traveling at such speeds would require enormous amounts of energy and face numerous technical and practical challenges.
How long would it take to go 46 billion light years? Traveling 46 billion light years is currently impossible with our current understanding of physics and technology. Additionally, it’s important to note that the universe is estimated to be about 13.8 billion years old, so a journey of 46 billion light years would exceed the age of the universe itself.
How long ago is 13 billion light years? 13 billion light years is an estimate of the age of the universe itself. It represents the distance that light has traveled since the Big Bang, which is believed to have occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
How big is our universe? The observable universe is estimated to be about 93 billion light-years in diameter. However, the full extent of the universe, including regions beyond the observable universe, is not currently known.
How far can light travel in 1 hour? Light travels approximately 671 million miles (1.08 billion kilometers) in 1 hour.
How far does light travel in 1 day? Light travels approximately 16.1 billion miles (25.9 billion kilometers) in 1 day.
Is there anything longer than a light-year? In terms of standard units of distance used in astronomy, a light-year is already a very long unit. However, for even larger cosmic scales, astronomers may use other units such as parsecs or megaparsecs.
Is 1 light-year 1 year ago? No, 1 light-year is not equal to 1 year ago. A light-year represents the distance that light travels in one year, not a measurement of time.
How old is our universe? The estimated age of the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years.
How many galaxies are there? There are estimated to be billions of galaxies in the observable universe, each containing billions to trillions of stars.
How long would it take to travel 4.24 light-years? Assuming you could travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light, it would take 4.24 years to travel a distance of 4.24 light-years.
How long would it take to get to Pluto? The time it takes to travel to Pluto depends on the spacecraft and trajectory used. NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, for example, took about 9.5 years to reach Pluto when it was launched in 2006.

GEG Calculators is a comprehensive online platform that offers a wide range of calculators to cater to various needs. With over 300 calculators covering finance, health, science, mathematics, and more, GEG Calculators provides users with accurate and convenient tools for everyday calculations. The website’s user-friendly interface ensures easy navigation and accessibility, making it suitable for people from all walks of life. Whether it’s financial planning, health assessments, or educational purposes, GEG Calculators has a calculator to suit every requirement. With its reliable and up-to-date calculations, GEG Calculators has become a go-to resource for individuals, professionals, and students seeking quick and precise results for their calculations.
Related posts:
- Light Years to Human Years Calculator
- Speed of Light to Light years Calculator
- Bear Years to Human Years Calculator
- Fish Years to Human Years Calculator
- Rabbit Years to Human Years Calculator
- Horse Years to Human Years Calculator
- Elf Years to Human Years Calculator
- Convert Cat Years to Human Years Calculator
- Chicken Years to Human Years Calculator
- Turtle Years to Human Years Calculator
- Human Years to Dog Years Calculator Pitbull
- Human Years to Dog Years Calculator Jack Russell
- Wolf Years to Human Years Calculator
- Demon Years to Human Years Calculator
- 31 Dog Years to Human Years Calculator
- 16 Dog Years to Human Years Calculator
- 15 Dog Years to Human Years Calculator
- Parallax Angle to light years Calculator
- Mph to Light Years Calculator
- Parsecs to light years Calculator
- Arcseconds to Light Years Calculator
- Miles to light years Calculator
- Au to Light Years Calculator
- Light Years to MPH Calculator
- Light Years to Parsecs Calculator
- Light Years to Minutes Calculator
- Light Years to AU Calculator
- Light Years to KM Calculator
- Normal Distribution Probability Calculator with Mean and Standard Deviation
- Tangential and Normal Component of Acceleration Calculator
- Normal Acceleration Vector Calculator
- Normal Approximation with Continuity Correction Calculator
- Normal Shock Calculator
- Vampire Years to Human Years Calculator
- Dragon Years to Human Years Calculator
- Shih Tzu Dog Years to Human Years Calculator
- Dog Years to Human Years Calculator Labrador
- Light Years to Seconds Calculator
- Is It Normal For My Gpu To Reach 74 Degrees Celsius?
- Is The Normal Body At 98.6 Or 98.4 Degrees?
- How Was 72 Degrees Established As A Normal Room Temperature?
- Is It Normal If A Girl Is Just 155cm In Height?
- How Much Does an Average Tune up Cost for a normal Sized Car?
- What’s The Cost of a Normal Cargo Ship?
- How Cold Is 15-18 Degrees Celsius? Is It Like Chilly, Cool, Windy, Normal, Or Warm?
- What’s A Normal American Dinner You Would Eat On A Weekday?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How Long Would It Take to Travel 1 Light Year?

On Earth, we measure distance through steps, meters, kilometers, miles, or some other unit of measurement by which we can determine distance. The universe is so large, that sometimes measuring in kilometers or miles is pointless. In space, it is easier to measure distance with the help of light years. We can easily determine how long it takes us to cover a certain distance in kilometers if we know how fast we are going, but we never calculate how long it takes us to travel a light year. Maybe it’s time to answer that question. How long would it take to travel one light year?
To travel one light year, if we travel at the speed of light, it would take us one year. In spacecraft, time would pass differently, so one would not even have the feeling of traveling and the travel time would fly by in less than a second. Time stops for a man, as does his aging, as long as his spacecraft travels at the speed of light.
For people on Earth, however, the journey of one light year would take one year. The difference in the experience of traveling one light year occurs due to different perceptions of time on Earth and in space. On Earth, we have learned to count time in seconds, minutes, hours, days and years. For an object traveling at the speed of light, time is irrelevant. A journey lasting one light year or a billion light years for a person traveling at the speed of light will seem absolutely the same in time. Less than a second, almost zero time.
How long is a light year?
First thing you need to know: a light year is a unit of measurement for distance, not for time! It is a unit of distance that represents the total distance that the beam of light travels in one year moving in a straight line in empty space. It is assumed that there are no strong magnetic or gravitational fields at this distance. This unit of measurement is used primarily in astronomy to calculate the distance between celestial objects. It would be a bit complicated to use kilometers or miles to measure distances in space given that the distance between certain celestial bodies would require numerous zeros.
The speed of light is 299 792458 meters per second. One Julian year, the year how we measure it, has 365.25 days, or 31,500,000 seconds. The light year is equal to 9,460,730,472,580,800 meters or approximately 9,461 × 1015 meters.
How many days is a light year in human years?
A light year is used to calculate the distance that light travels in a human year. One light year is therefore the same as one human year. Fifty light years is 50 human years. There is no difference in the length of the light year and human year.
A light year is just a name used for a unit of distance, not time. When we hear the term light year, we immediately think of time, but a light year has nothing to do with calculating the year. The distances in space are becoming so great that it is impractical to express them in common units of measurement, so we turn to light years.
There is even a unit that is larger than a light year, and that is the parsec. It is used to measure the distance between celestial bodies located outside the Solar System. One parsec is equal to 3.3 light years or 31 trillion kilometers.
How fast can we travel in space?
The speed at which we will travel in space depends on the spacecraft we use.
The human speed record was set by astronauts during the Apollo 10 mission. Apollo 10 was a test mission just before sending a man to the Moon. When returning from lunar orbit, their spacecraft reached a speed of 39,897 kilometers per hour. Such speed is still not possible to reach with today’s technology. Its successor, the Apollo 11, reached tremendous speeds at times but traveled at an average speed of 5,000 km / h.
In order to stay in space orbit, the shuttle must reach a speed of 28,000 km / h. That’s 9 times faster than a bullet. However, the space shuttle doesn’t go that fast all the time. The speed at which it will fly depends on the orbital altitude, which is approximately between 304 kilometers to 528 kilometers above sea level depending on the mission.
SpaceX, a private company whose goal is to enable the colonization of Mars, is one of the most modern spacecraft companies. In 2012, it began supplying the International Space Station with supplies. In 2020, SpaceX sent its Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station for the first time. The spacecraft was transporting two astronauts traveling at an average speed of 28 163 kilometers per hour. The International Space Station is quite close to Earth, so it’s hard to reach a higher speed on such a short journey.
The fastest object that humans have made is the NASA Helios 2 rehearsal. During the mission, Helios 2 reached a speed of 252,793 km / h. This rehearsal was launched back in 1976, so it is surprising that no one has overtaken it so far.
Parker Solar Probe will soon break the record set by Helios 2. Parker solar probe is a NASA probe launched in 2018 whose mission is making observations of the outer corona of the Sun. In 2025, it should come closest to the Sun and at that time it will travel at a speed of 690,000 km / h or 0.064% of the speed of light.
When we study the speed that modern spacecraft can reach, we are still years, and perhaps centuries, far from reaching the speed of light, if we ever reach it at all.
We know, however, to what extent we can go. The first discussions about the speed of light began with the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle who considered light travel instantaneously. Albert Einstein later in 1905 wrote a paper on special relativity. Einstein’s theory of special relativity proved that there is a limited speed of travel that we can reach: the speed of light. Nothing can travel faster than 300,000 kilometers per second which is the speed of light. The object should have an infinite amount of energy to make the object reach the speed of light.
How long would it take us right now to travel 1 light year?
With today’s technology, it would take us approximately 37,200 years to travel the distance of one light year.
For example, if we were to travel at a speed of 58,536 km / h, which is the speed at which the New Horizons rehearsal travels on its way to Pluto, it would take us just under 20,000 years to cross the path of one light year.
If the spacecraft were traveling at the speed at which Helios 2 was traveling, the spacecraft would have traveled one light-year in 4269 light-years.
If a Saturn V rocket that took the man to the moon were to travel, it would take 108,867 years to travel.
If we set out on that journey by the fastest plane, we will need 305975 human years.
If we were to set out on foot on a journey one light year long, it would take us 225 million years to cross it. At this time, the breaks that you would definitely need along the way are not even included.
A snail would cross a distance of one light-year by 83304201370000 years.
How long would it take to travel 1 light year at the speed of light?
If spacecraft traveled at the speed of a light year, it would travel the distance of one light year in one human year. If we were to travel at a speed of half a light year, it would take us 2 years. If we could travel at the speed of light, we could go around the Earth 7.5 times in one second.
However, for a man traveling in a spacecraft at the speed of light, time would not flow the same as outside the spacecraft. The man in the spacecraft would not age, and the time it took to cross one light-year would seem like a second. Even less than a second. This is not just an assumption. Numerous experiments have proven that indeed time flows differently when it travels at the speed of light.
It’s hard to explain what it would feel like to travel at the speed of light because we’re still a long way from technology that could allow us to do so at that speed. We currently need three days to the moon, but if we traveled at the speed of light, we would cross that path in just 1.3 seconds. Exploring the universe at the speed of a light year would significantly speed up the whole process, and we can only hope for that for now.
https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/Numbers/Math/Mathematical_Thinking/how_long_is_a_light_year.htm
https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/light-year/en/
https://futurism.com/how-long-would-it-take-to-walk-a-light-year
Recent Posts
Why Geothermal Energy Is Not Used More Often
Geothermal energy is the most efficient renewable energy source that exists on our planet today. Because geothermal energy is made using the heat from the center of the earth, it is an abundant...
5 Ways to Save Energy at the Cottage
Keeping an entire house fully powered can be an expensive ordeal, but did you know that just keeping a cottage warm and fully lit can be costly too? Whether you just use your cottage as a vacation...
Privacy Overview
Convert Light Years to Kilometers
Search calculateme.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For Voyager 1 to travel 39 light-years, it would take the spacecraft 685,000 years. But Voyager 1 isn't going there anytime soon, or ever. Instead, the spacecraft is heading for a different star ...
Using the fastest man-made vehicle, NASA's Juno spacecraft, which travels at 165,000 mph (365,000 kmph), it would take 2,958 years to travel a light year. A light year is equivalent to about 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).. Traveling at the speed of light would be the fastest way to cover vast distances in space, but current technology makes it impossible for humans or even ...
The final step is to calculate the total distance that the light has traveled within the time. You can calculate this answer using the speed of light formula: distance = speed of light × time. Thus, the distance that the light can travel in 100 seconds is 9.46×10¹² km/year × 2 years = 1.892×10¹³ km.
Exactly how far away is this system? How long would it take to get there? A light year is a measurement of distance based on the speed of light. Light travels at 186,282 miles per second. By my ...
420.168 times 3 days is 1,260.504 days to travel 1 light year. 1,260.504 times 40 light years is 50,420.168 days . 50,420.168 divided by 365 days in a year is 138.137 years to reach them. Share. ... How long does it take to travel 36 light years with tolerable acceleration and deceleration?
The discovery of seven Earth-size planets around a nearby star, TRAPPIST-1, is certainly exciting news. TRAPPIST-1 is 39 light-years away from Earth, or about 229 trillion miles (369 trillion kilometers). It would take 39 years to get to its current location traveling at the speed of light.
Athena say: 39 years, earth time, if you traveled near the speed of light. Less time on the ship of course. Much longer if you took a train.-poornakumar b say: If your spaceship travels at a speed of a 'n ͭ ͪ of speed of Light', it takes n times 39 Light years to reach there. A maximum speed of a two thousandth of Light speed is bandied about ...
According to Futurism, there are just about 31,500,000 seconds in a year, and if you multiply this by 186,000 (the distance that light travels each second), you get 5.9 trillion miles (9.4 trillion kilometres) which is the distance that light travels in one year. The time that it takes humans to travel one light year is considerably longer than ...
This means that light travels 5.88 trillion miles a year (9.5 trillion km). So 1,400 light-years equals about 8.2 quadrillion miles. If we took one of our fastest probes to the planet, New ...
But in the physical world, 39 light years is 369 trillion kilometres (229 trillion miles) away. Even if you were piggybacking on a beam of light, it would take around 39 years to get there. That is a crazy long trip (about as long as some of your parents have been alive!), but it is a length of time that a human being could technically survive.
The recent discovery of HD85512b only 36 light years from Earth has promising attributes to harbor life. Assuming we want to travel there, we cannot instantaneously jump to light speed, (StarTrek euphemisms aside), we'll have to accelerate the conventional way by building momentum.
But how long would it take to travel one light year? The fastest human-made vehicle, NASA's Parker Solar Probe, would take 1,698 years to travel one light-year, the sum of roughly 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers), the distance light travels in one year. In September 2023, NASA's Parker Solar Probe set a new record, clocking a ...
A light year is the distance that light travels in one year, which is about 5.88 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers.Because the speed of light is constant, this distance provides a useful way to measure the vast distances in space. For example, the closest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is about 4.24 light years away, meaning that the light we see from that star today left it over ...
In Scientific Notation. 39 light years. = 3.9 x 10 1 light years. ≈ 2.29266 x 10 14 miles.
A light year is defined as exactly 9,460,730,472,580.8 kilometers. Kilometers. A kilometer, or kilometre, is a unit of length equal to 1,000 meters, or about 0.621 miles. In most of the world, it is the most common unit for measuring distance between places. Convert Light Years to. Astronomical Units. Kilometers. Miles ...
Using lightyears to measure distance in the Universe and how long it would take to travel one lightyear by foot, car, plane and rocket.
A light-year is the distance light can travel in one year. Light is the fastest thing in our Universe traveling through interstellar space at 186,000 miles/second (300,000 km/sec). In one year, light can travel 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion km). A light year is a basic unit astronomers use to measure the vast distances in space.
No, a light-year is not equal to 4 years. It is a measure of distance, and it represents the distance that light travels in one year. How many human years is 500 light-years? 500 light-years is still a measure of distance, not time. It would take an extremely long time to travel that distance with our current technology.
How long is 40 light years in human years? 40 light years is approximately 377.8 trillion kilometers (234.3 trillion miles). In human years, it depends on the context you mean. If you're asking about the time it would take to travel 40 light years at a significant fraction of the speed of light, it would still take many years, possibly decades or even centuries with current technology.
In Scientific Notation. 39 light years. = 3.9 x 10 1 light years. = 3.9 x 10 1 light years.
9,800. 5.7611 x 10 16. 9,900. 5.8198 x 10 16. 10,000. 5.8786 x 10 16. How many miles are in a light year? Use this easy and mobile-friendly calculator to convert between light years and miles. Just type the number of light years into the box and hit the Calculate button.
If we set out on that journey by the fastest plane, we will need 305975 human years. If we were to set out on foot on a journey one light year long, it would take us 225 million years to cross it. At this time, the breaks that you would definitely need along the way are not even included.
A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. The year used by the International Astronomical Union is 365.25 days. A light year is defined as exactly 9,460,730,472,580.8 kilometers.